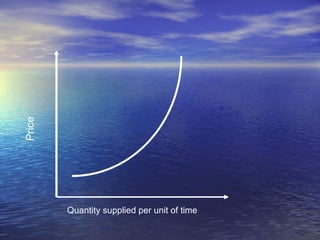
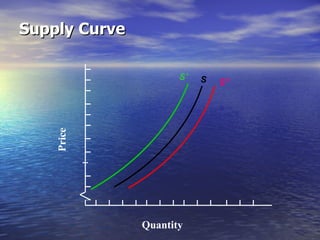
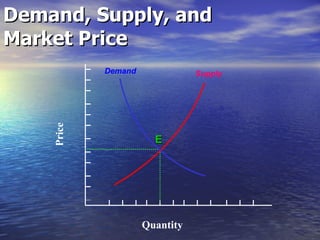
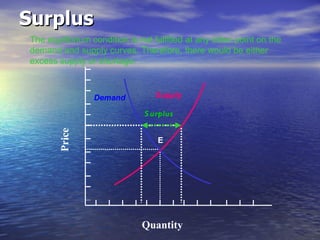
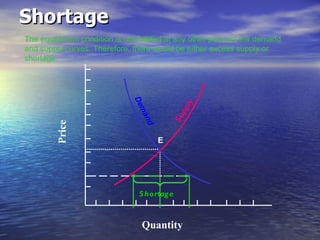
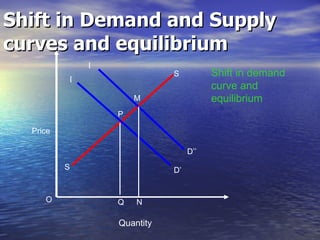
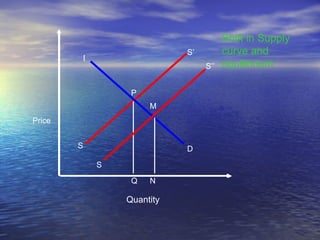
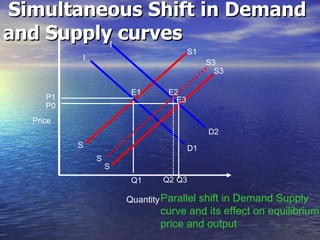
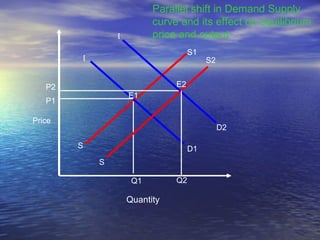
The document discusses market mechanisms and how supply and demand determine market equilibrium price. It defines a market as a place where buyers and sellers interact to determine price and quantity. The market mechanism is governed by the laws of supply and demand. Equilibrium is reached at the price where quantity supplied equals quantity demanded, clearing the market. If supply exceeds demand, prices fall until equilibrium is attained, and if demand exceeds supply then prices rise until equilibrium is reached.