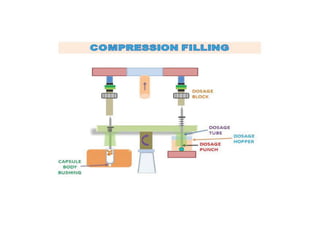
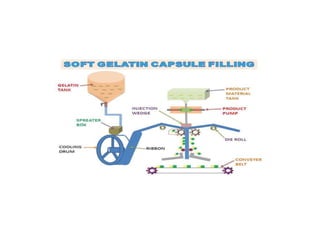
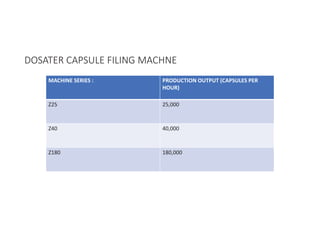
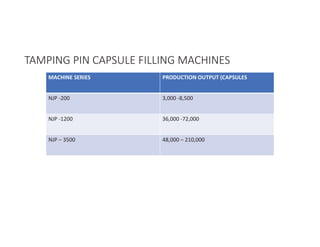
Capsules come in both hard and soft gelatin forms, containing a single dose of active ingredients for oral administration. Hard gelatin capsules consist of gelatin, plasticizers, and water in their shell. The process of manufacturing capsules is similar to tablets, where granules are filled into capsule shells instead of being compressed. Quality control tests are conducted on capsules to test for disintegration, dissolution, assay, content uniformity, weight variation, and stability. Machine settings like speed, pressure, and temperature need to be monitored during the encapsulation process. User requirement specifications provide documentation of manufacturing needs to ensure project success.



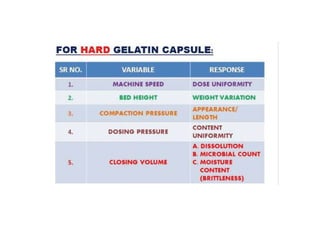




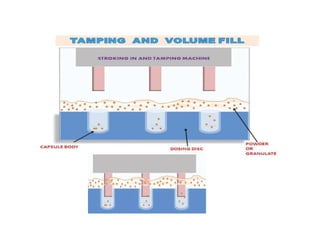
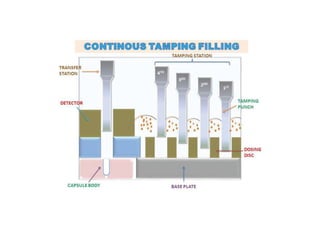
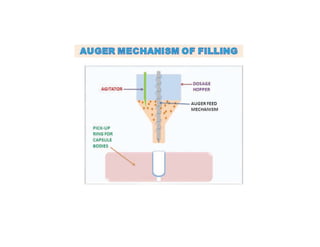
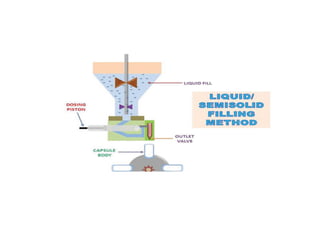







![• Dose uniformity, weight variation, appearance /length, content
uniformity, dissolution, microbial count, moisture content [brittleness]
• Elegance /color, capsule fill weight, capsule shell weight, capsule wall
thickness assay and content uniformity, dissolution {where
appropriate}, moisture content, leak test.
QC FOR HGC](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/processvalidationcapsule-240415164430-57f06516/85/PROCESS-VALIDATION-FOR-CAPSULES-SOLID-DOSAGE-FORM-pdf-28-320.jpg)


