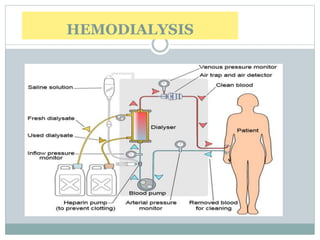
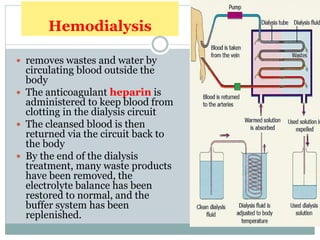
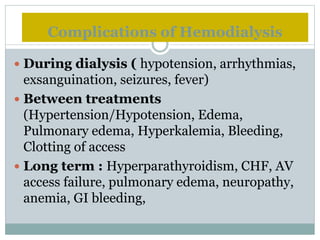
Dialysis is a medical technique used to remove waste products and excess fluids from the blood, primarily in individuals with kidney failure. There are two main types: hemodialysis, which requires a machine to cleanse the blood, and peritoneal dialysis, which utilizes the peritoneal membrane for filtration. Both methods have specific indications, procedures, and potential complications, emphasizing the importance of proper management and monitoring.