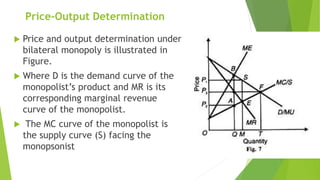
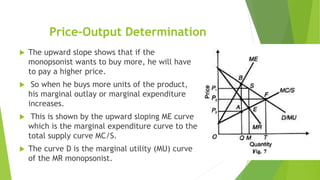
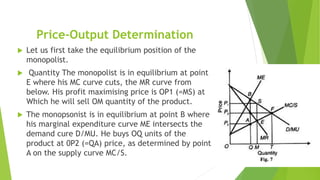
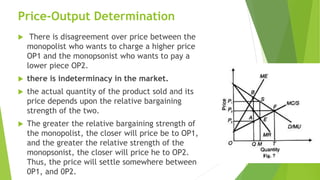
This document discusses bilateral monopoly, which refers to a market situation with a single seller (monopolist) and single buyer (monopsonist) of a product. It outlines the assumptions of bilateral monopoly and describes how price and output are determined. Specifically, it notes that the monopolist will seek to sell at a higher price where marginal cost equals marginal revenue, while the monopsonist will seek to buy at a lower price where marginal expenditure equals marginal utility. The actual price and quantity transacted will depend on the relative bargaining strengths of the monopolist and monopsonist, settling somewhere between the two preferred prices.