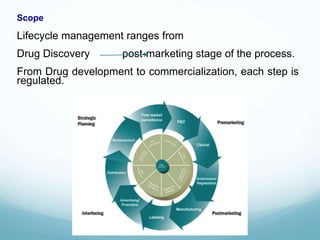
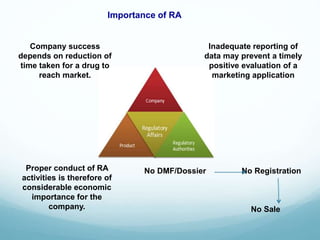
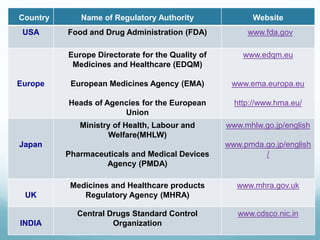
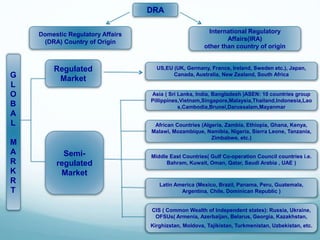
The document provides an overview of regulatory affairs (RA) in the pharmaceutical industry. It discusses that RA ensures pharmaceutical products comply with regulatory standards by acting as the link between companies and regulatory authorities. RA is responsible for guiding drug development and submissions for market approval. The document outlines the historical development of regulations from 1900 to present day. It also reviews the roles and responsibilities of RA professionals which include maintaining knowledge of regulations, preparing submissions, and ensuring compliance. Finally, it lists some major regulatory authorities around the world and their roles in overseeing drug development and approval processes.