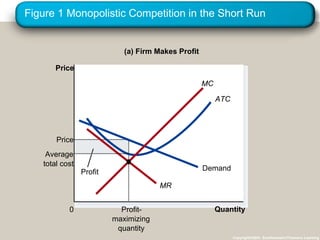
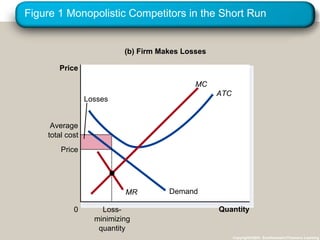
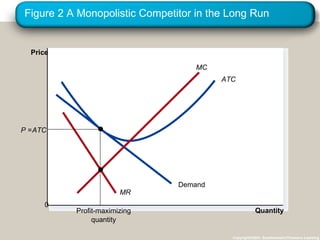
Monopolistic competition is an imperfect market structure between perfect competition and pure monopoly. It is characterized by many small sellers offering differentiated products, free entry and exit into the market, and firms facing downward-sloping demand curves. In the short run, firms can make profits or losses, but in the long run free entry and exit will cause the number of firms to adjust until all firms earn zero economic profits and price equals average total cost.