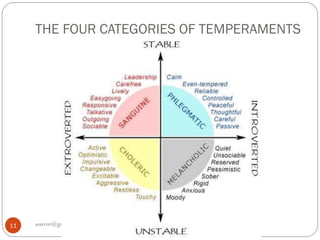
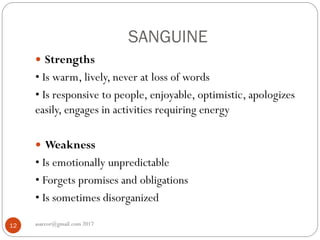
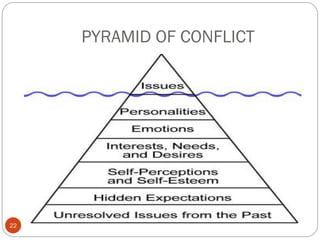
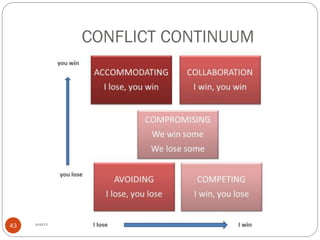
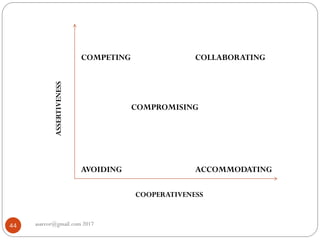
The document discusses personality types, causes of conflict, and strategies for managing conflict. It defines personality and describes the four main personality types: sanguine, choleric, melancholic, and phlegmatic. It also outlines five styles for managing conflict: competing, collaborating, compromising, accommodating, and avoiding. The document emphasizes that understanding personality differences is key to resolving conflicts effectively in work environments.