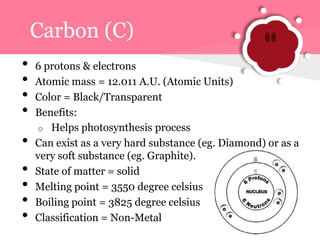
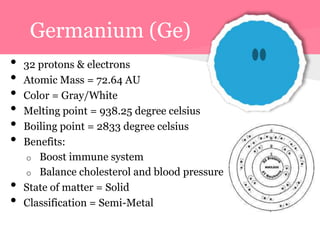
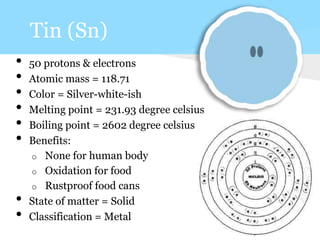
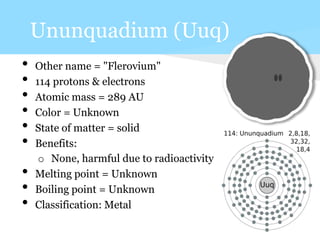
This document summarizes information about 7 elements - carbon, silicon, germanium, tin, lead, ununquadium, and their properties including atomic number, mass, state, color, melting and boiling points, classification, and benefits or harms. Key similarities are that most are solids and have neutral colors. Differences are that the first 3 have benefits while later ones are harmful or have no benefits. Melting and boiling points decrease with increasing atomic mass while density and conductivity increase.