Embed presentation
Downloaded 245 times


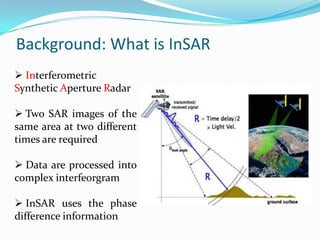

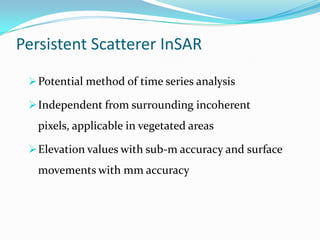
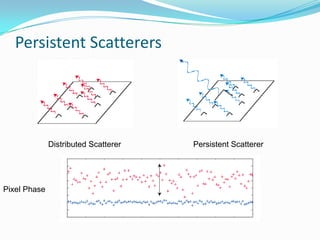
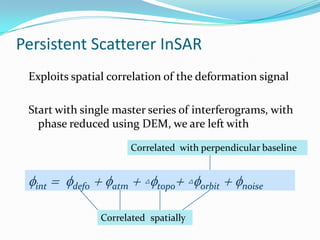
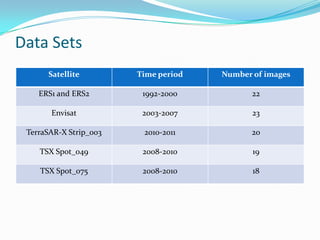












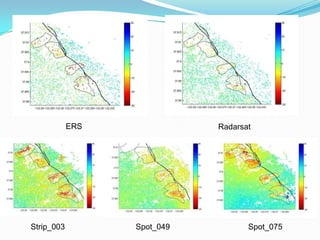


This document discusses the application of persistent scatterer interferometry (PSI) to study landslides in the Berkeley Hills. PSI uses phase information from SAR images taken at different times to measure surface deformation with millimeter accuracy. It was applied using Envisat, ERS, Radarsat, and TerraSAR-X data. Thousands of persistent scatterers were identified, allowing measurement of surface motion along the Hayward Fault and within landslides. Future work will continue monitoring with additional SAR data to better resolve three-dimensional landslide motions.






















