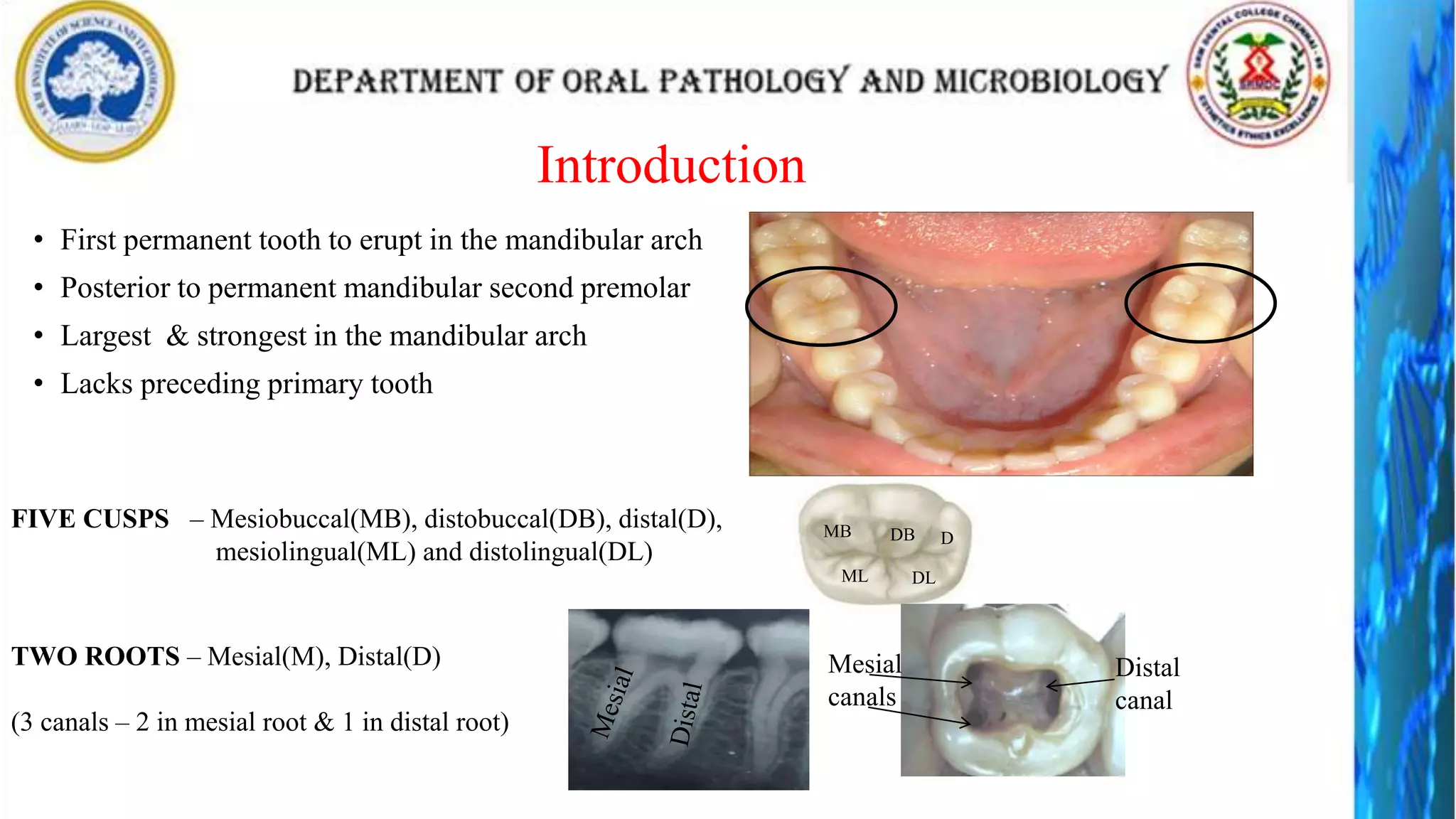
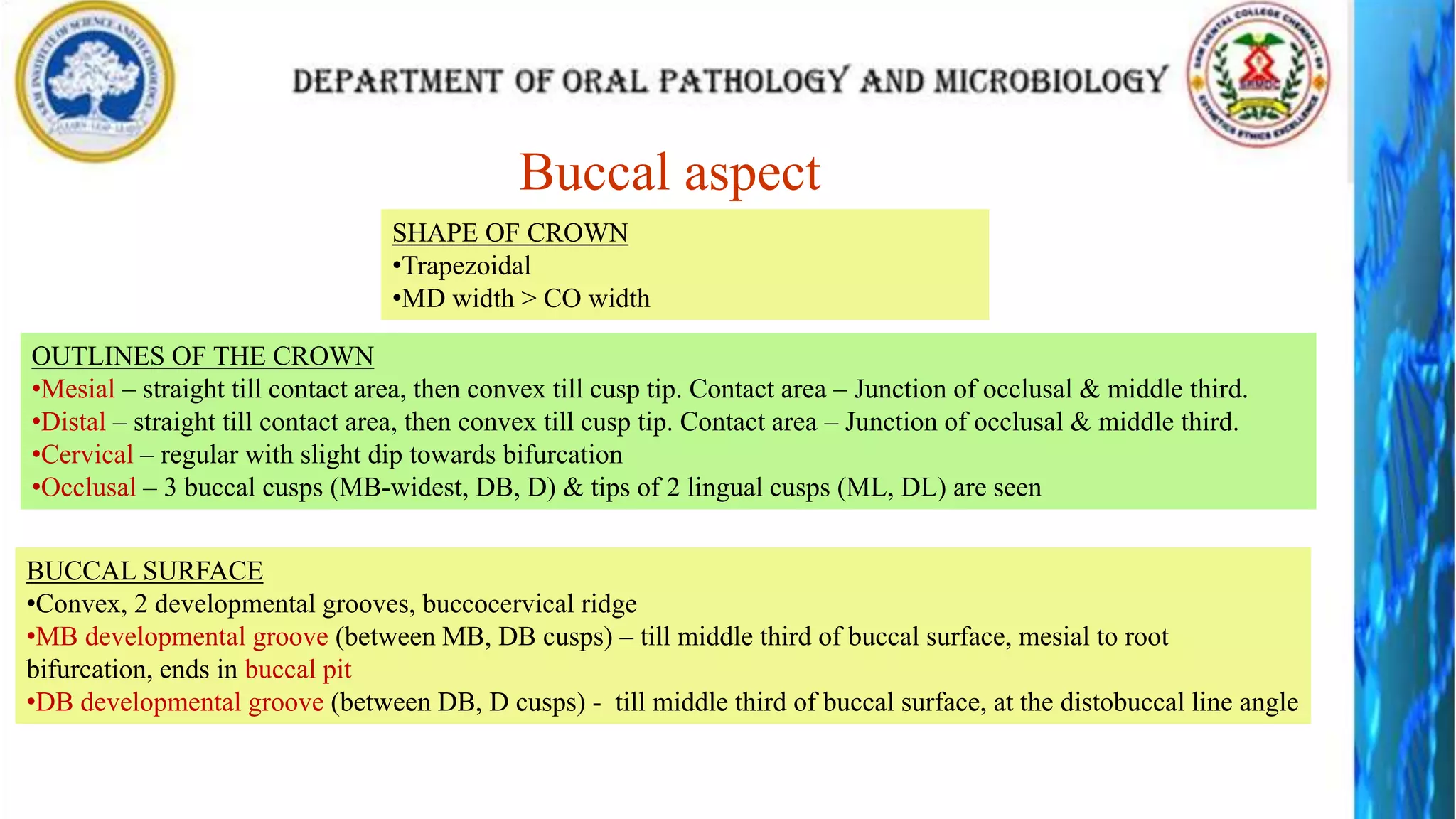
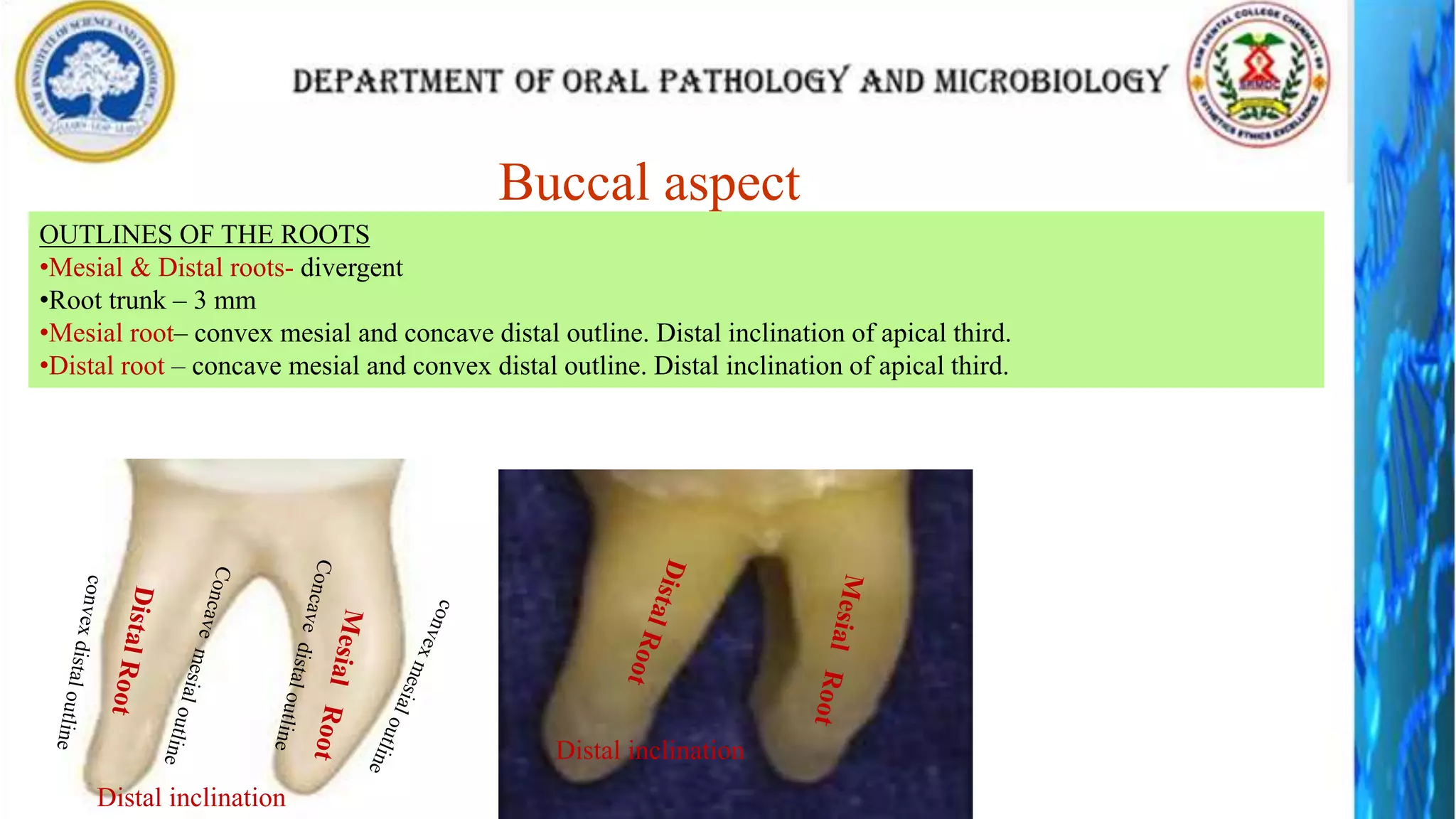
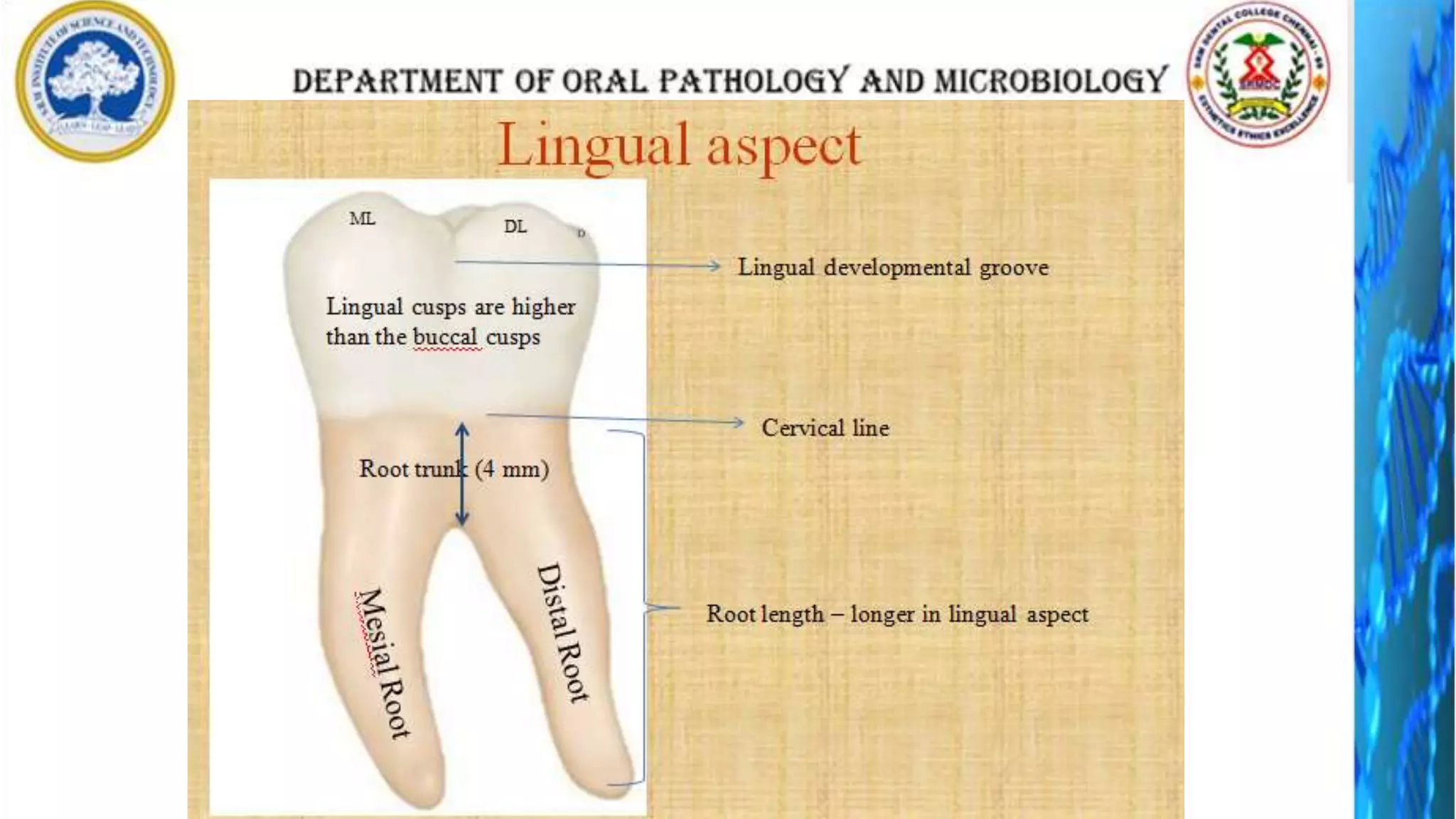
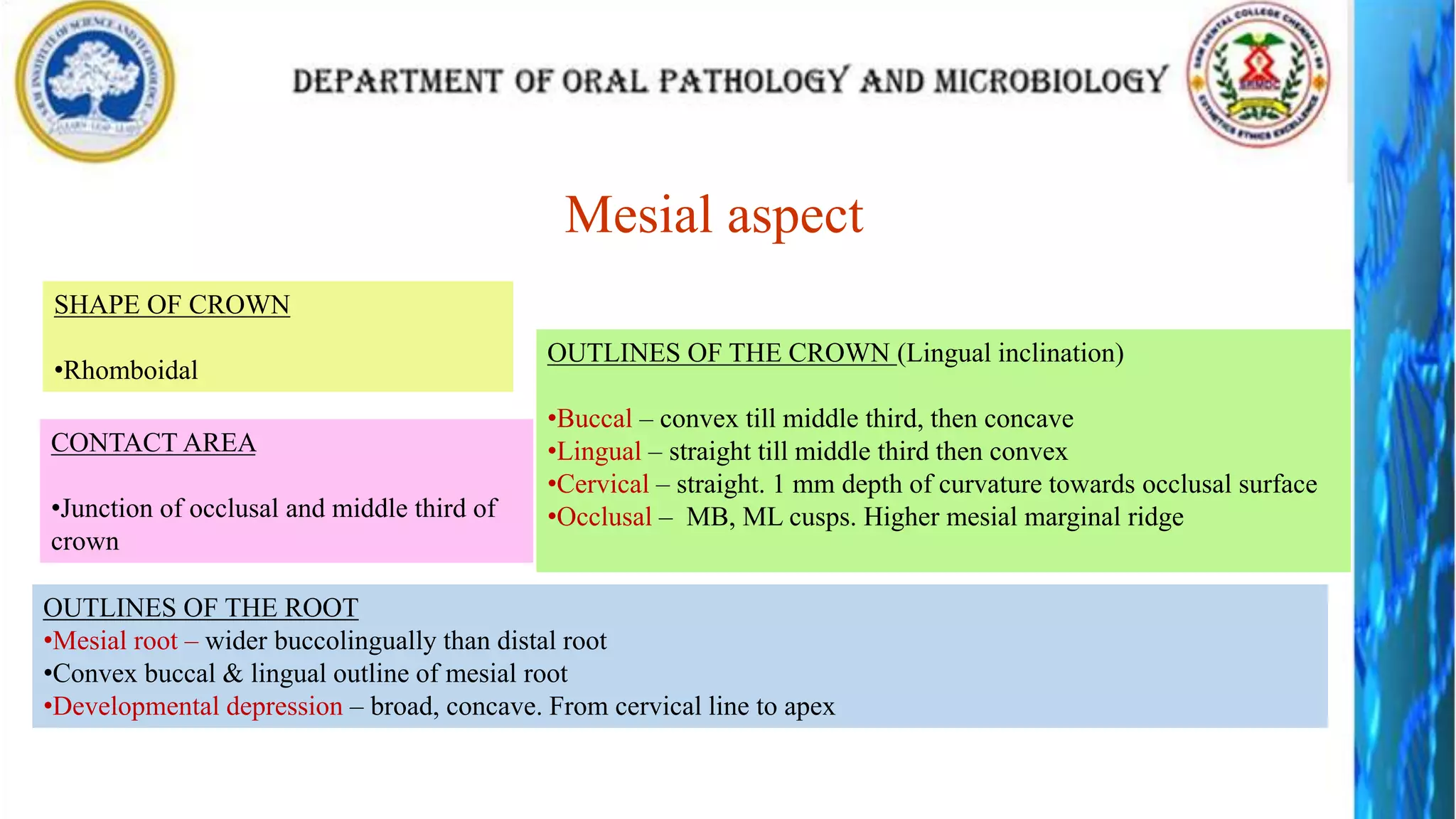
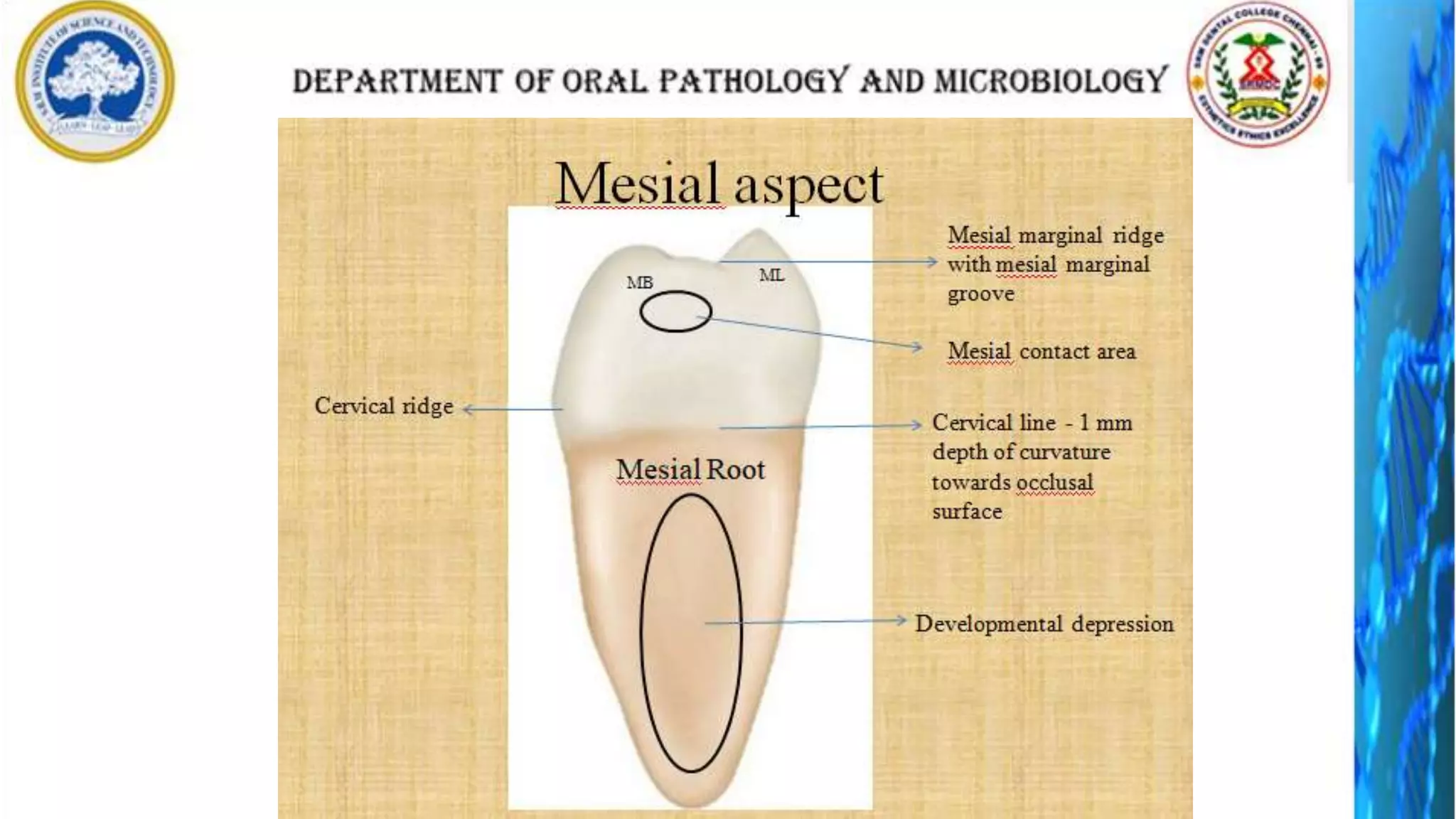
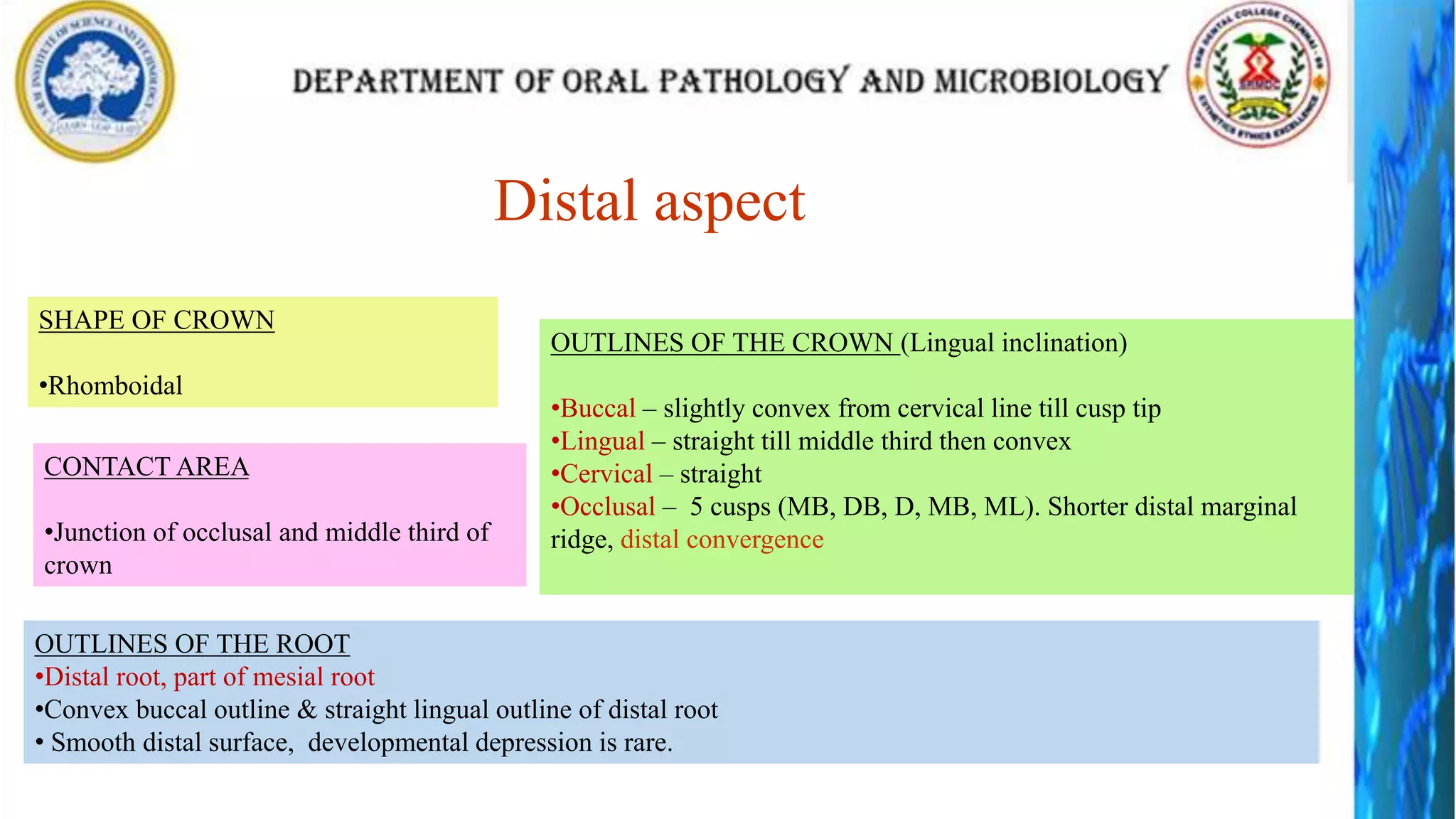
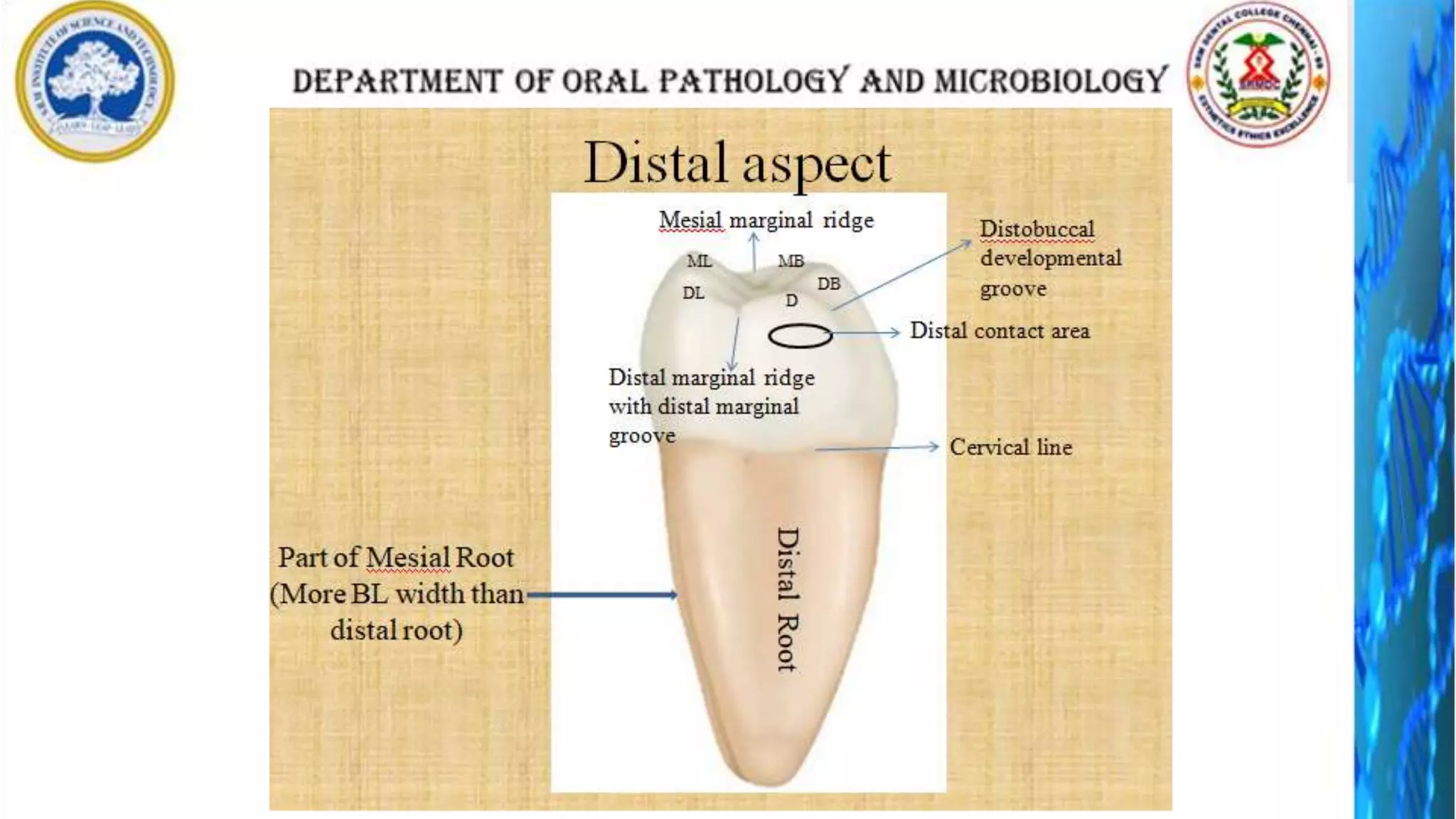
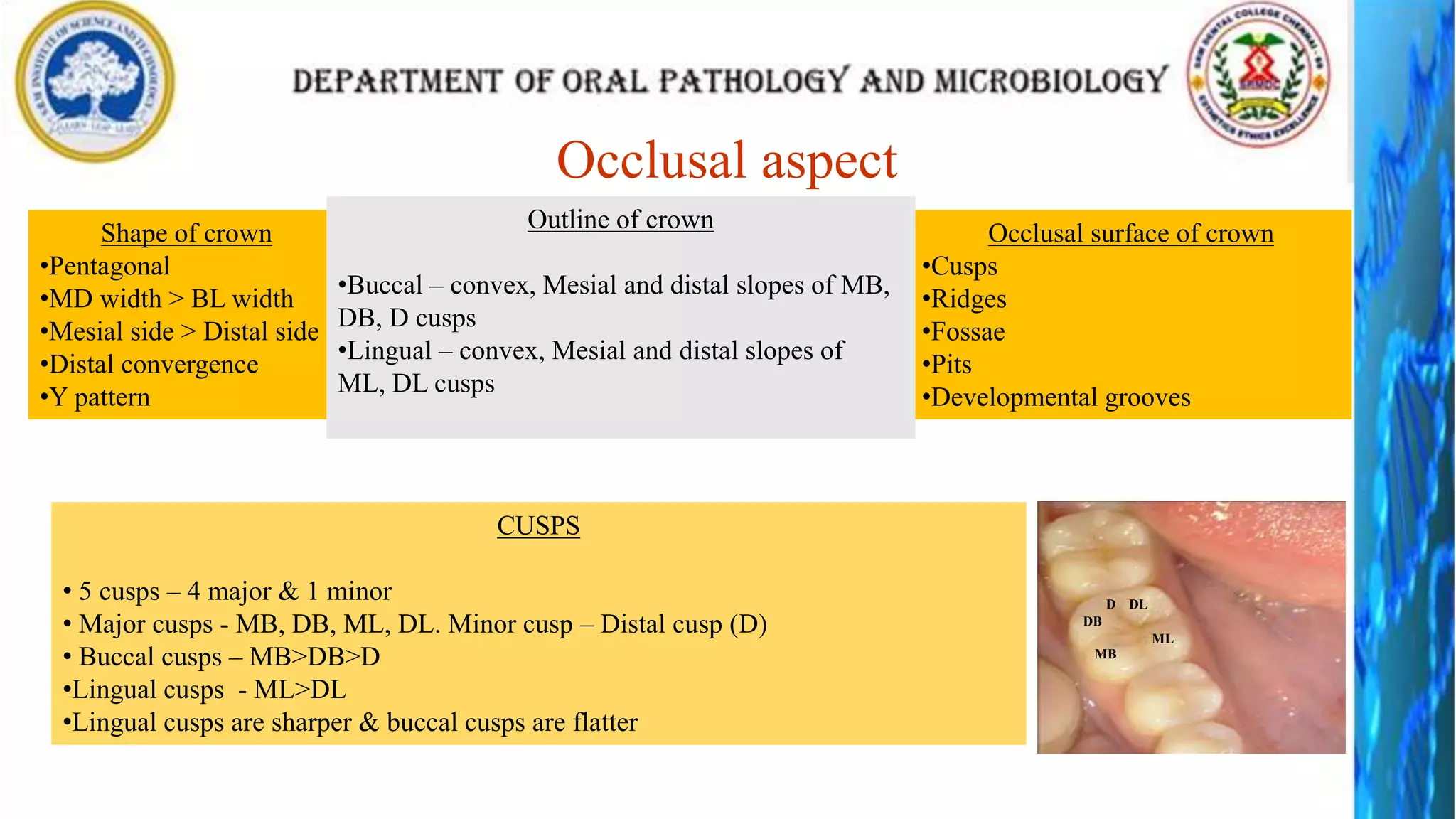
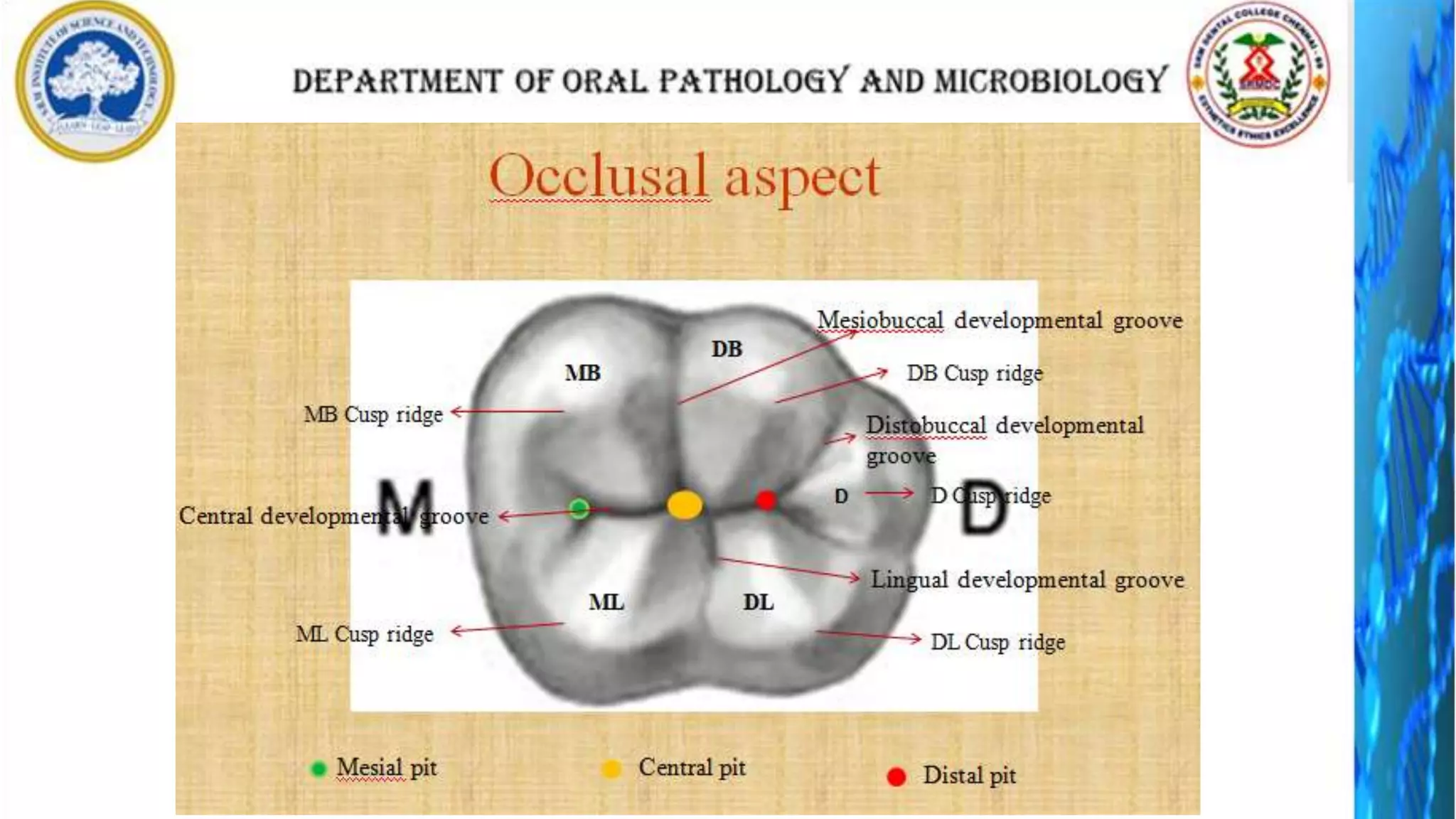
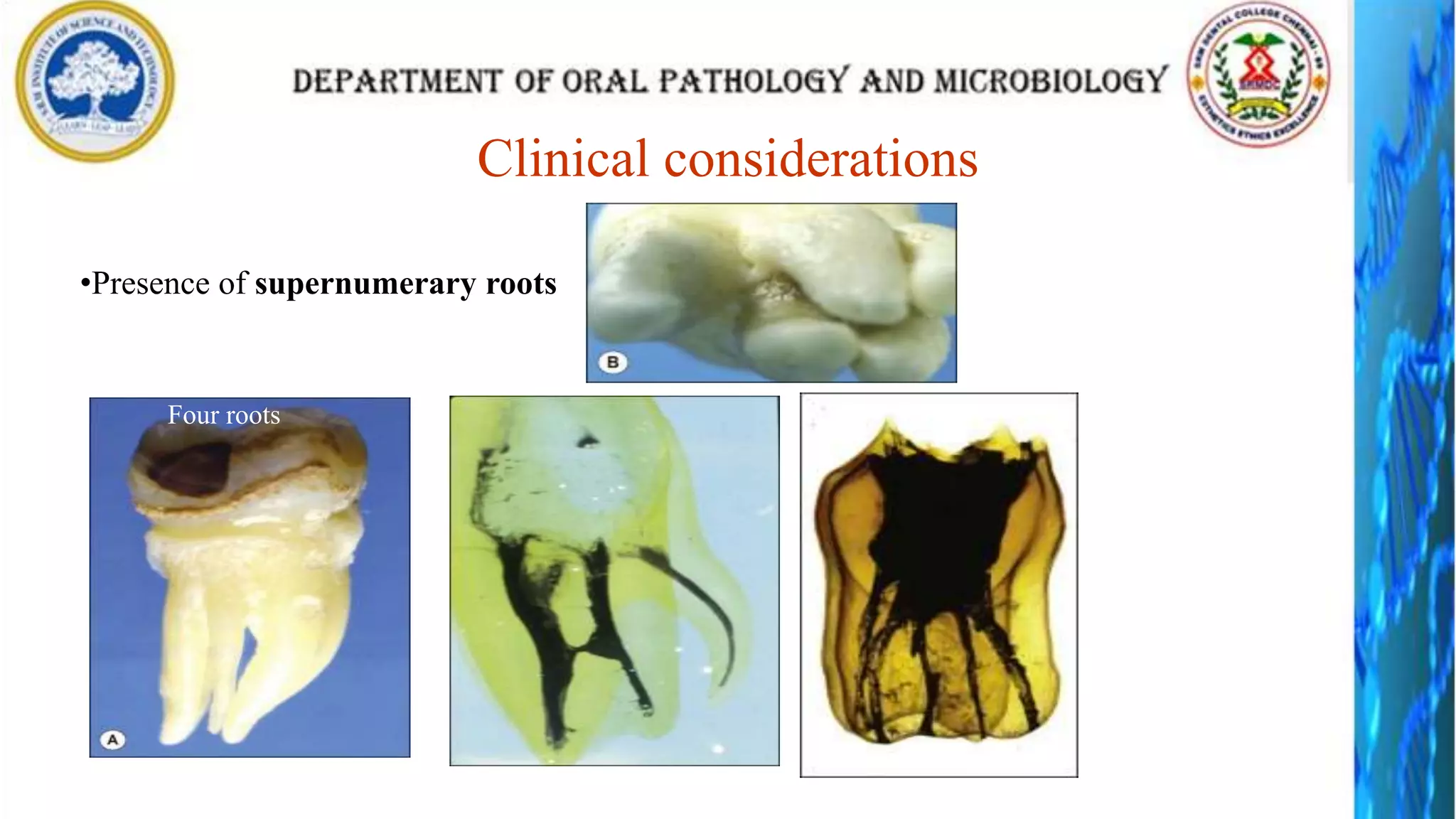
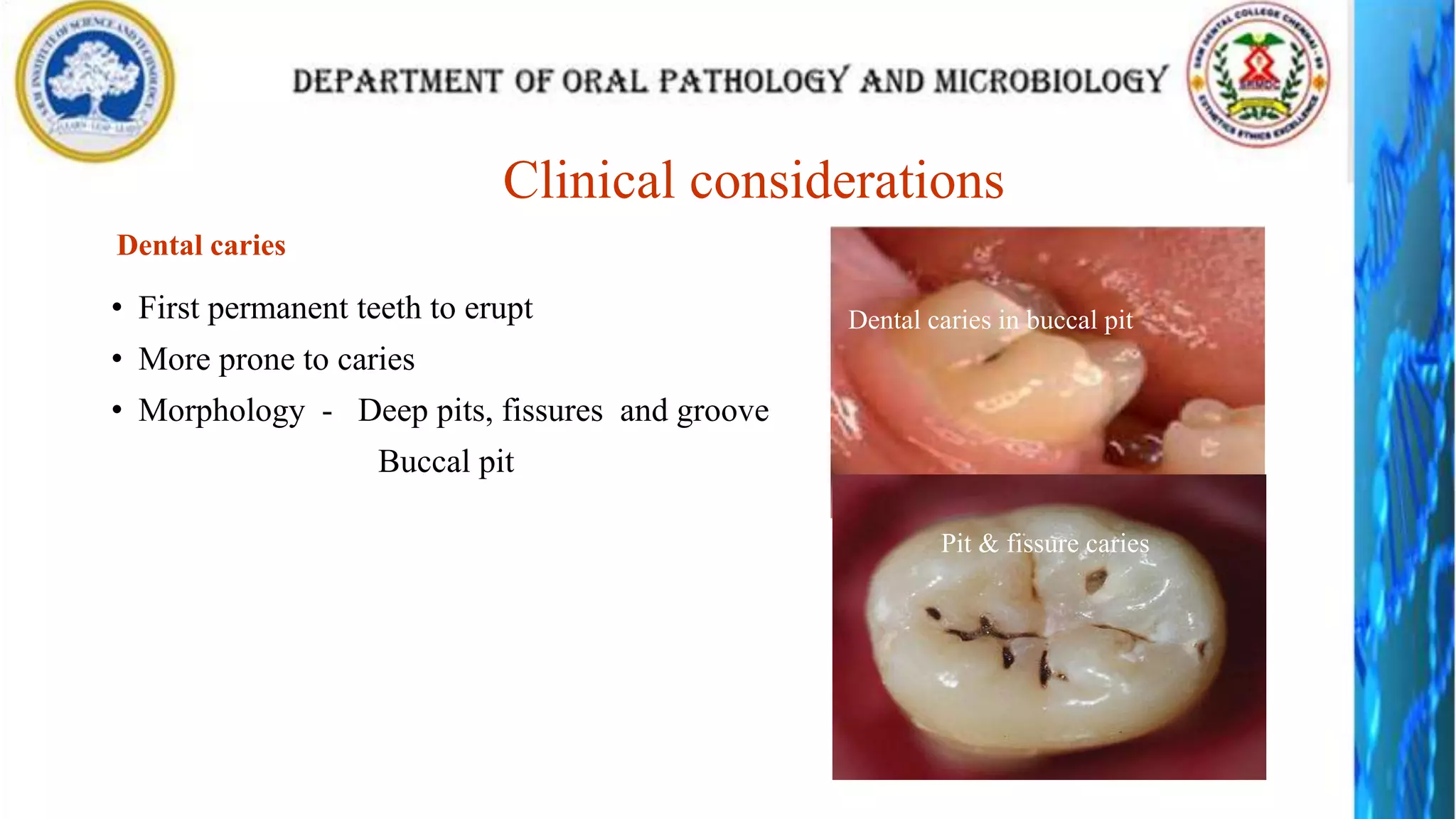
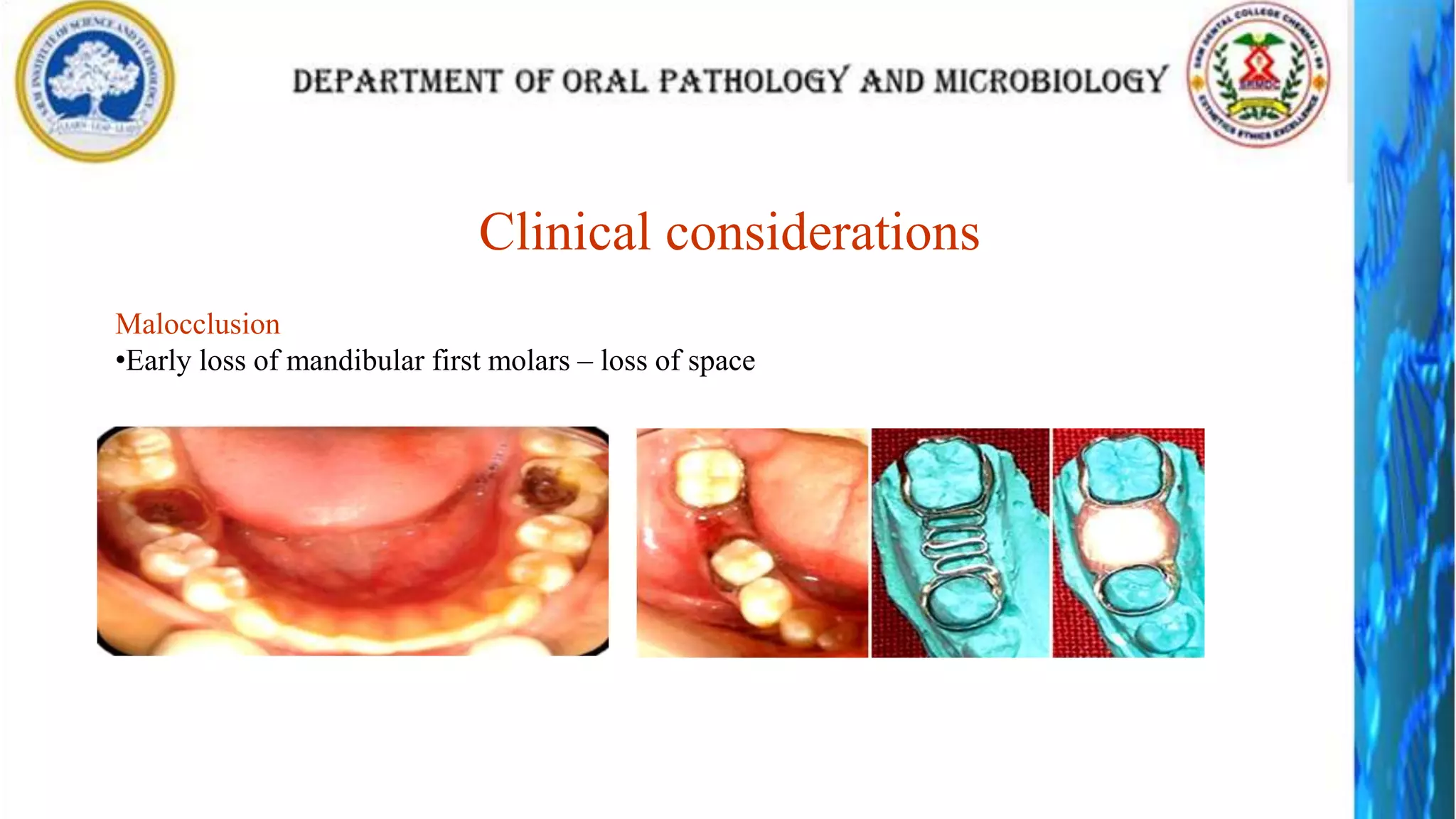
The document discusses the anatomy and morphology of the mandibular first molar tooth. It notes that the tooth has 5 cusps, 2 roots, and 3 canals. It then describes the dimensions, eruption timeline, and importance for functions like mastication and anchorage. The buccal, lingual, mesial, distal, and occlusal surfaces are outlined along with ridges, fossae, pits and developmental grooves. Clinical considerations include susceptibility to caries due to deep fissures and grooves, importance for space maintenance, and role in orthodontic anchorage.