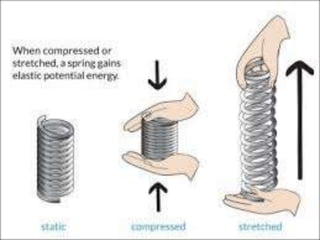
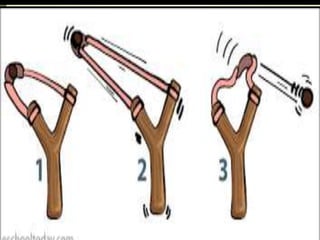
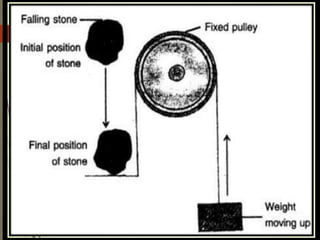
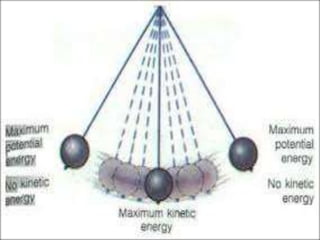
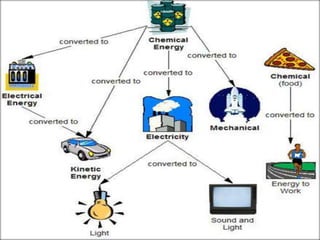
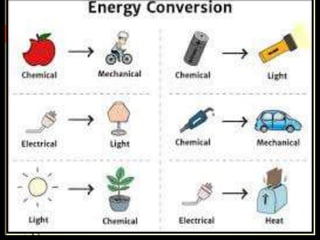
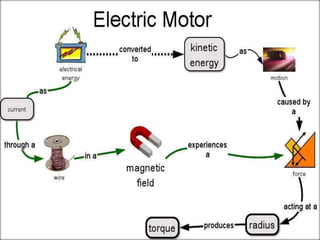
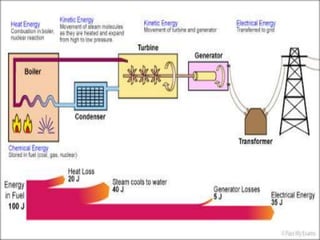
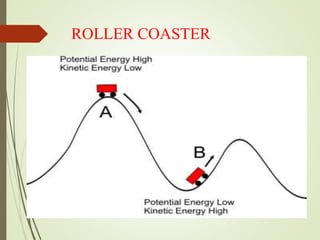
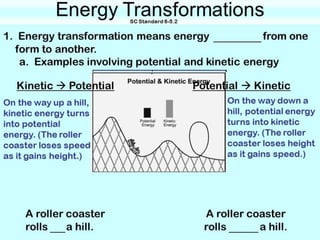
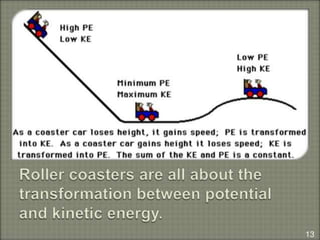
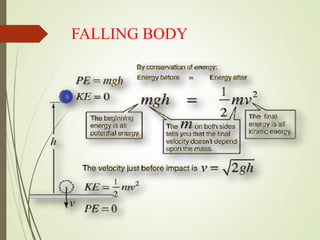
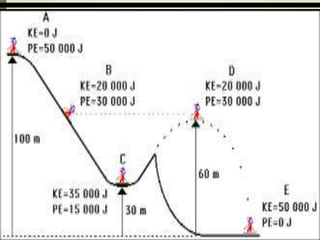
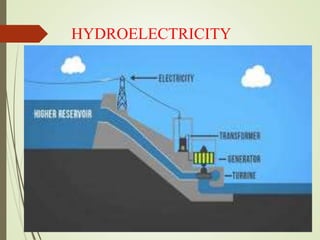
The document explains the concepts of energy and work, highlighting their definitions, measurements, and relationships. It describes various types of energy including mechanical, heat, light, chemical, sound, magnetic, electrical, and atomic energy, alongside examples and formulas for potential and kinetic energy. Additionally, it covers the conversion of energy between forms, conservation of energy principles, and practical applications like hydroelectricity.