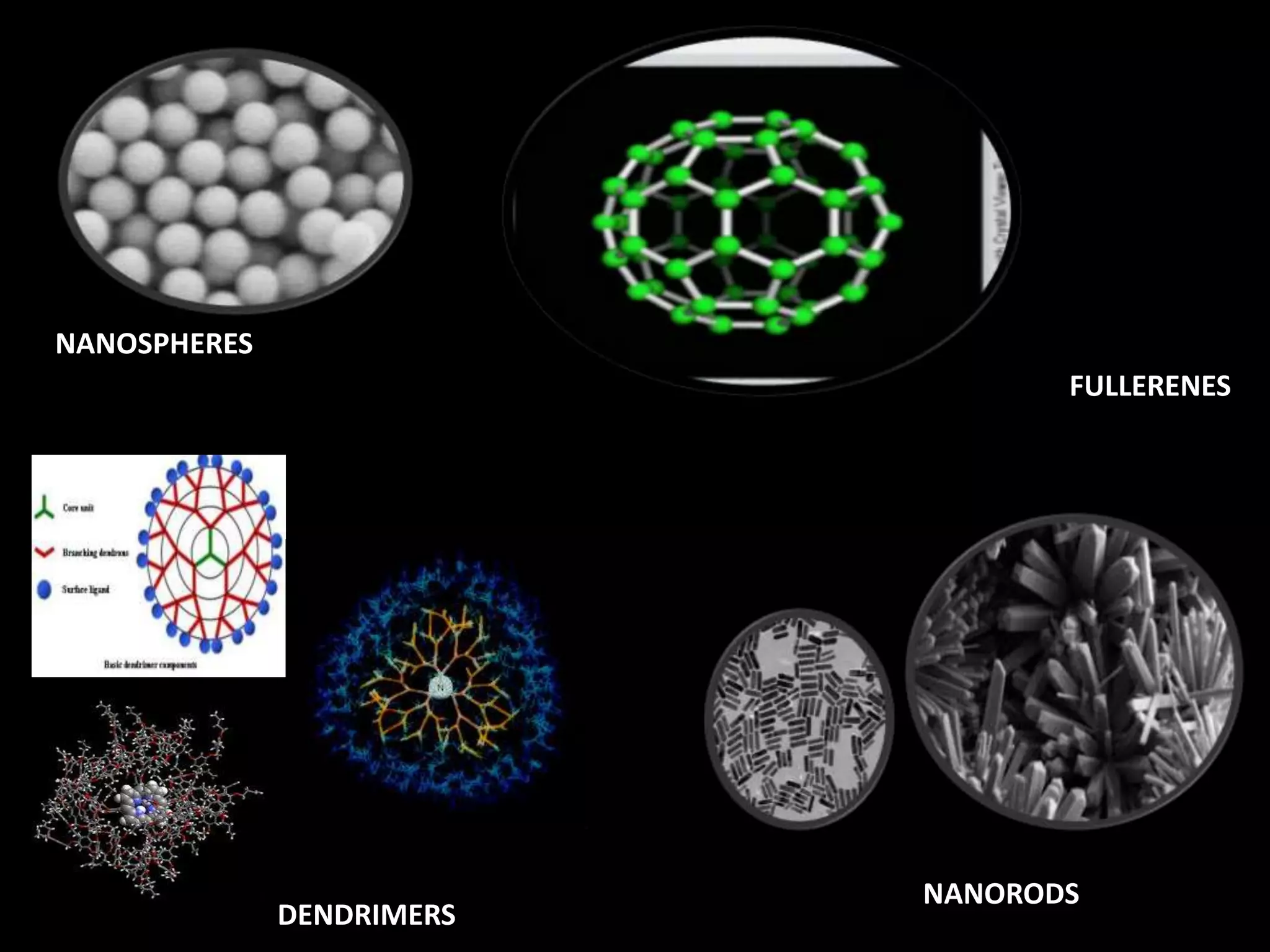
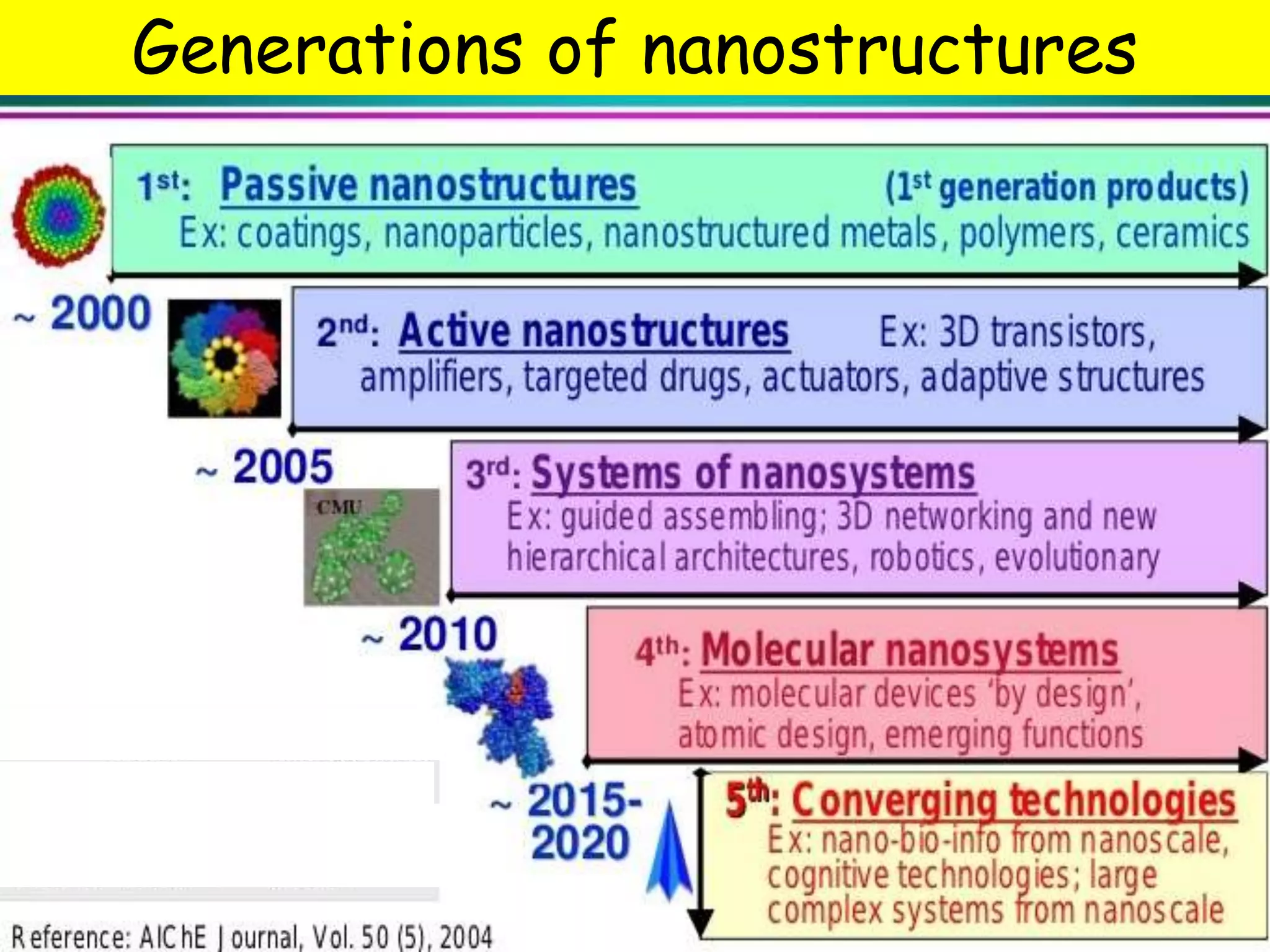
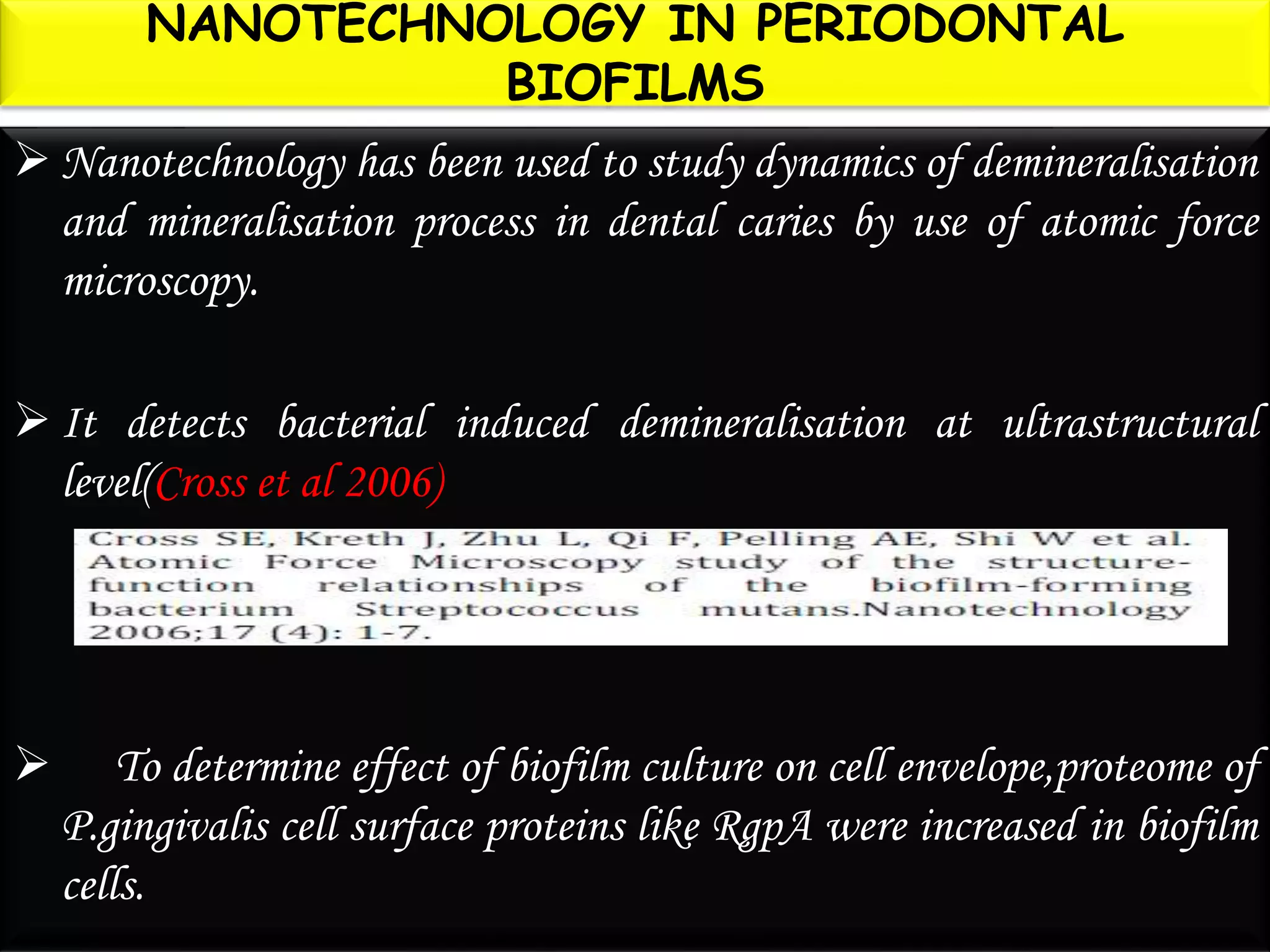
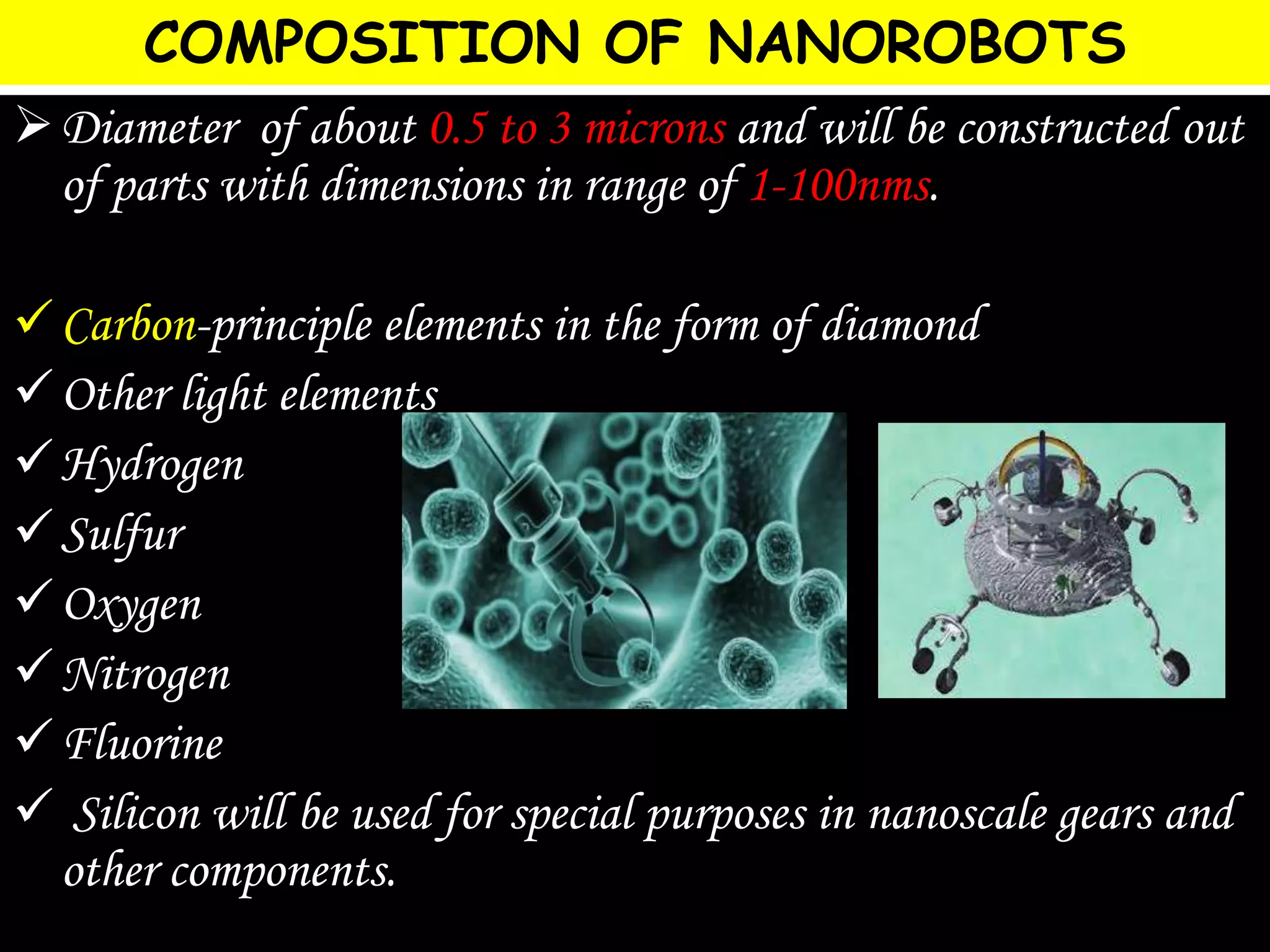
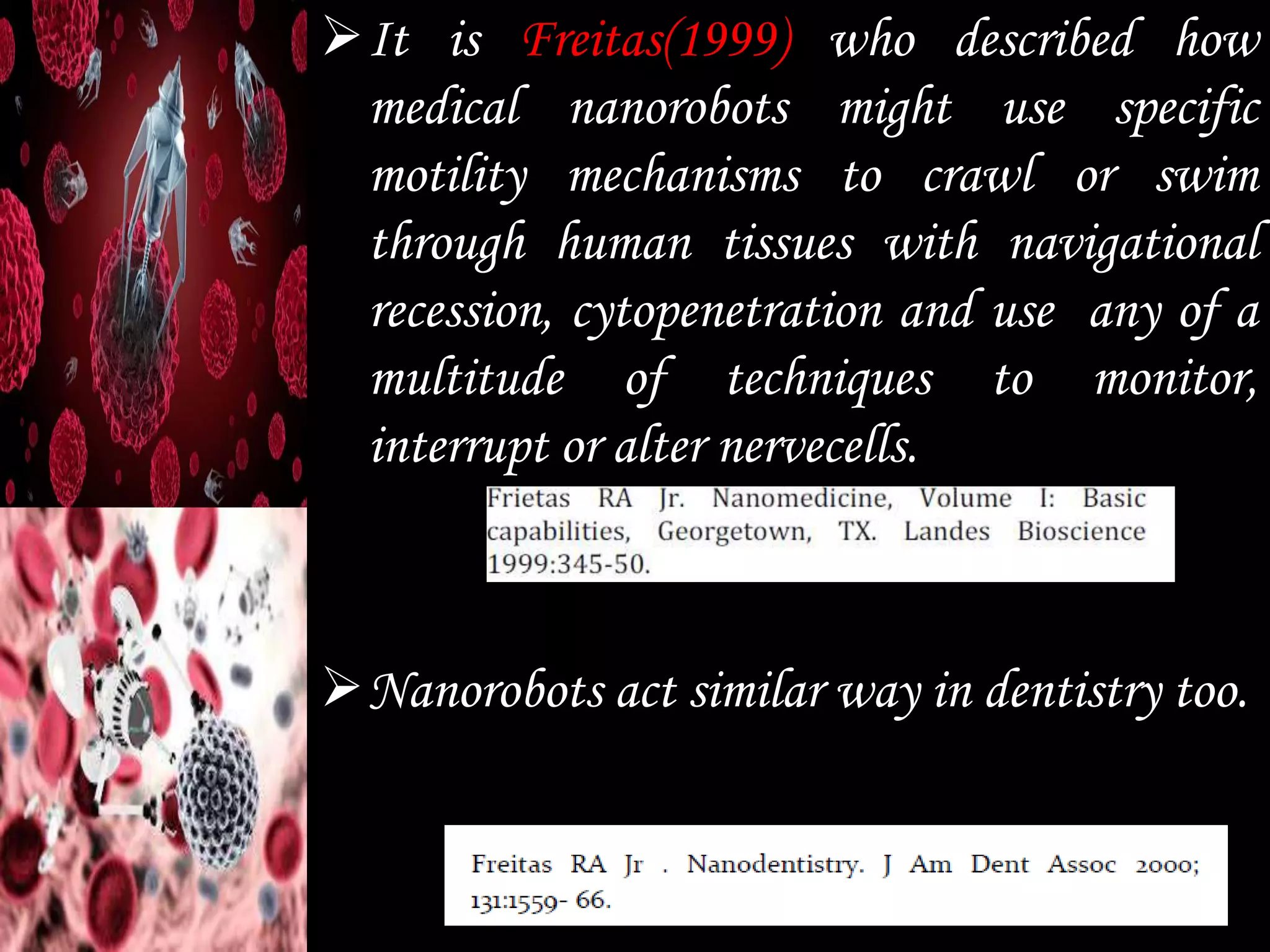
This document discusses the potential applications of nanotechnology in periodontics. It begins with background on nanotechnology and describes various nanoparticles and how nanoproducts are made. It then discusses the properties of nanomaterials and how they are used for drug delivery, tissue engineering, biofilm studies, tooth repair, dental implants, and bone replacement. The document concludes by describing hypothetical nanorobots that could one day be used to treat periodontal disease at the molecular level through precise, targeted actions guided by external monitoring.