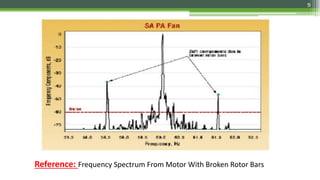
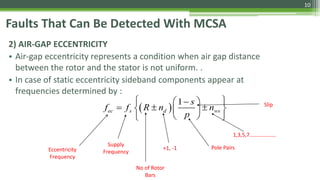
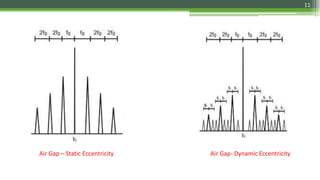
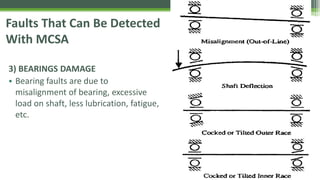
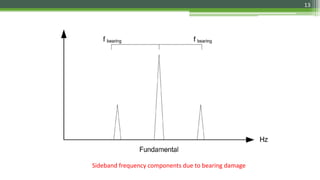
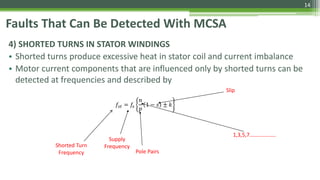
Motor Current Signature Analysis (MCSA) utilizes electrical signature analysis techniques to diagnose faults in electric motors and other equipment. Key methods used include Fast Fourier Transform, Wavelet Analysis, and Artificial Intelligence to detect faults such as broken rotor bars, air-gap eccentricity, bearing damage, and shorted turns in stator windings. MCSA enhances predictive maintenance by monitoring motor current to identify issues early and prevent failures.