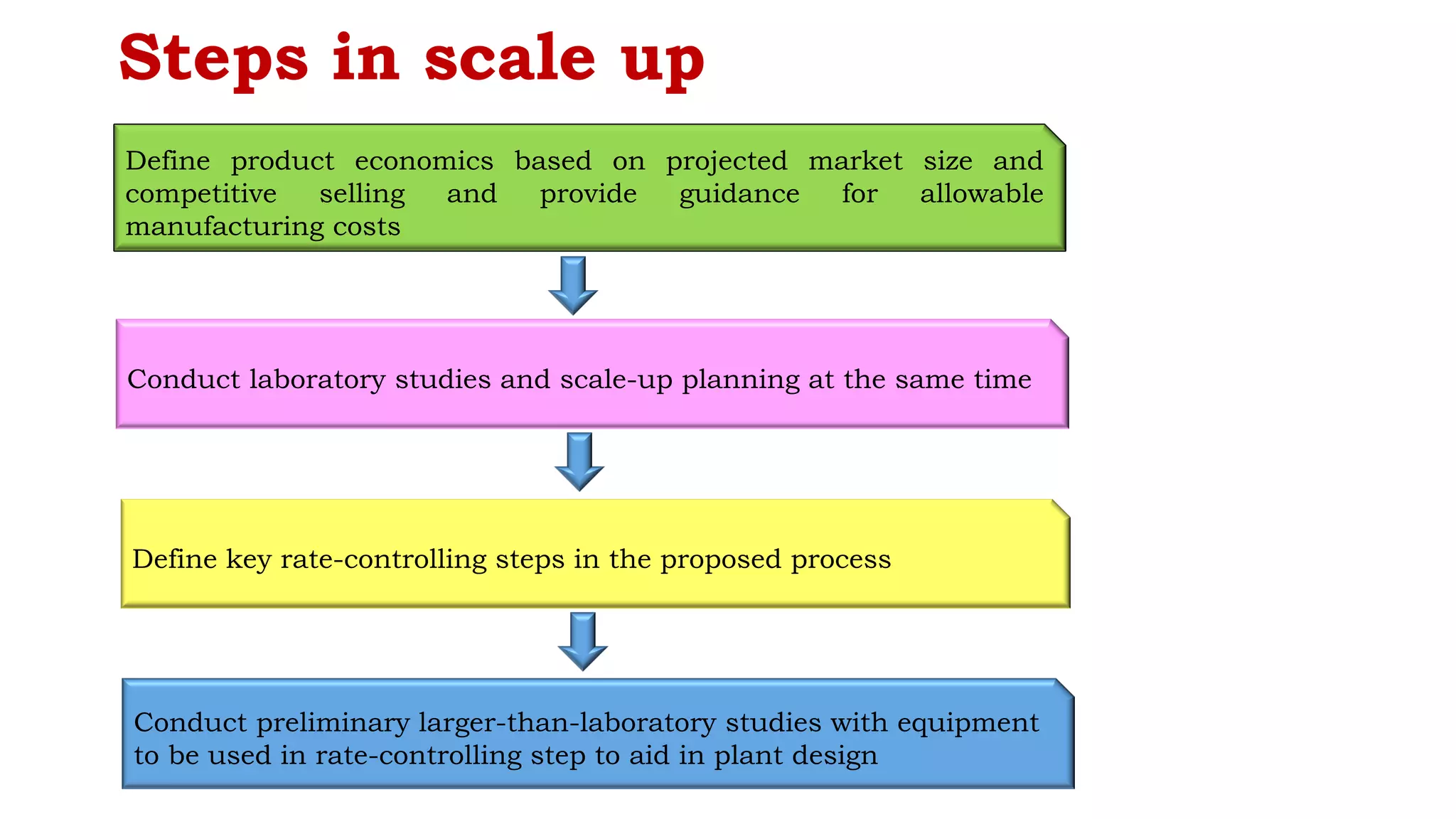
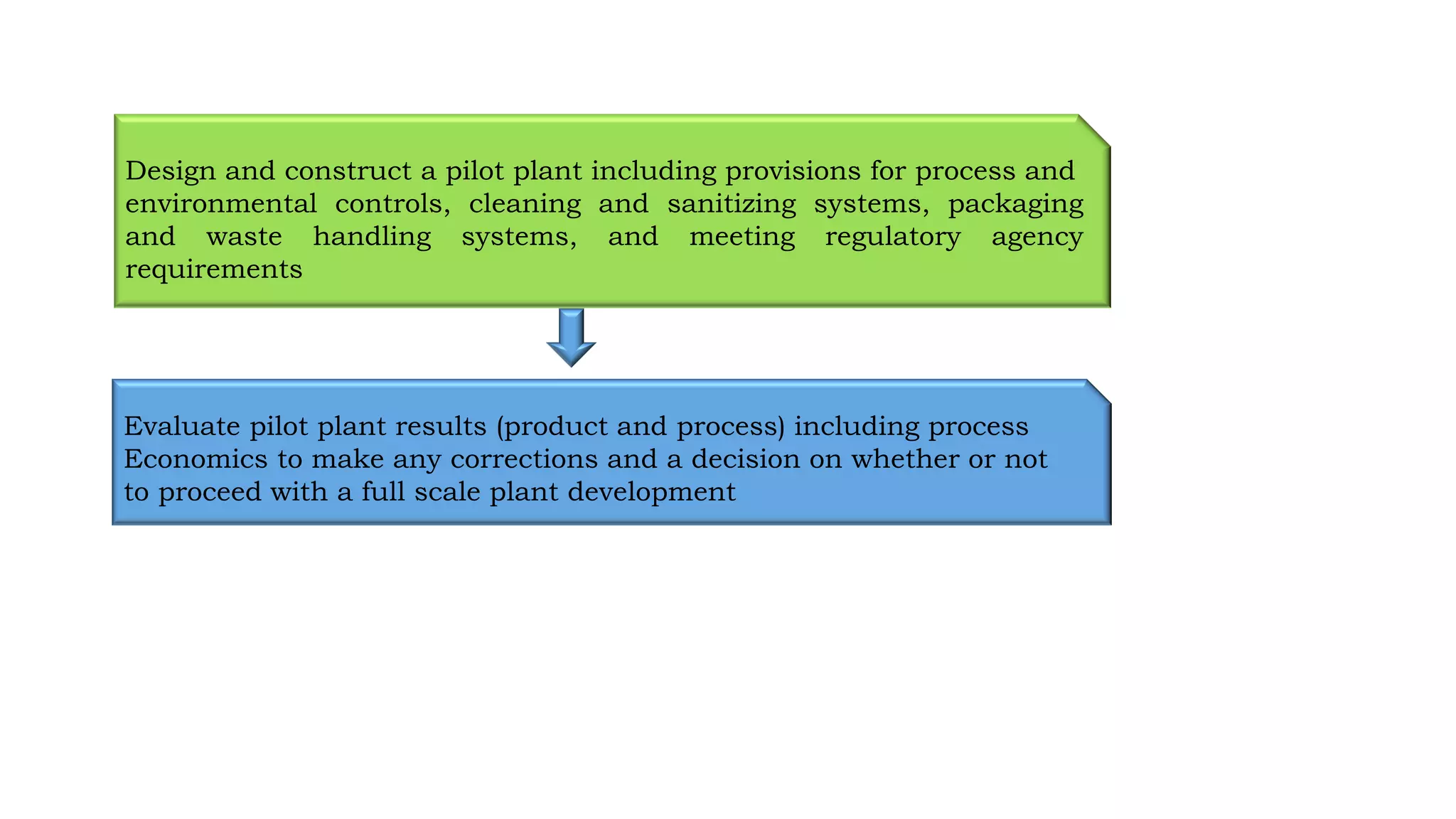
The document outlines the process and significance of pilot plant scale-up techniques in pharmaceutical manufacturing, explaining its role in transforming lab-scale formulas into viable products. It details objectives, the importance of pilot studies, and key considerations including product economics, equipment requirements, and process validation. Furthermore, it emphasizes the collaborative nature of the process involving R&D, production, and quality assurance personnel to ensure successful scale-up.