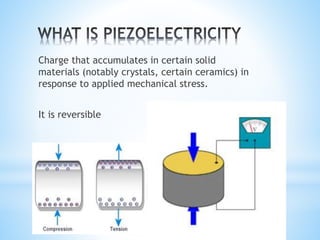
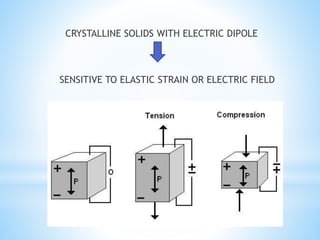
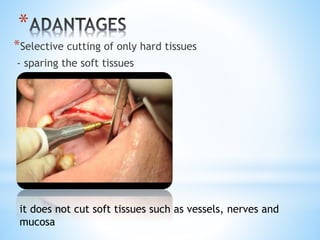
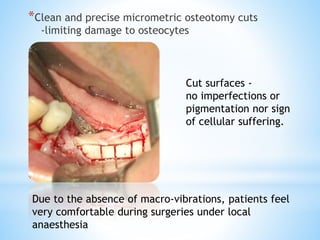
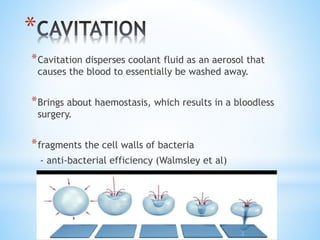
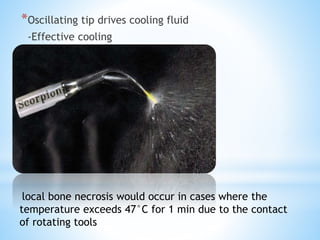
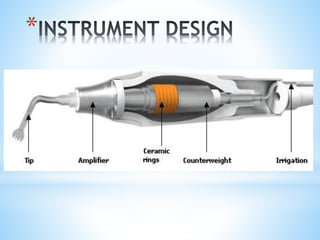
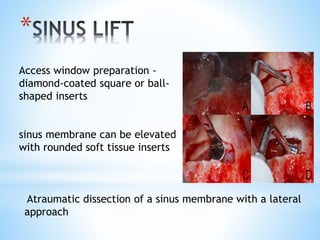
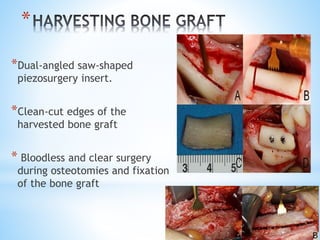
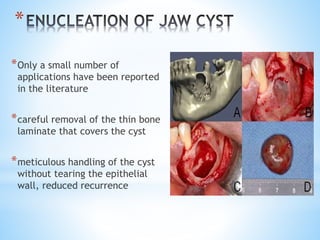
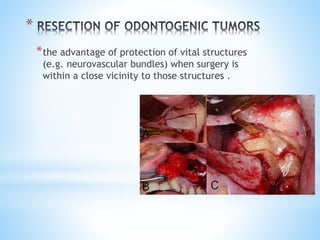
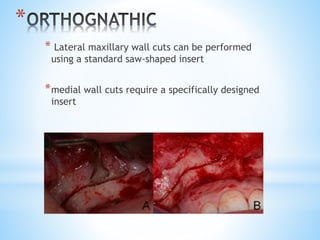
This document discusses piezoelectricity and its use in maxillofacial surgery procedures through a tool called piezosurgery. Piezoelectricity was discovered in 1880 and involves generating electric charges in response to mechanical stress in certain solid materials. Piezosurgery uses this principle with piezoelectric ceramic materials in surgical instruments to precisely cut bone. It allows for selective cutting of hard tissues while sparing soft tissues. Some advantages of piezosurgery include clean cuts with limited damage to bone cells and bloodless surgery. The document outlines several maxillofacial procedures where piezosurgery has been applied and its benefits compared to traditional techniques, such as reduced blood loss and nerve injury.