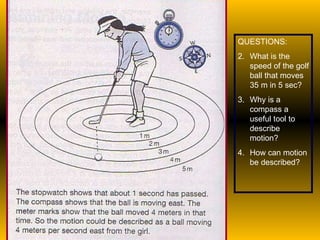
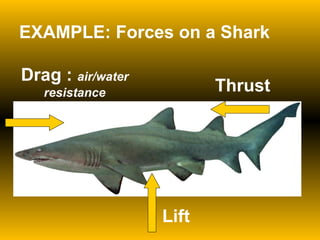
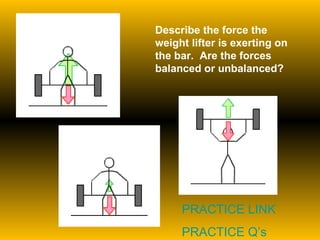
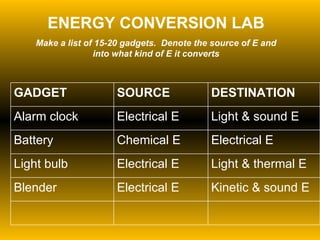
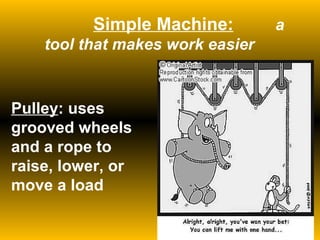
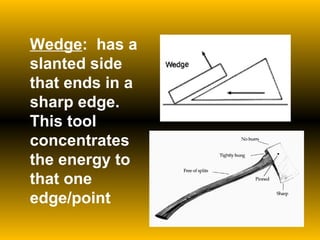
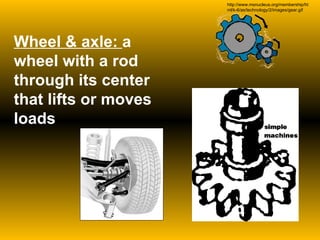
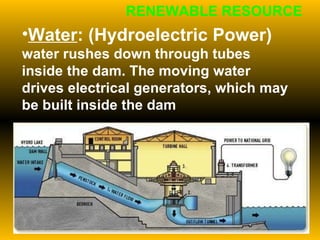
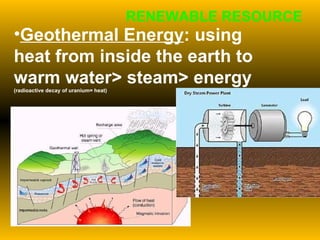
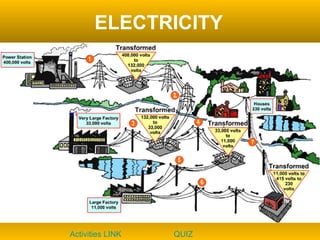
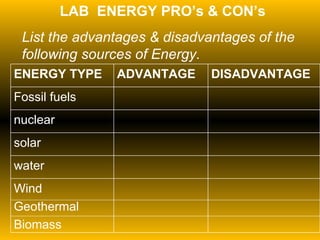
The document discusses fundamental concepts of physics including motion, force, and energy. It covers various forms of energy, Newton's laws of motion, energy conversions, and the role of machines in facilitating work. Additionally, it explores energy resources and their advantages and disadvantages.