Embed presentation
Download to read offline






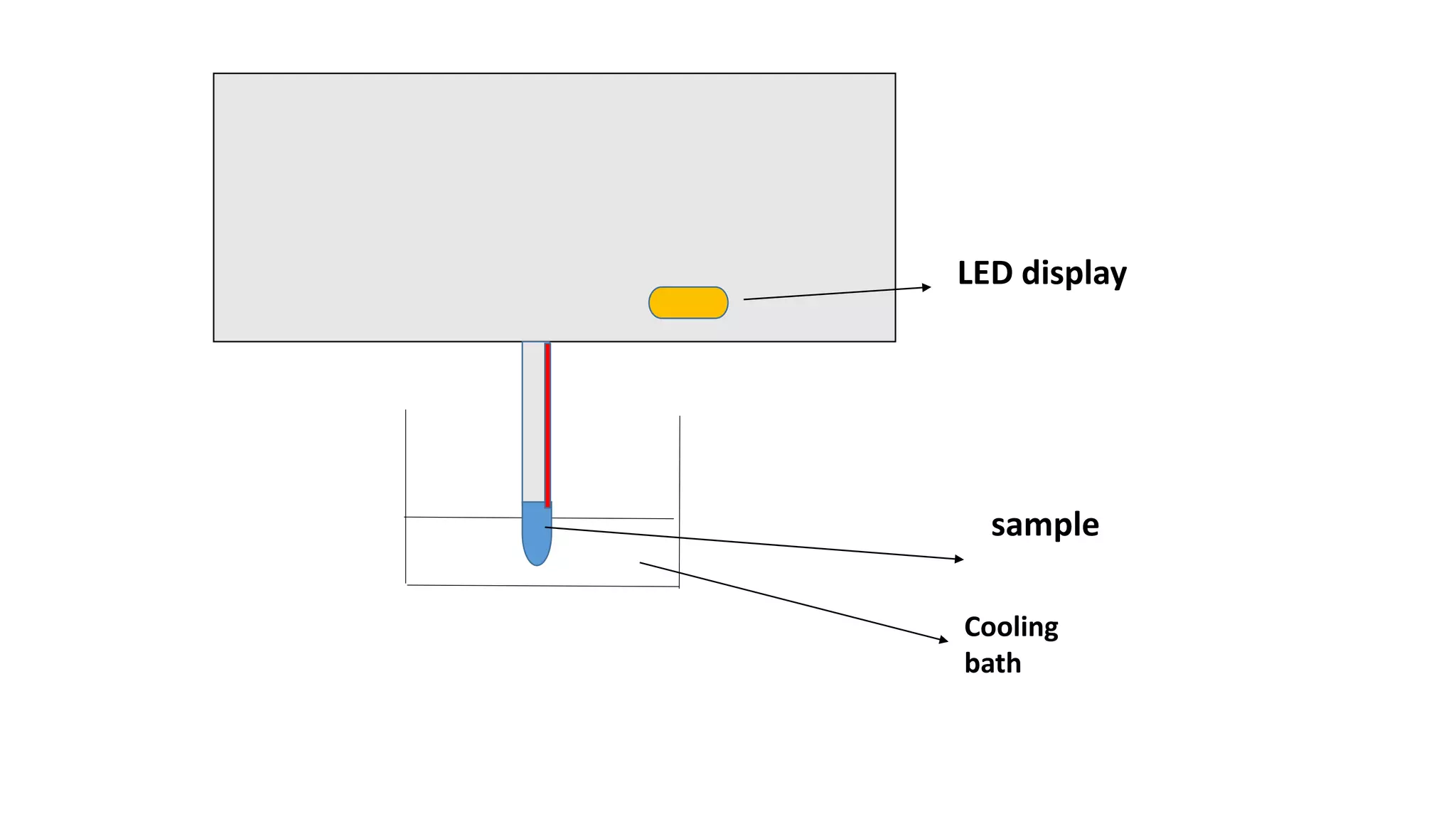


Osmometry is a technique that measures the concentration of solute particles contributing to the osmotic pressure of a solution by measuring its freezing point depression. It works by cooling a sample below -7°C in a cooling bath with stirring until it freezes solid, allowing the osmometer to measure the temperature change and display the osmolarity result. Normal osmolarity ranges are 60-1200 mosm/kg H2O for urine and 280-303 mosm/kg H2O for serum, with increases indicating dehydration or diabetes insipidus and decreases suggesting renal failure.








