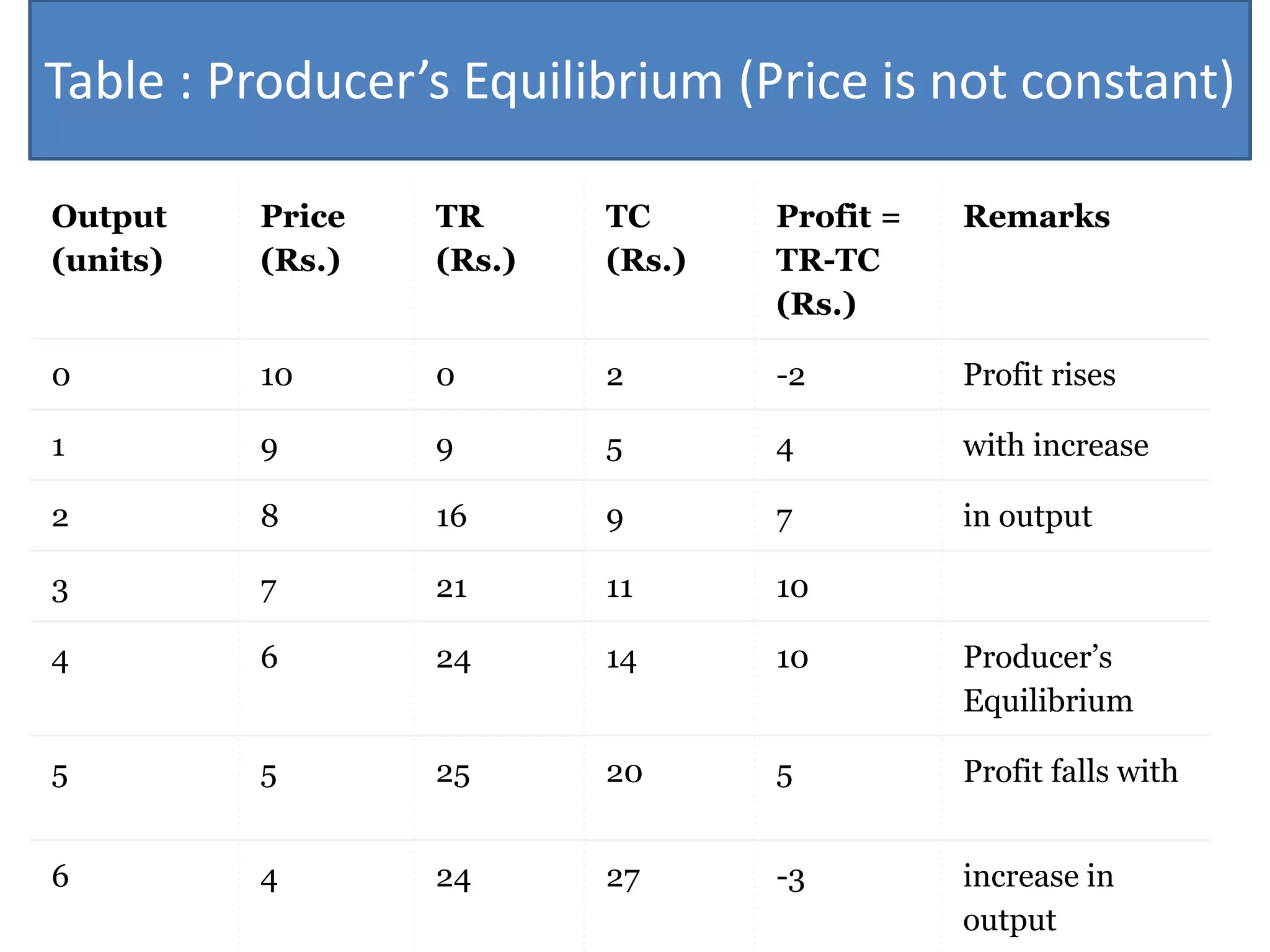
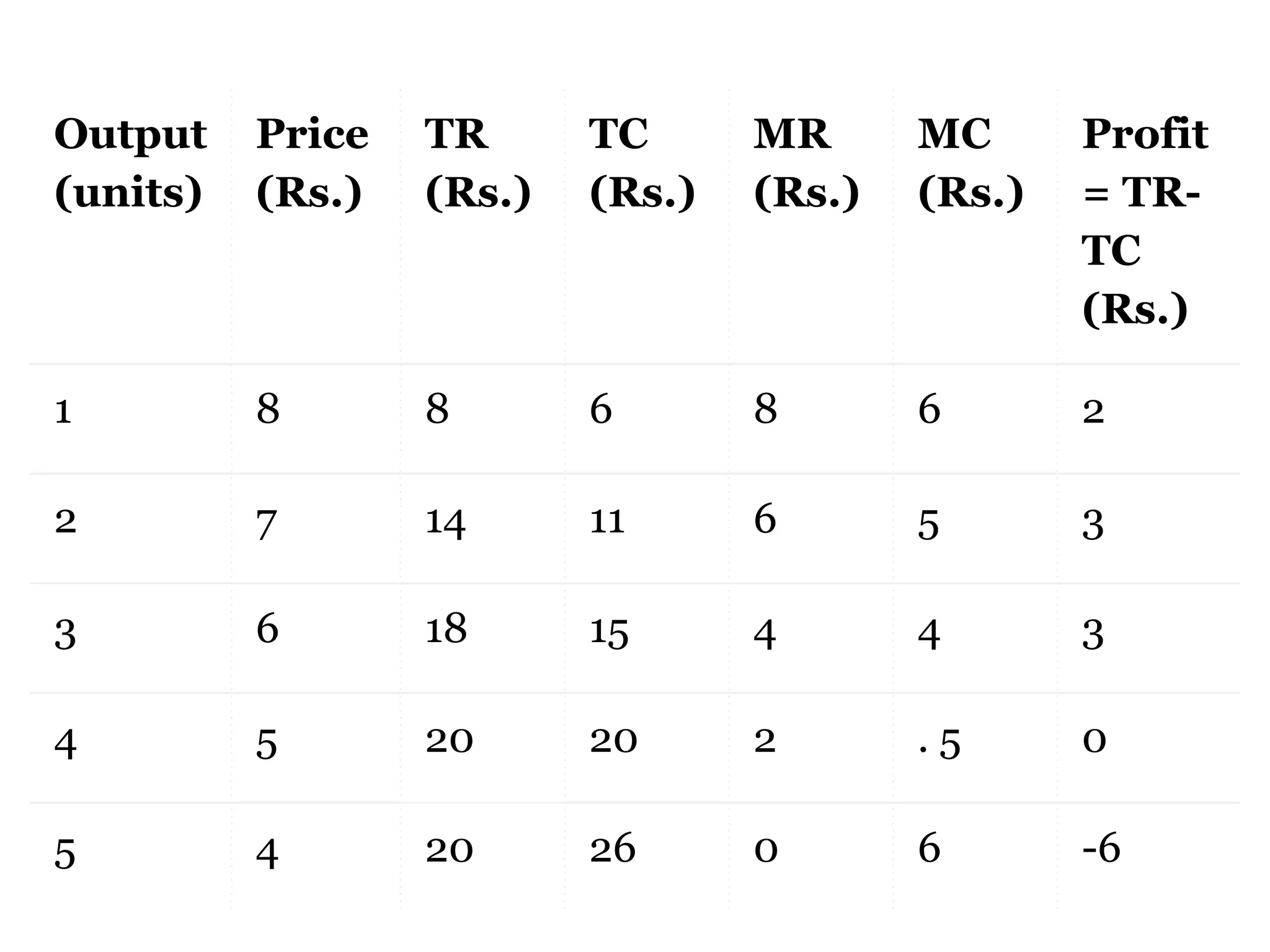
Producer's equilibrium refers to a state where a firm neither wants to expand nor contract its output, typically reflecting maximum profits or minimal losses. It can be determined using either the total revenue and total cost approach or the marginal revenue and marginal cost approach, with key conditions allowing equilibrium to occur when price remains constant or falls with increased output. The essential concepts include maximizing the profits by ensuring that marginal cost equals marginal revenue, and the conditions that guide this equilibrium state.