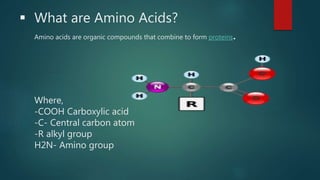
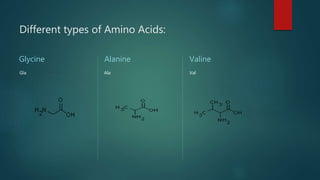
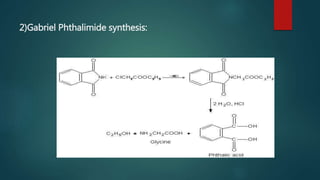
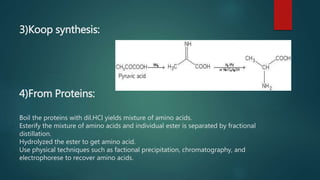
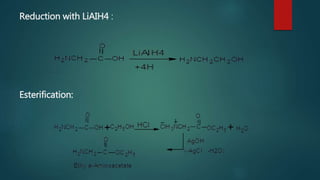
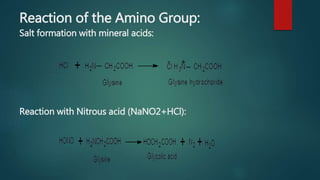
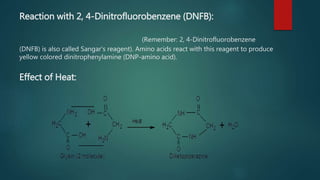
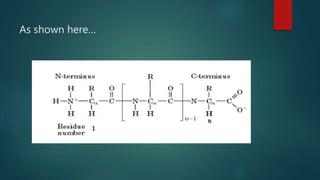
This document summarizes key information about amino acids and peptide bonds. It defines amino acids as organic compounds that combine to form proteins. Amino acids contain carboxyl, central carbon, alkyl, and amino groups. There are 20 different amino acids found in the human body, which are important for storing nutrients, influencing organ function, and healing wounds. Peptide bonds form when amino acids combine, eliminating a water molecule. Polypeptides and proteins are chains of amino acids connected by peptide bonds.