Embed presentation
Downloaded 164 times



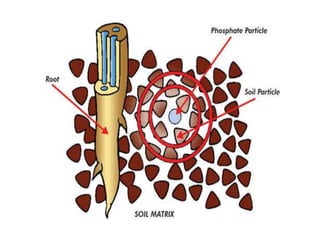
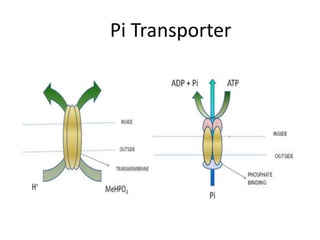

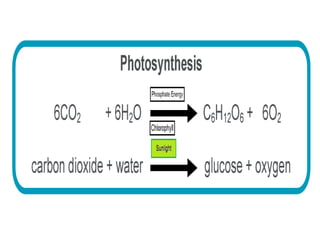




Phosphate is a vital macronutrient for plants, constituting about 0.2% of a plant’s dry weight and is crucial for nucleic acids, ATP, and metabolic pathways. It plays a key role in energy transfer and photosynthesis, where it is involved in the production of ATP from light energy. Phosphorus deficiency can lead to purple coloration in leaves, indicating the importance of adequate phosphate for optimal plant growth.