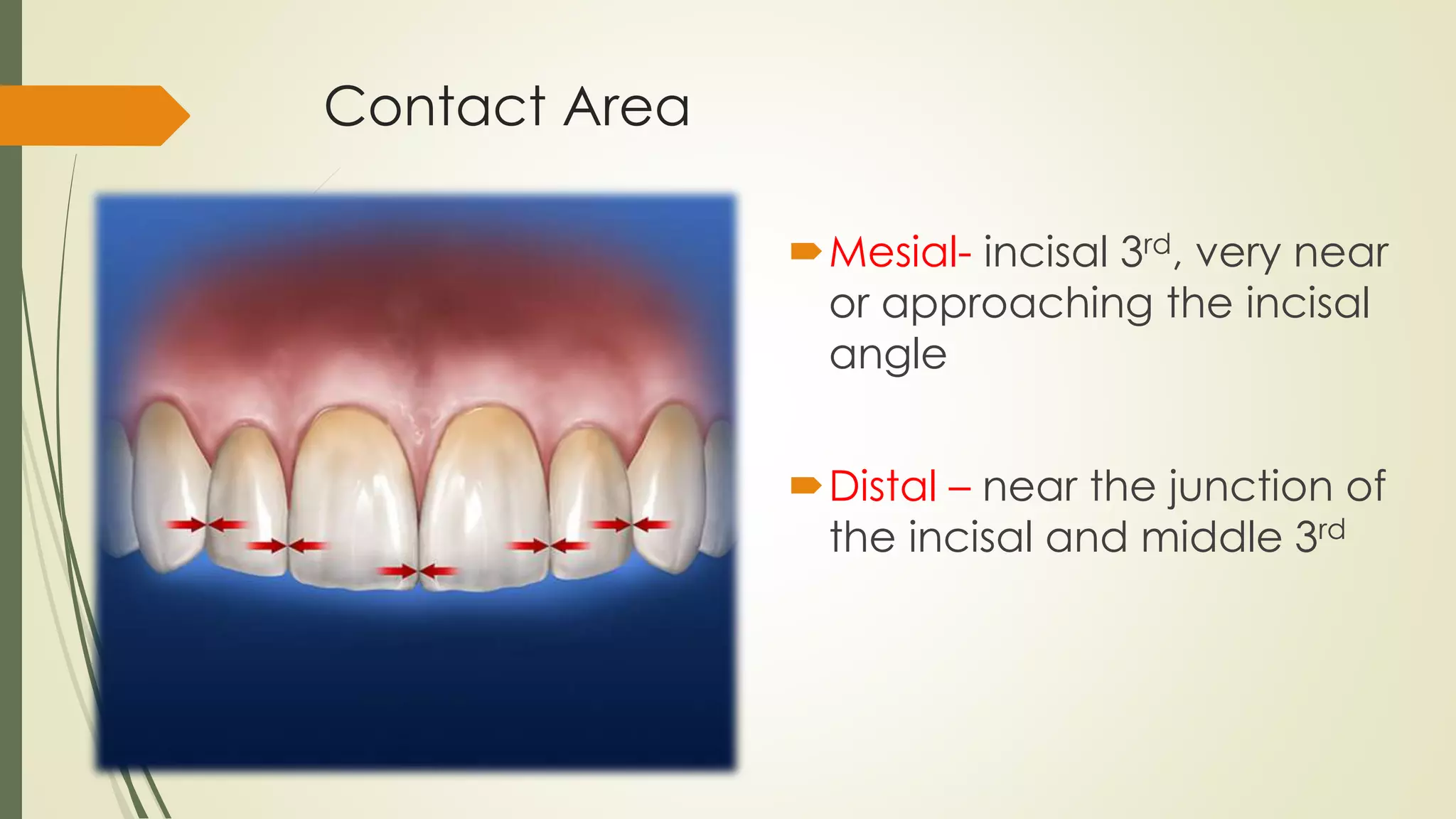
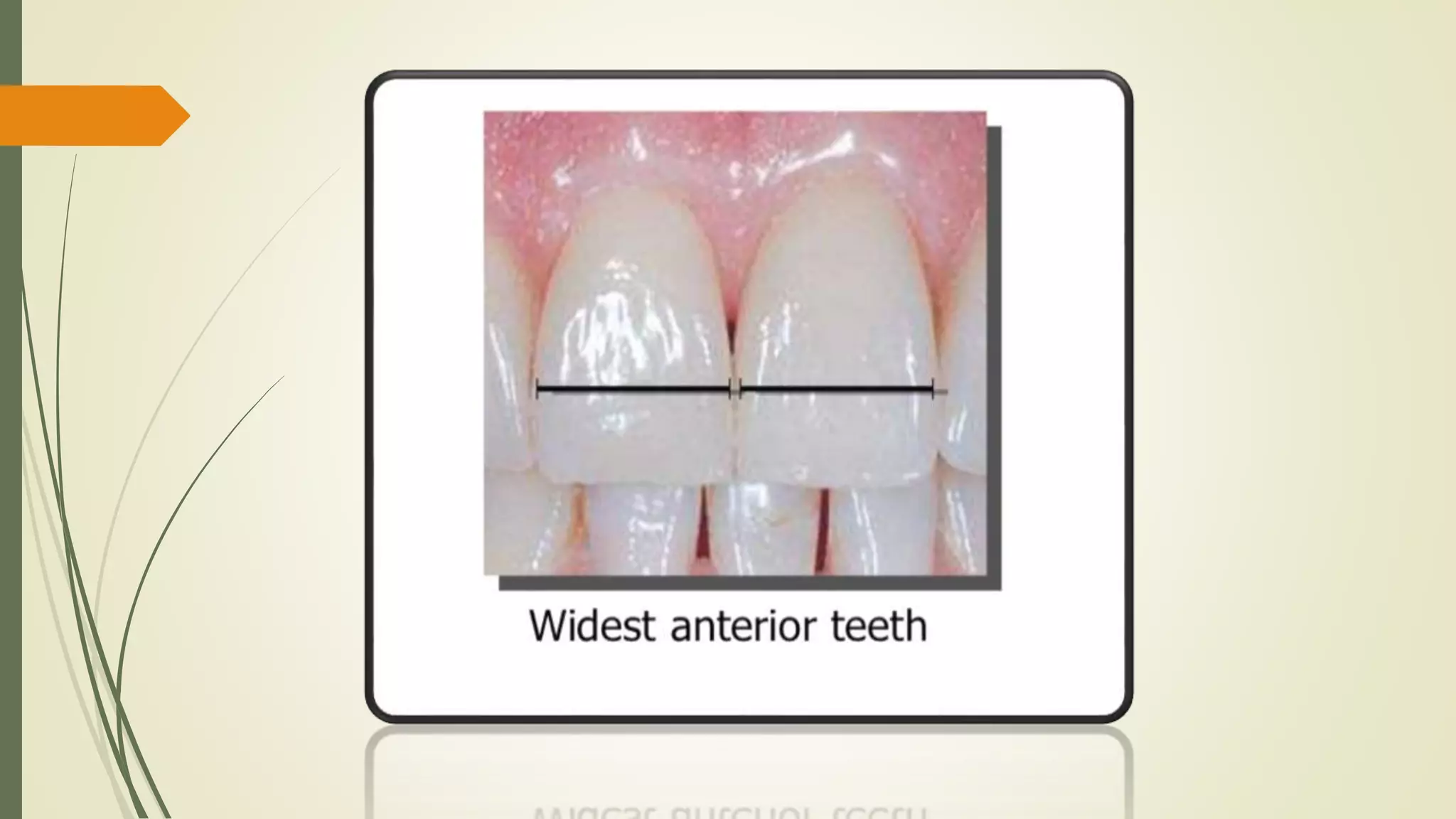
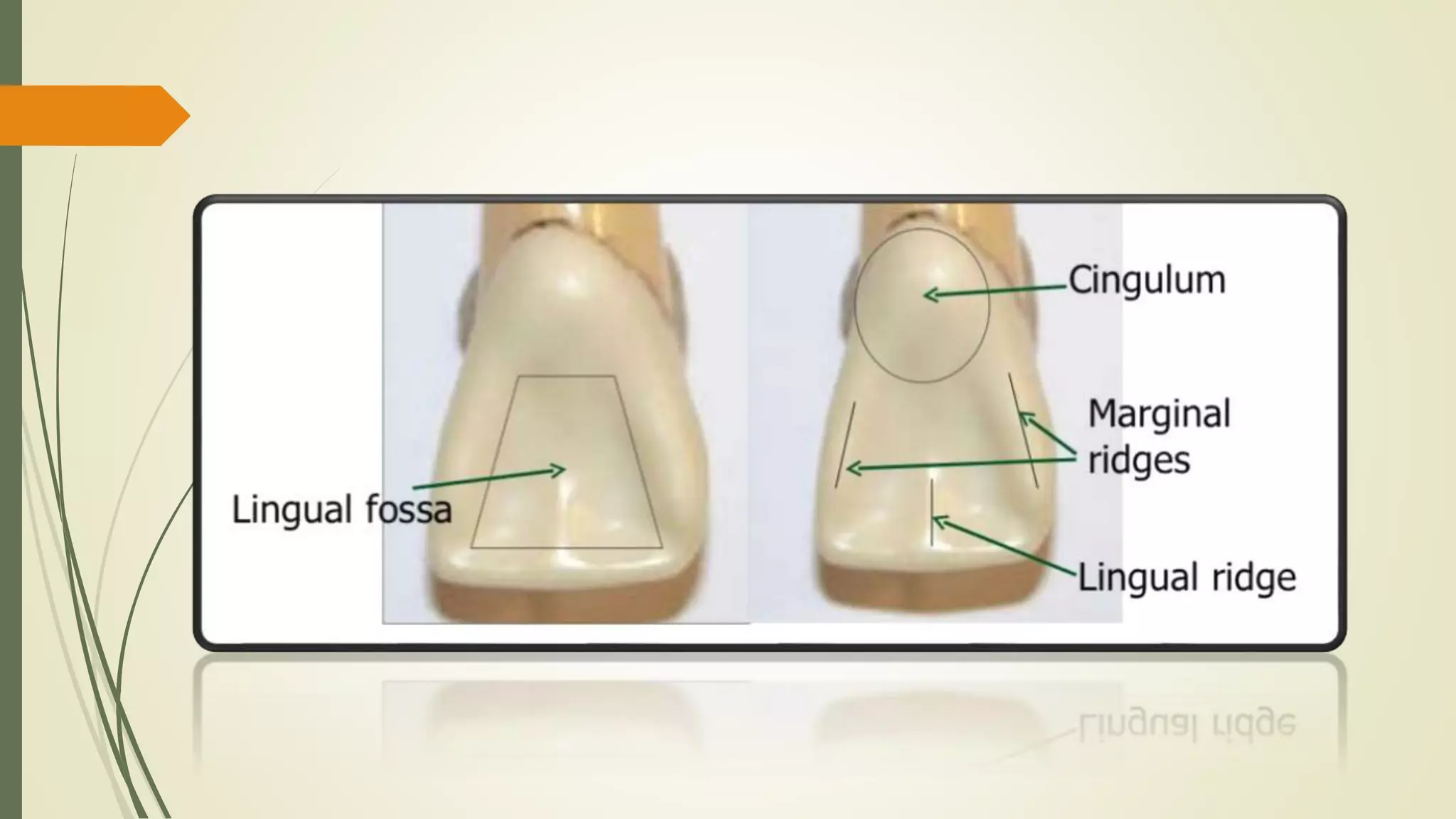
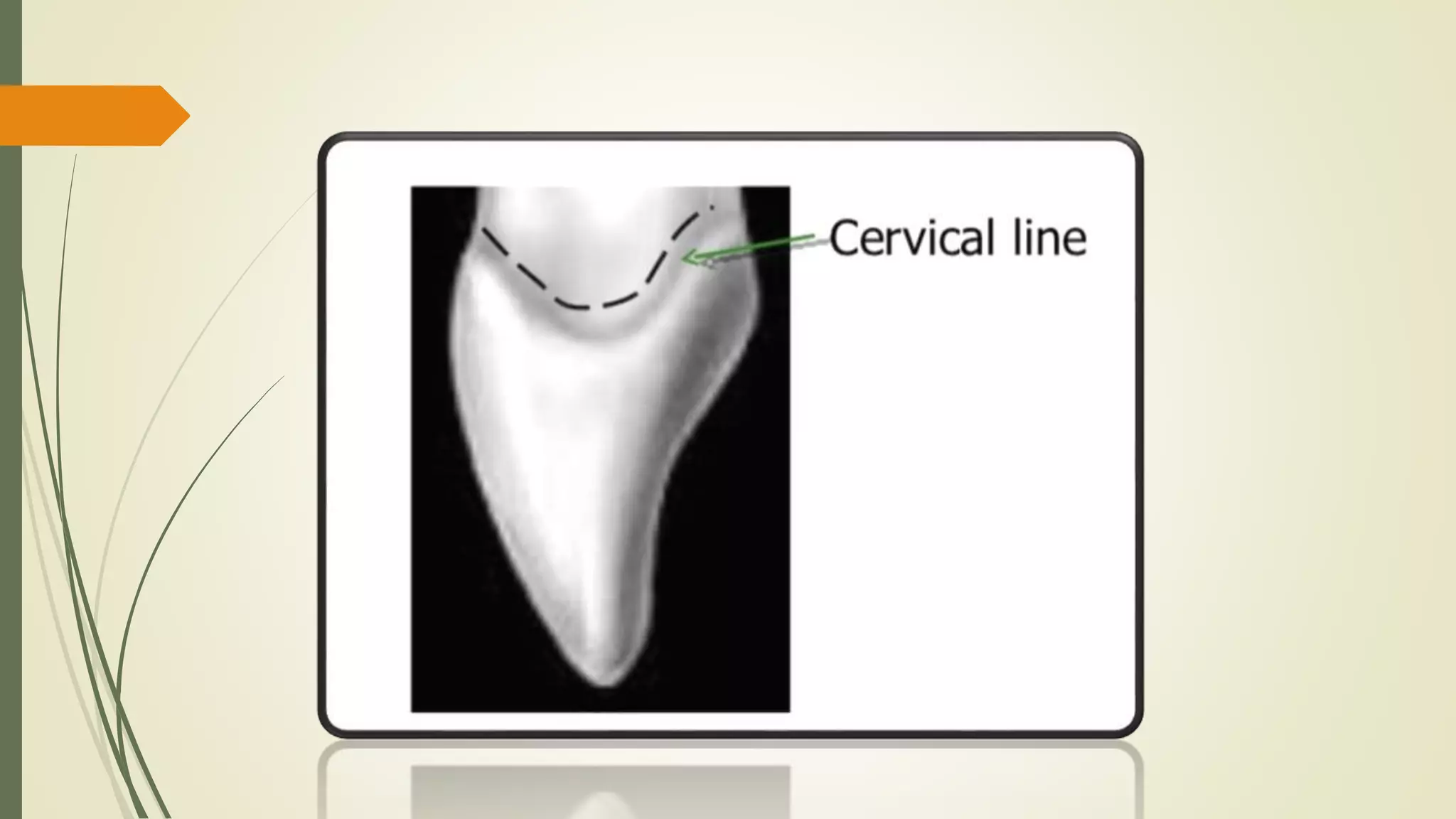
The maxillary central incisor develops from four primary lobes, featuring a trapezoidal crown outline with distinct anatomical characteristics such as mamelons and labial depressions. Variations exist in root length and shape, with a cone-shaped root that is longer than the crown, and differences in the curvature of the cervical line. The crown exhibits smooth convexities and tapering towards the cingulum, with specific mesial and distal contouring details.