The document discusses several perspectives on personality:
1) Psychodynamic perspective focuses on the unconscious mind in development. Behaviorist perspective examines environmental influences on behavior. Humanist perspective looks at experiences and choices shaping personality.
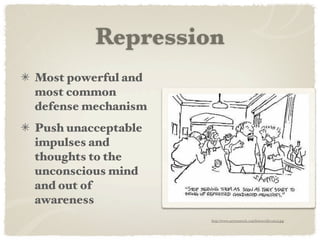
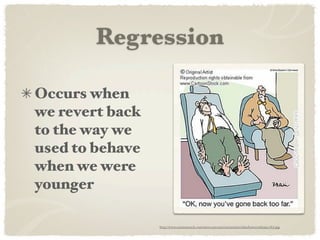
2) Freud and his psychoanalytic approach emphasized the unconscious and structures of ID, EGO, and SUPEREGO. Jung focused on the personal and collective unconscious. Adler stressed inferiority complexes. Horney argued against Freud's views.
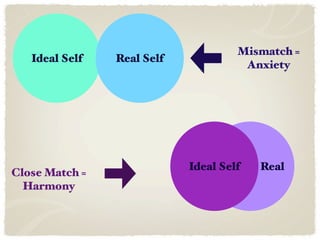
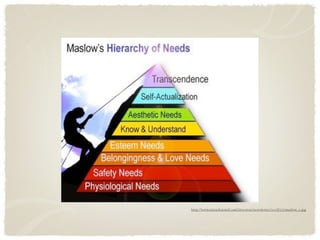
3) Behavioral theories examined associative learning and social learning influences on observable behaviors according to Skinner and Bandura respectively. Humanistic theories from Rogers and Maslow emphasized self-actualization and hierarchies of needs.