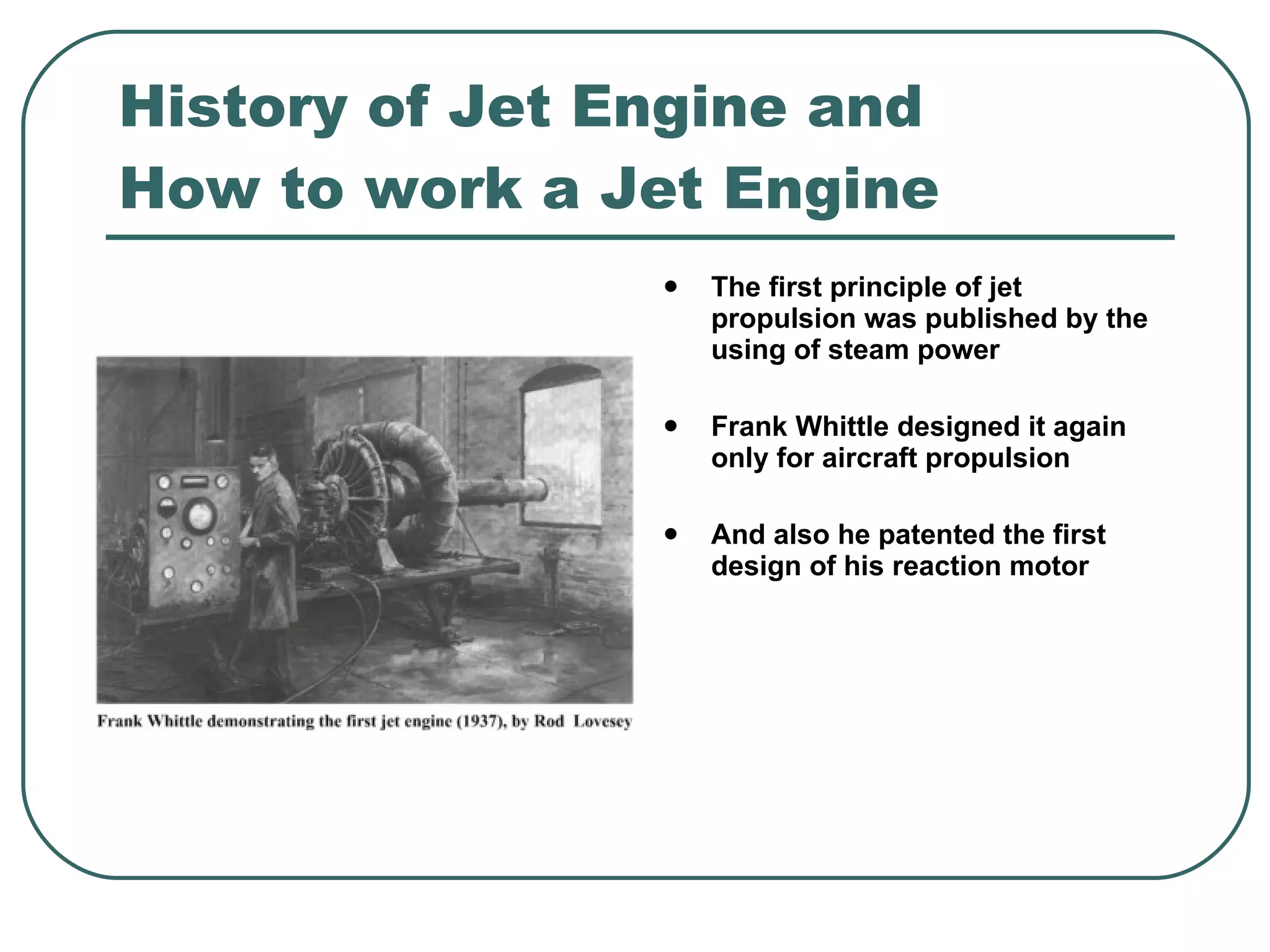
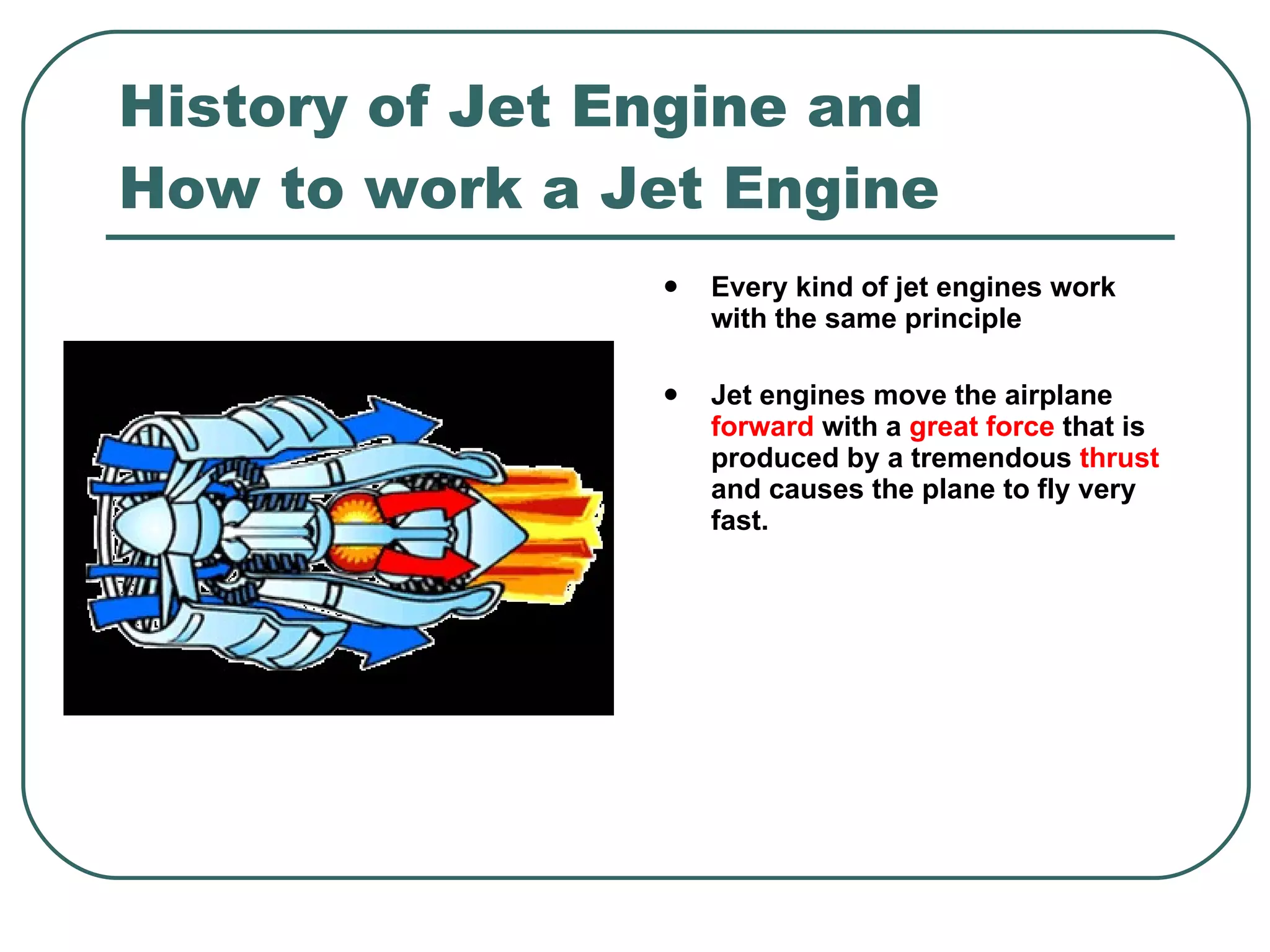
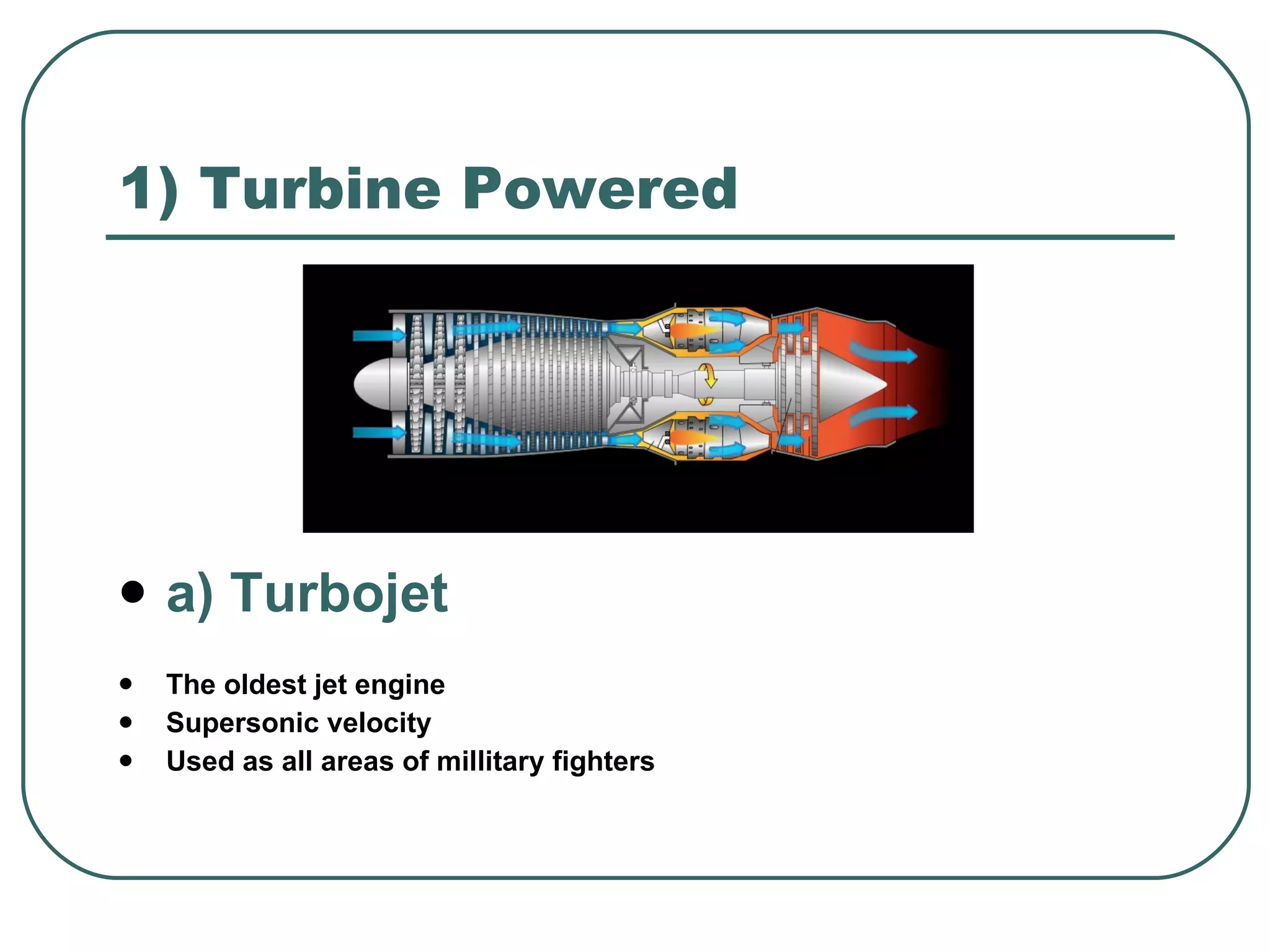
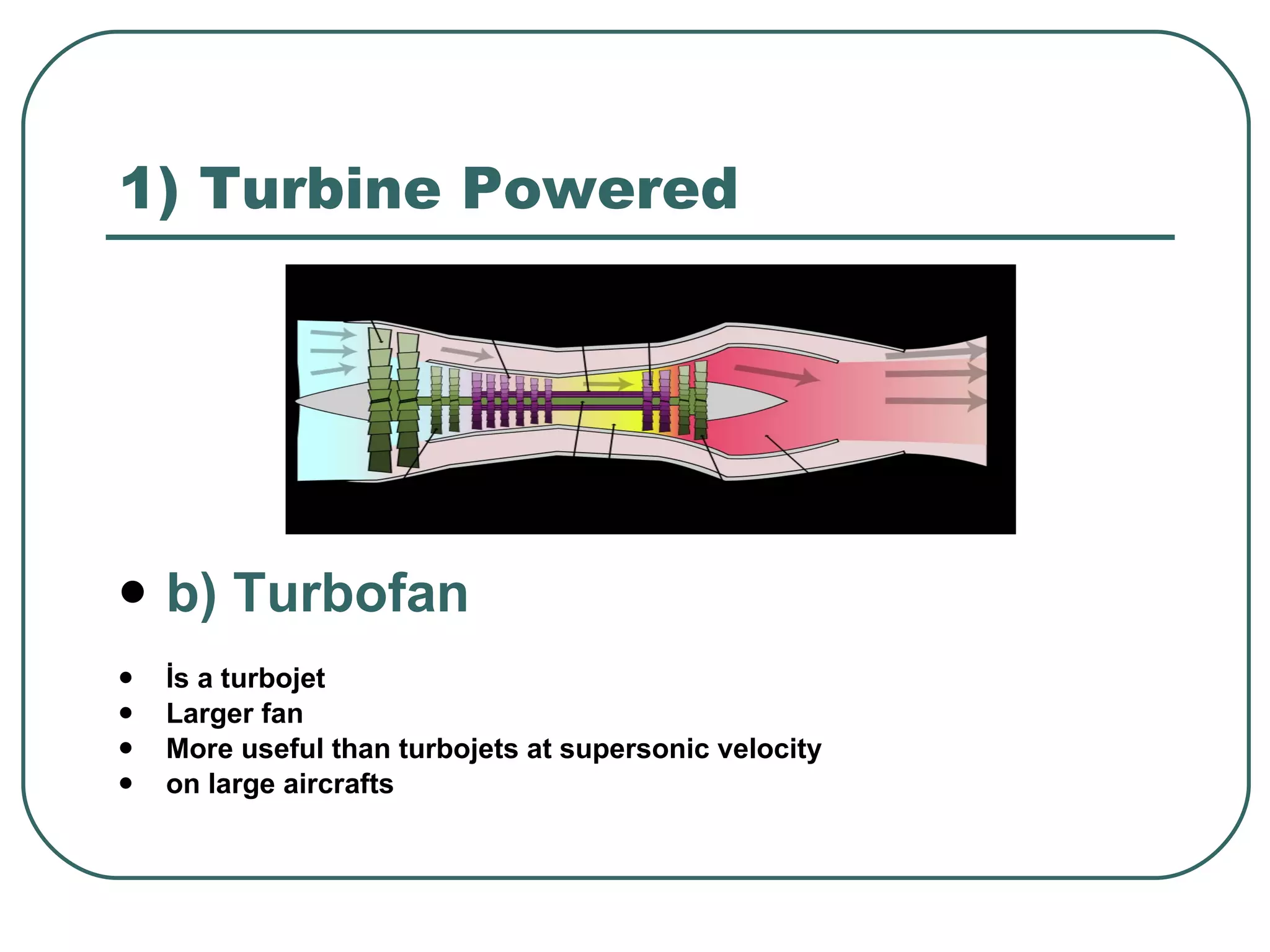
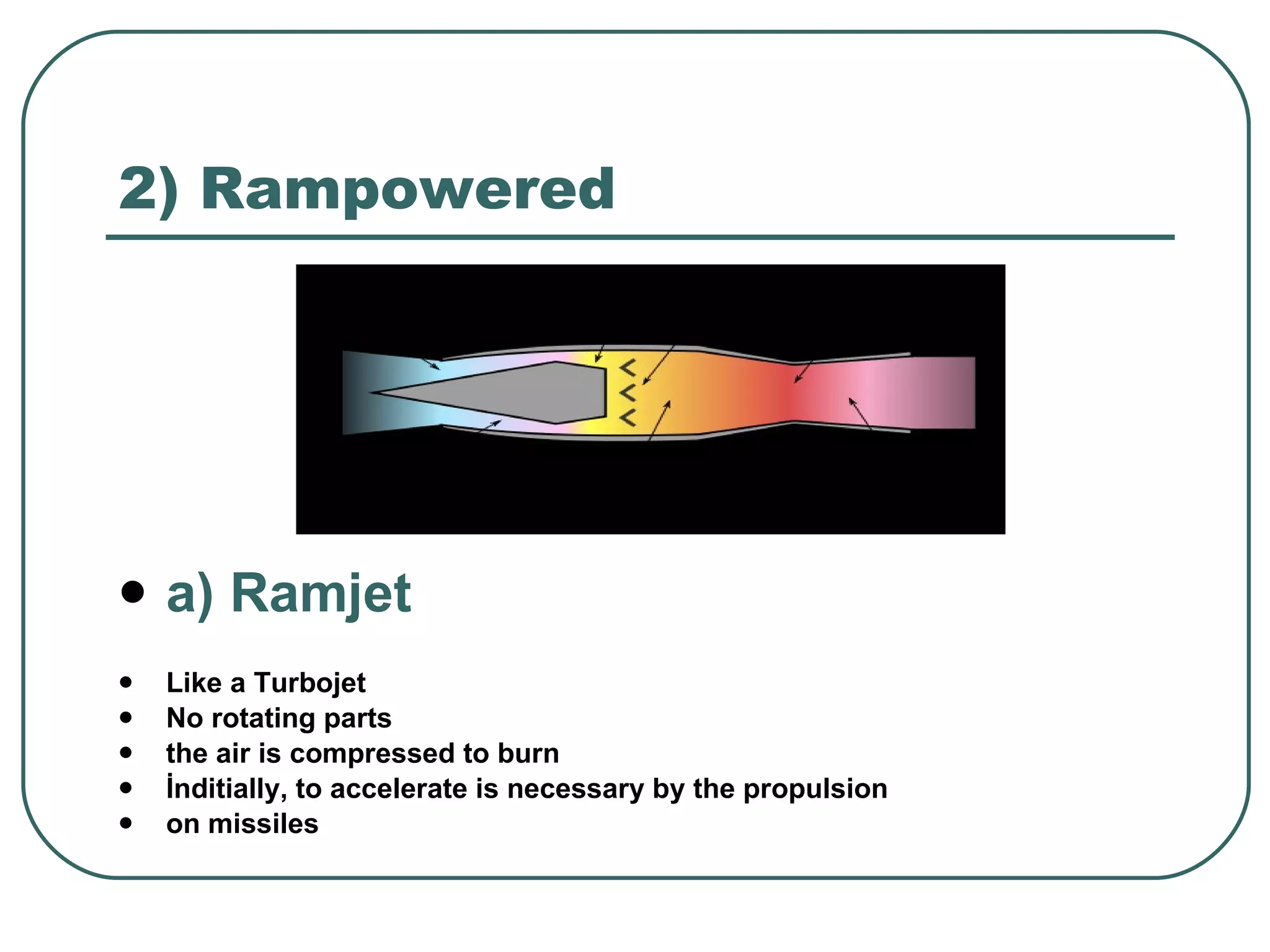
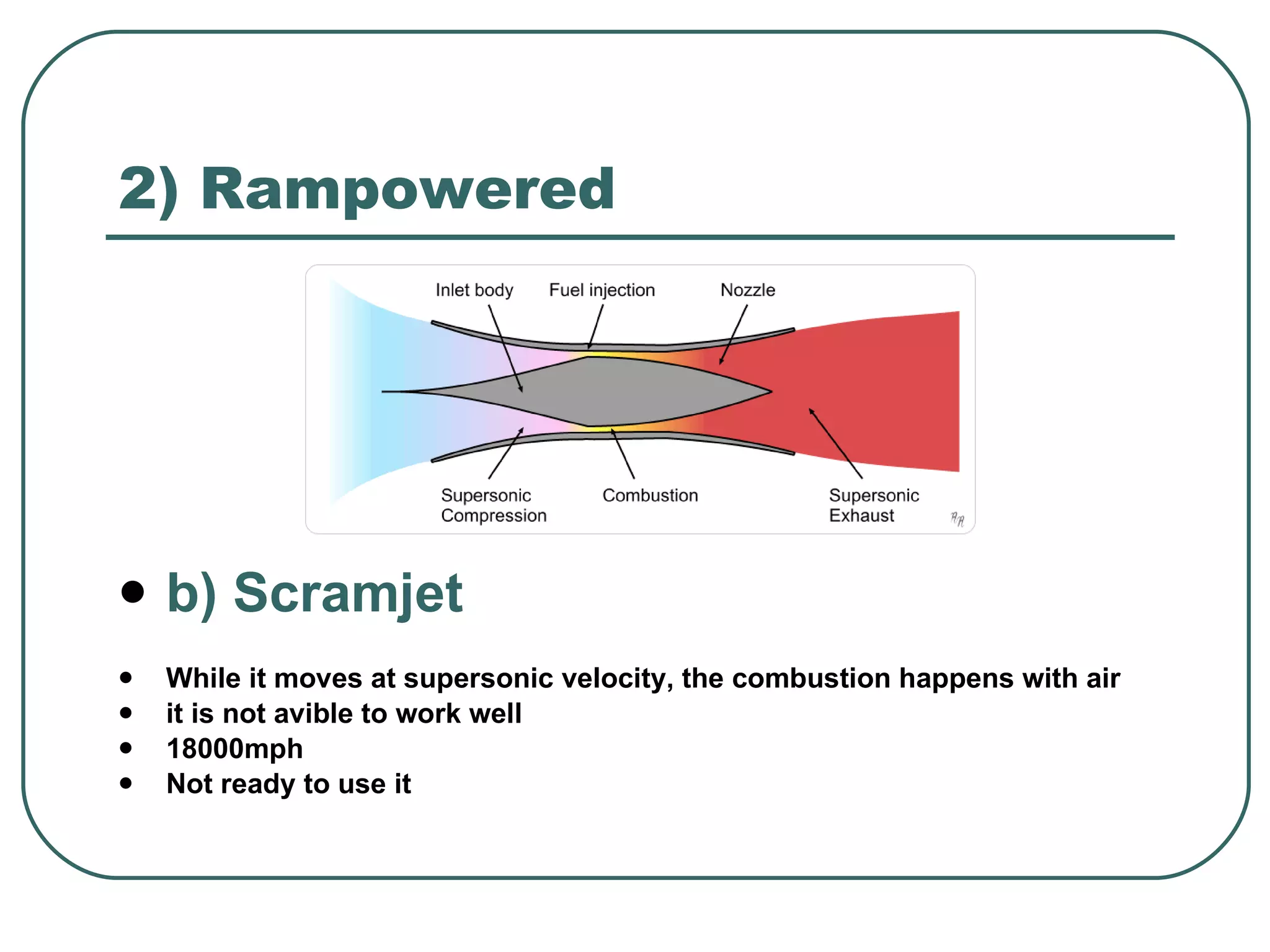
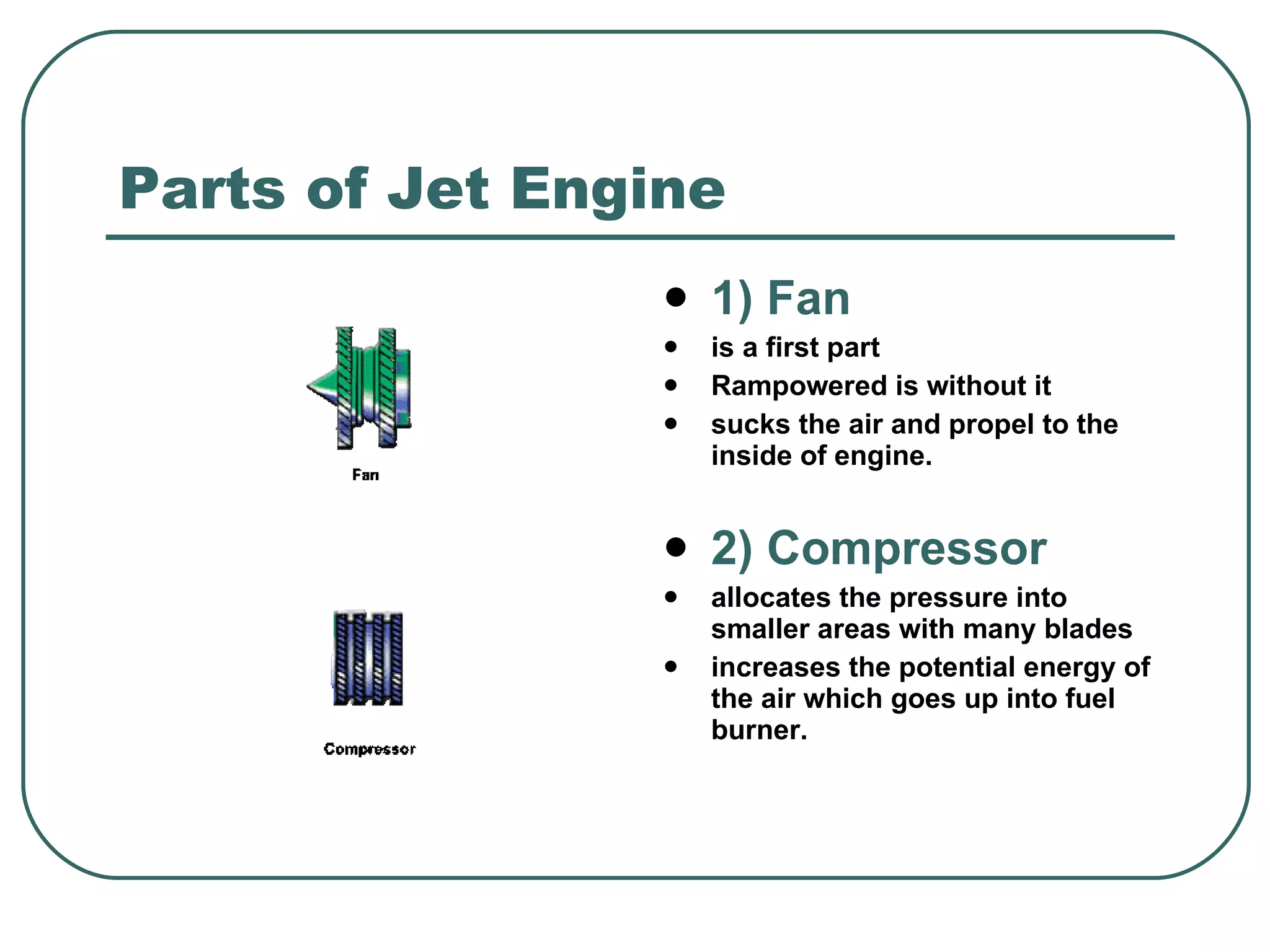
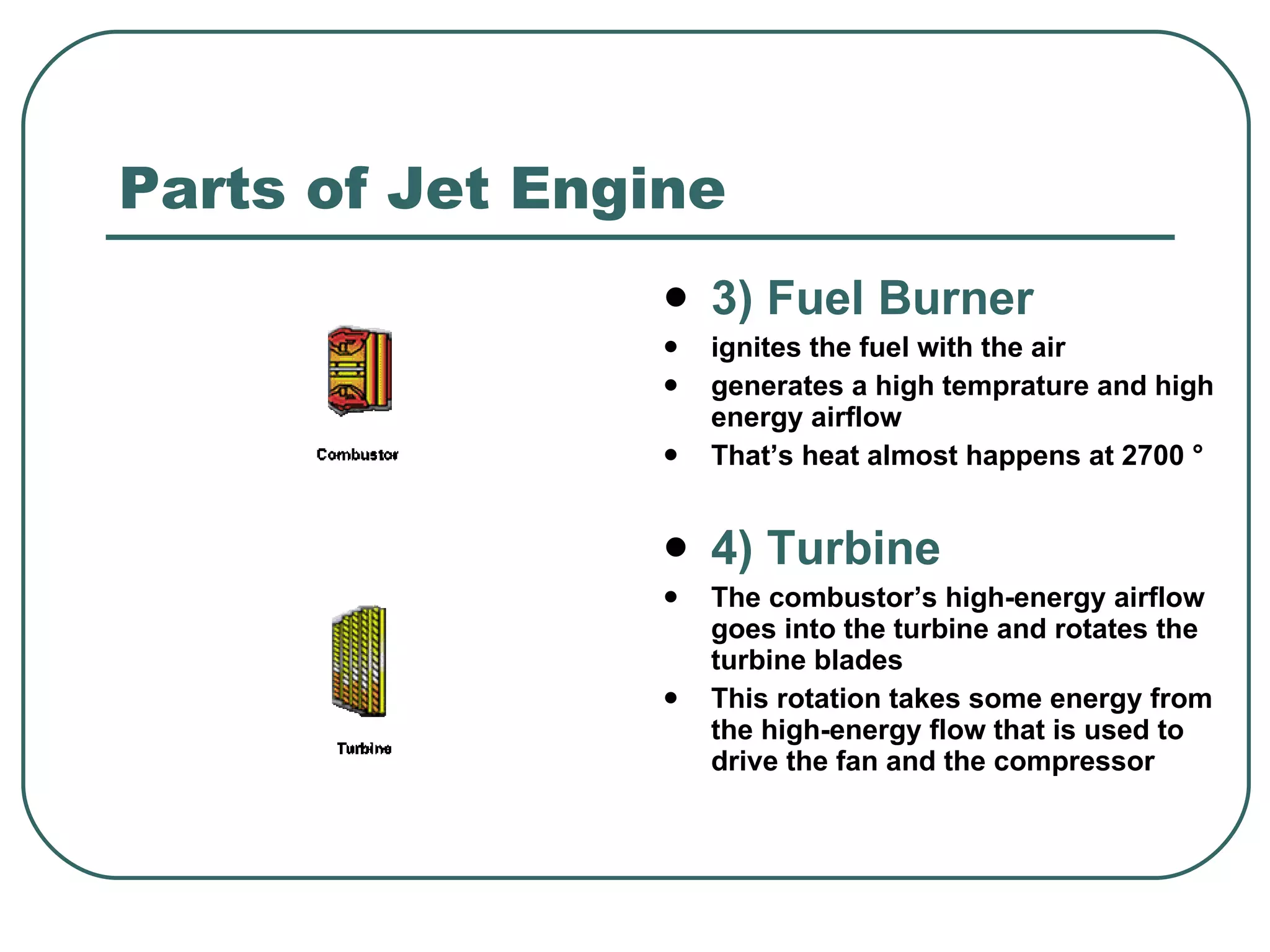
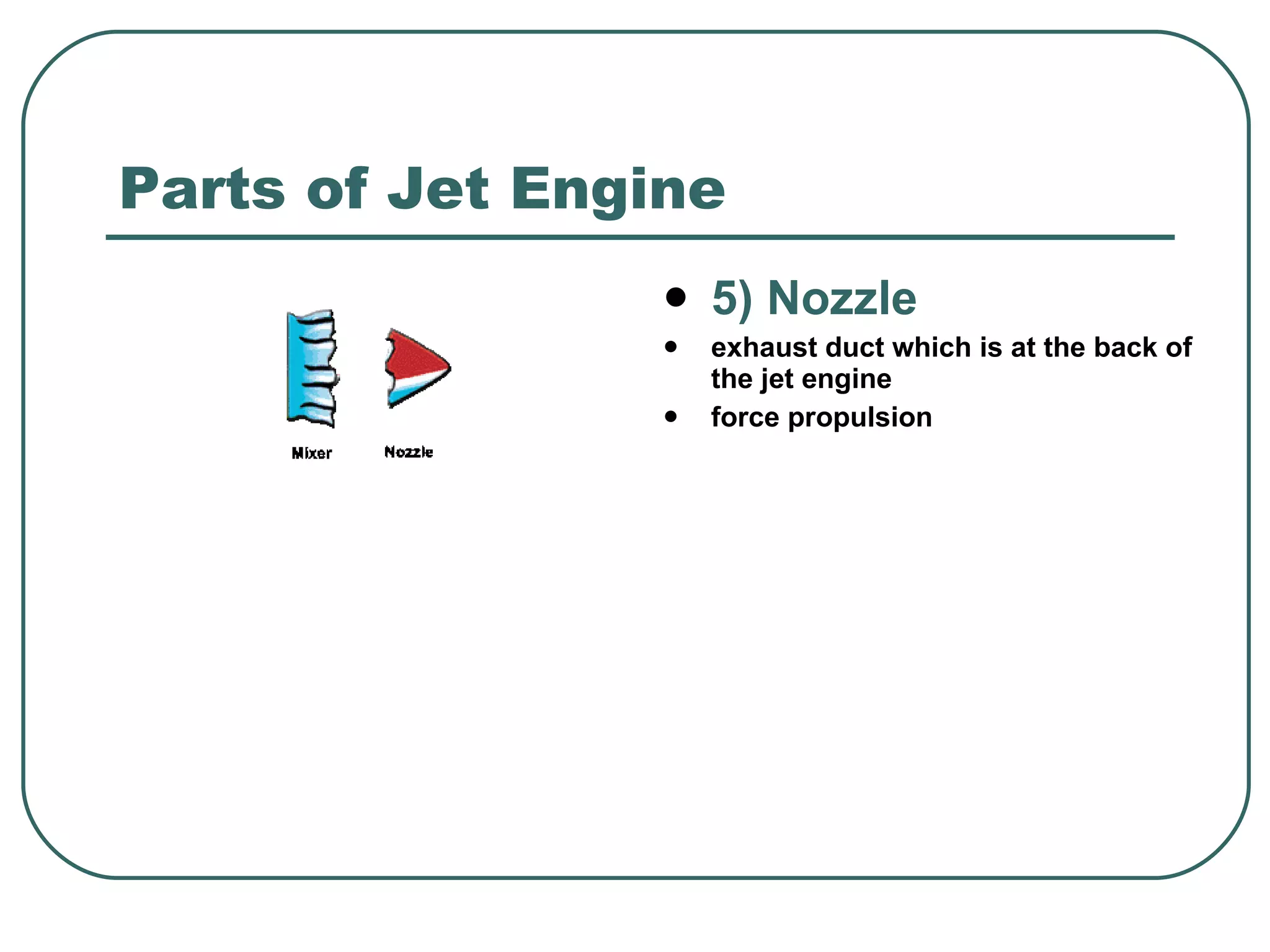
The document provides an overview of jet engines, including their history, types, and main parts. It discusses how Frank Whittle first designed and patented the jet engine in the early 1900s. The main types of jet engines are then described: turbine powered turbojets and turbofans, and ramjet and scramjet. Finally, the core parts of a jet engine - fan, compressor, fuel burner, turbine, and nozzle - are outlined and their functions explained.