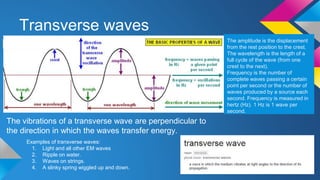
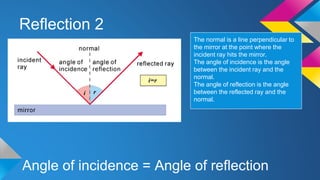
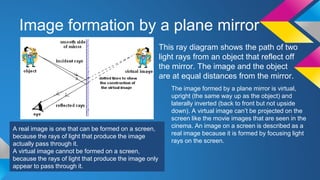
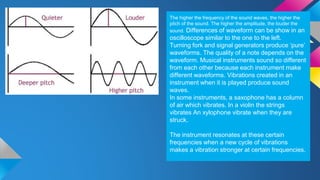
This document covers key concepts in physics related to waves, including types of waves (transverse and longitudinal), their properties (amplitude, wavelength, frequency, speed), and phenomena such as reflection, refraction, and diffraction. It details the electromagnetic spectrum and the use of waves for communication and sound. Examples of mechanical and electromagnetic waves, as well as the behavior of sound waves, are explained alongside their applications in real-world scenarios.