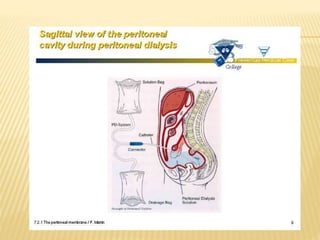
Peritoneal dialysis (PD) is a treatment for severe chronic kidney failure that uses the peritoneum in the abdomen as a membrane to exchange fluids and dissolved substances between the blood and dialysis fluid introduced into the abdomen. Fluid is introduced through a permanent abdominal catheter and removed periodically, either continuously throughout the day or automatically at night. PD provides an alternative to hemodialysis by allowing treatment without visiting a medical facility but carries risks like infection from the permanent catheter. Nursing management of PD includes monitoring for complications, supporting nutrition, managing discomfort, and providing health teaching.