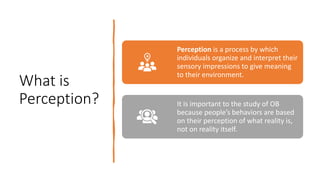
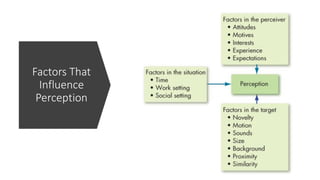
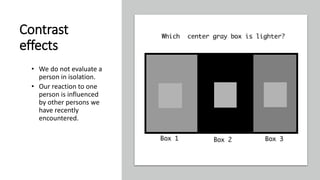
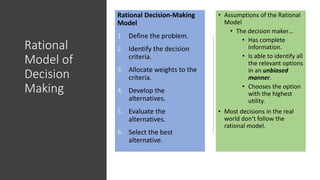
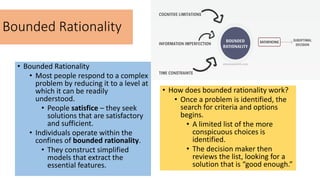
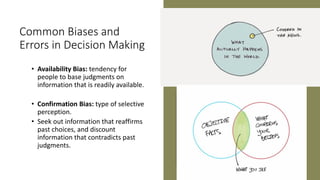
The document discusses various cognitive biases and heuristics that influence perception and decision making. It explains attribution theory, which suggests that people attempt to determine whether behaviors are internally or externally caused. Some common biases discussed are the fundamental attribution error, self-serving bias, selective perception, halo effect, and stereotyping. The rational model of decision making assumes people have complete information and choose the optimal option, but in reality people use bounded rationality and satisfice. Intuition also influences decisions. The document outlines several biases that impair decision making, like anchoring bias and availability bias, and provides some strategies for reducing biases and more ethical decision making.