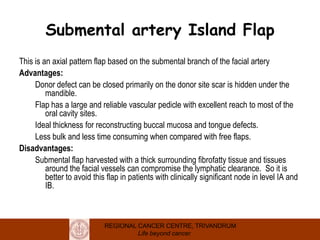
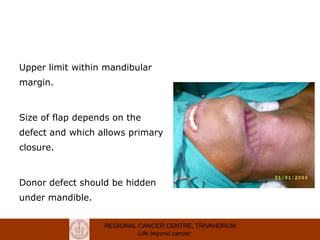
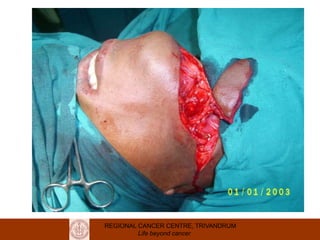
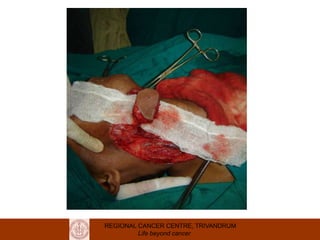
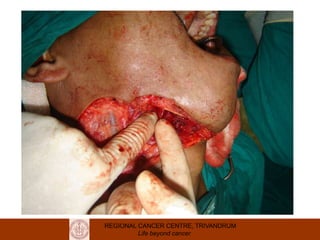
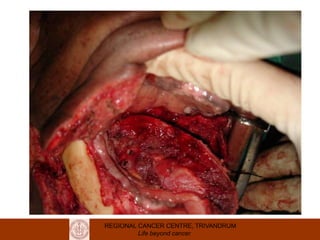
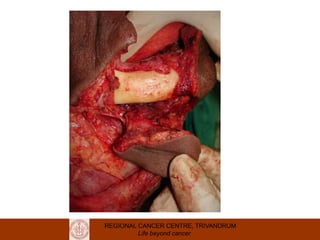
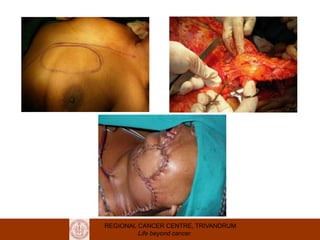
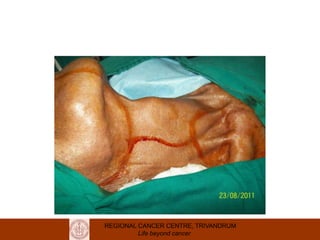
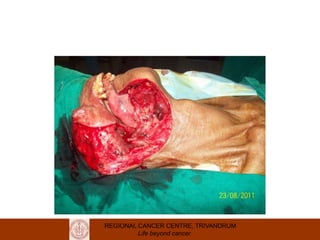
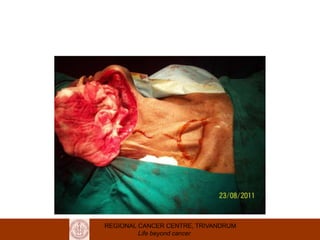
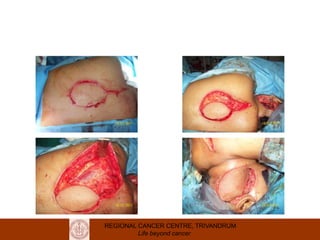
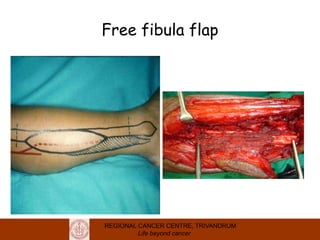
This document discusses reconstructive options after head and neck cancer surgery. It outlines the impact of major head and neck surgery and goals of reconstructive surgery to restore form and function. A reconstructive ladder is presented from primary closure to skin grafts to local and regional flaps to distant and free flaps. Specific flaps are described like pectoralis major and free fibula flaps. Reconstructive surgery improves quality of life after cancer surgery.