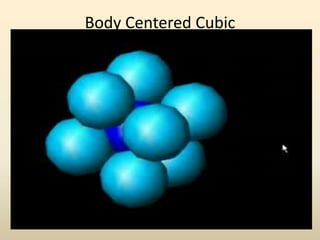
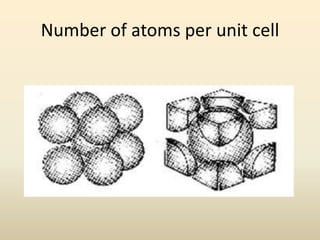
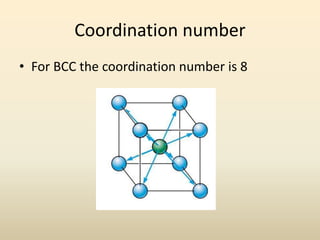
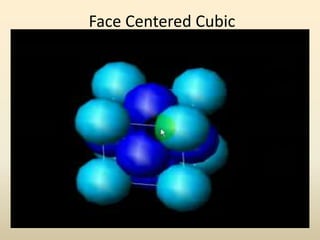
This document discusses key concepts in crystallography including:
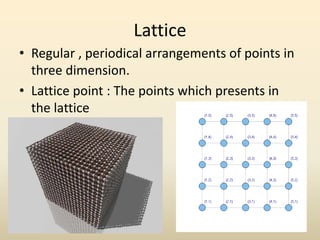
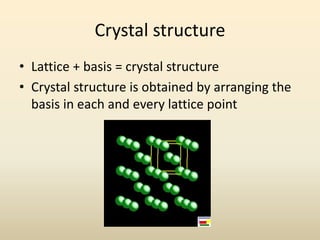
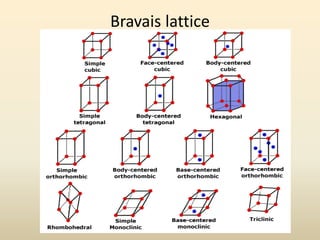
- Crystal structure is defined as a lattice plus a basis, where a lattice is a periodic arrangement of points in 3D and a basis is a group of atoms.
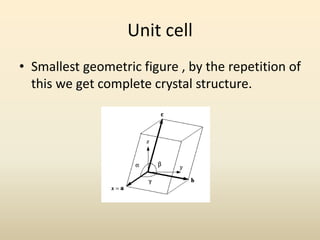
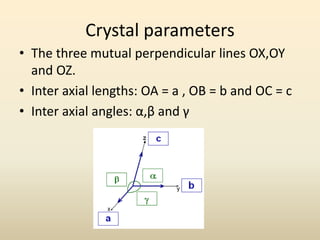
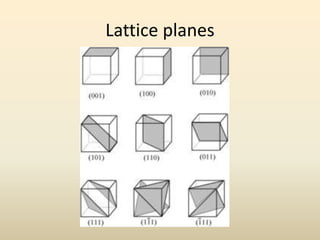
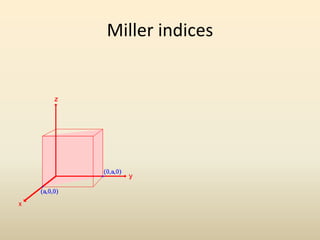
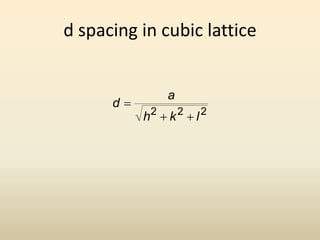
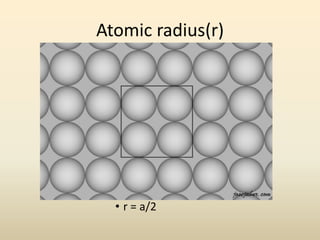
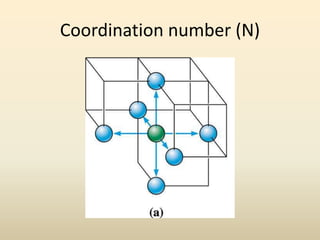
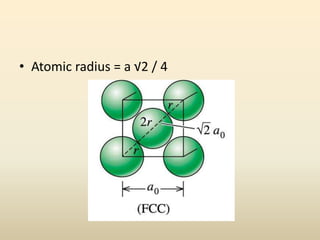
- A unit cell is the smallest repeating geometric shape that defines the lattice, and crystal parameters describe the lengths and angles of the unit cell axes.
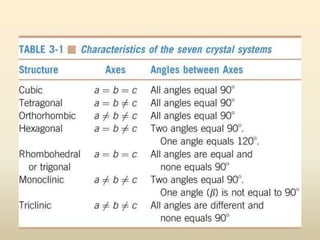
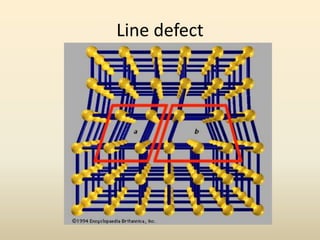
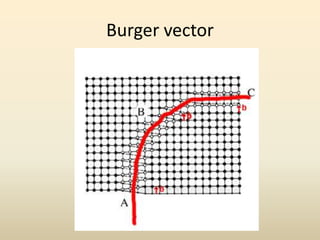
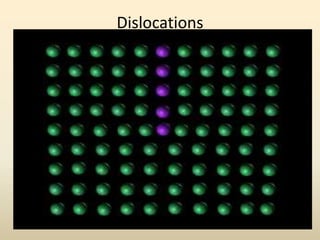
- There are 7 main crystal systems that describe the symmetry and geometry of unit cells. Crystal defects include point defects like vacancies or interstitials, line defects like dislocations, and surface defects like grain boundaries.