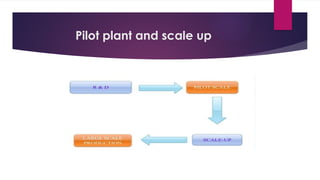
The document outlines the considerations for scaling up the production of solid pharmaceuticals from lab scale to pilot plant. Key stages in tablet production include material handling, dry blending, granulation, drying, and compression, with emphasis on preventing contamination and ensuring uniformity in the blend. It also discusses the specific equipment and methods used at each stage, highlighting the importance of optimizing parameters for effective and reproducible manufacturing outcomes.