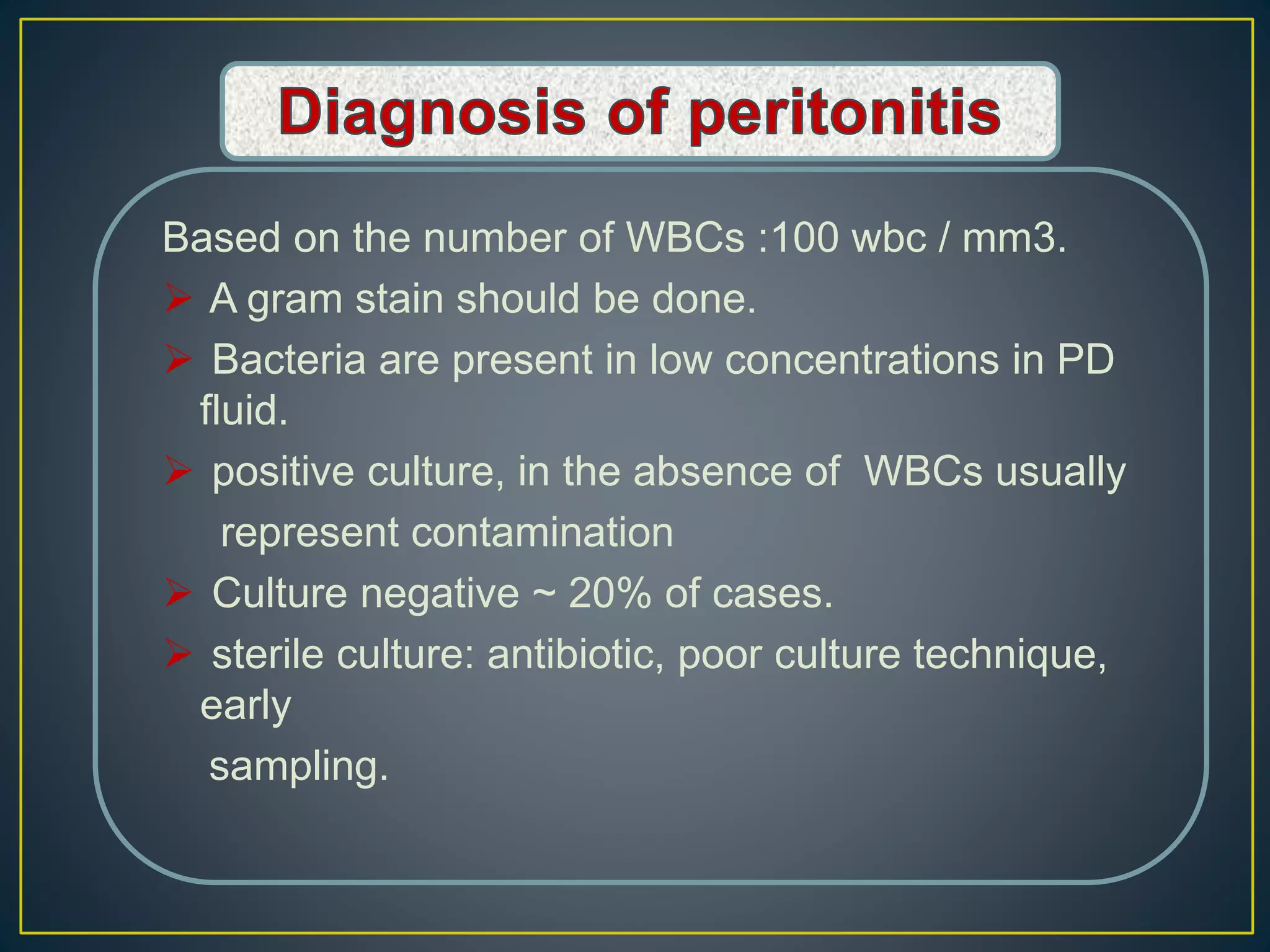
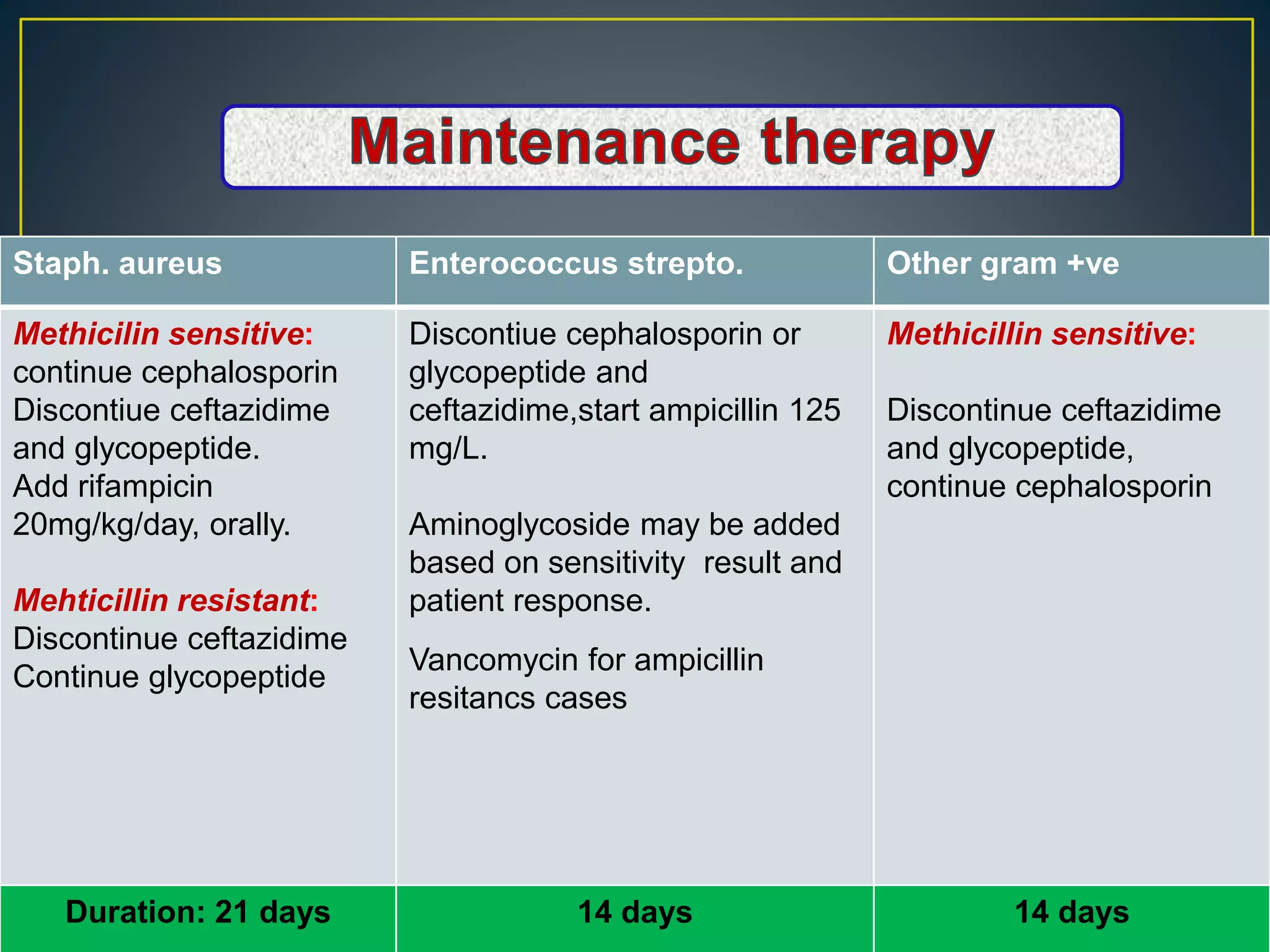
This document discusses complications of peritoneal dialysis (PD) therapy, including infectious and non-infectious complications. It provides guidance on diagnosing and treating peritonitis, the major infectious complication of PD. It recommends empiric antibiotic therapy for peritonitis including cefazolin/cephalothin and vancomycin or teicoplanin initially. Therapy should be adjusted based on culture results and patient response. Non-infectious complications discussed include mechanical issues like pain or hernias as well as metabolic disturbances like ultrafiltration failure or encapsulating peritoneal sclerosis. Overall the document provides clinical guidelines for managing common complications of peritoneal dialysis.