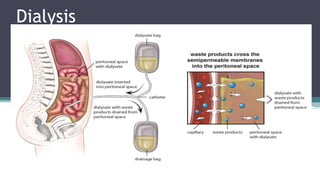
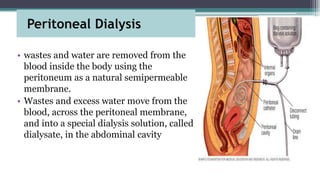
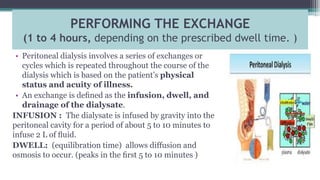
Dialysis is a process that removes waste and excess water from the blood when the kidneys fail. It uses the peritoneum as a natural membrane to remove wastes and water from the blood into a dialysate solution in the abdominal cavity. There are two main types of peritoneal dialysis - continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD) which is done manually throughout the day, and automated peritoneal dialysis (APD) which uses a machine at night. The peritoneal dialysis procedure involves infusing dialysate into the abdominal cavity, allowing it to dwell to enable diffusion and osmosis, then draining the used fluid and repeating the cycles. Nursing care focuses on infection prevention, assessing