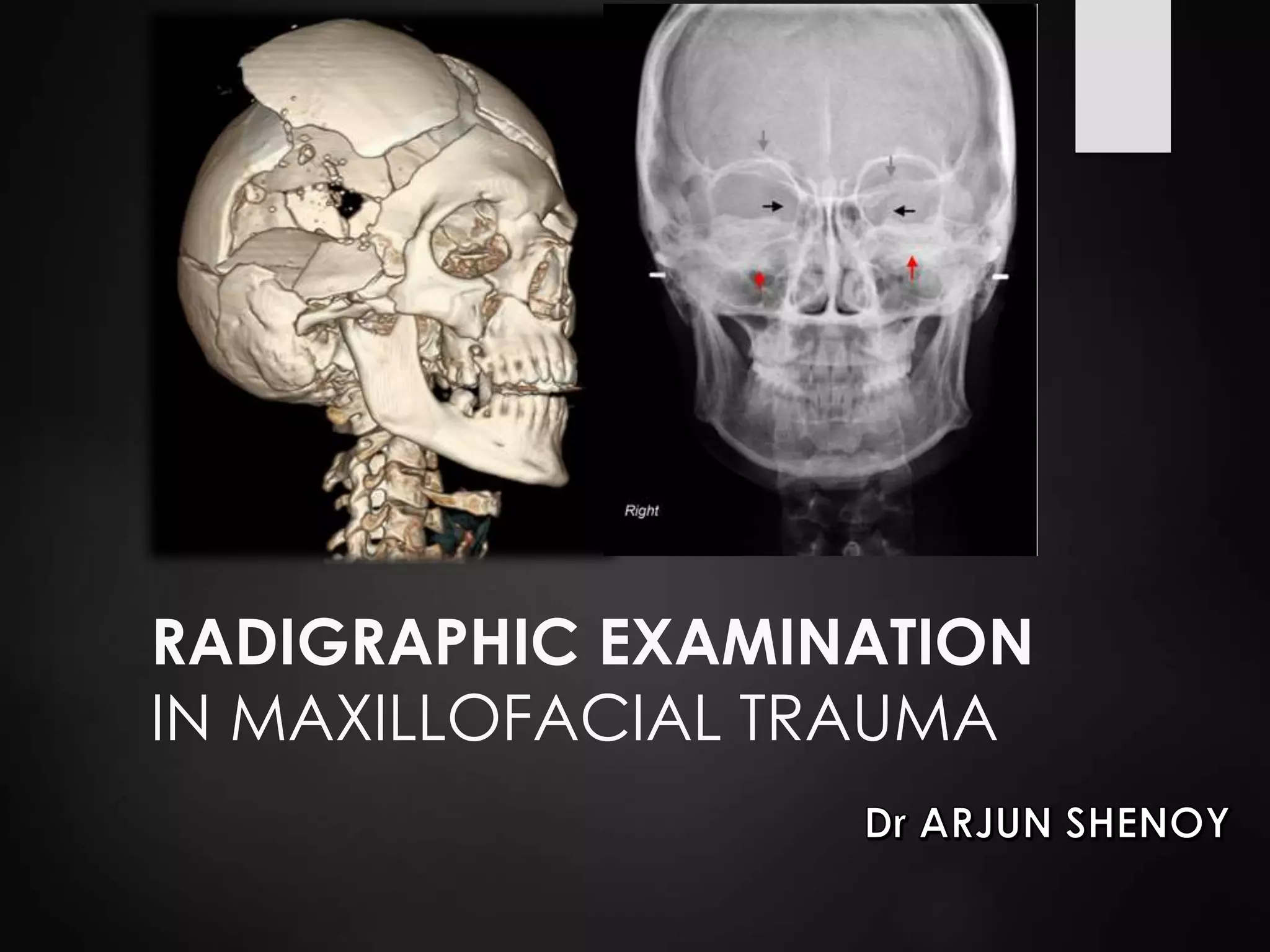
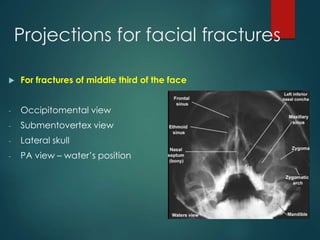
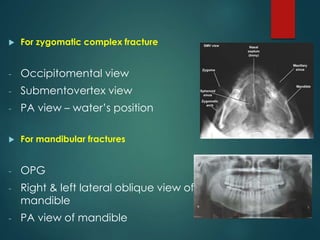
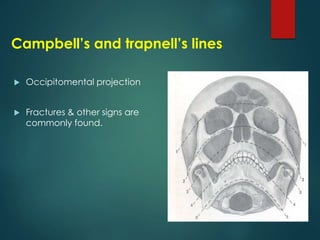
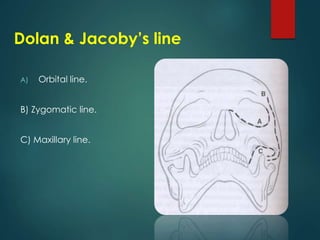
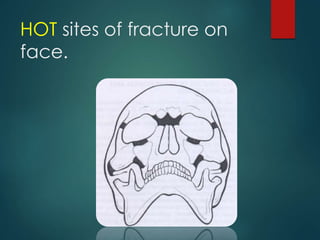
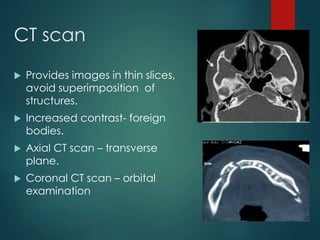
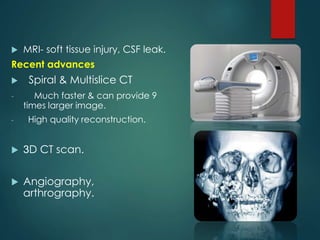
This document discusses the use of radiographic examination in evaluating maxillofacial trauma. It outlines various projections and views useful for fractures in different areas of the face. It also describes radiographic signs that indicate fractures and indirect signs like soft tissue swelling. While radiography is useful, it must be interpreted carefully alongside a clinical examination. The accurate diagnosis provided by radiography, along with recent advances like spiral CT, allow for effective treatment planning in maxillofacial trauma.