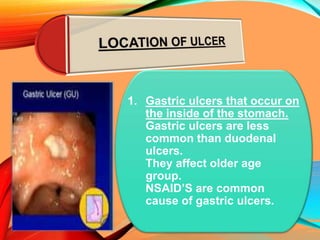
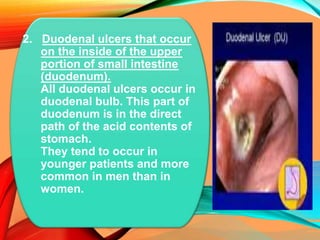
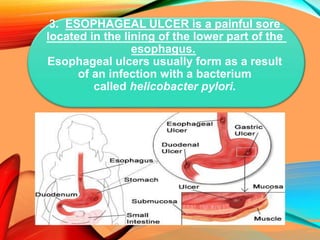
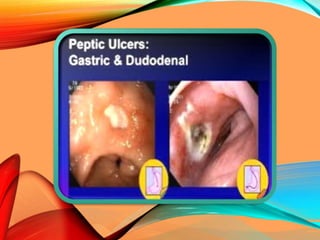
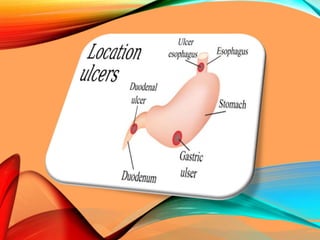
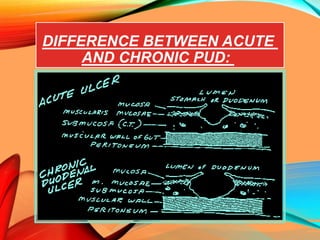
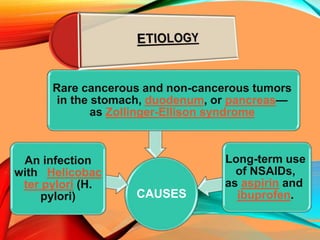
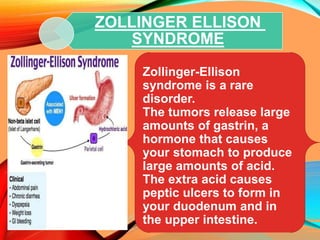
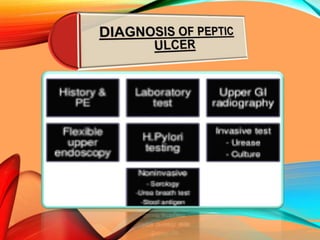
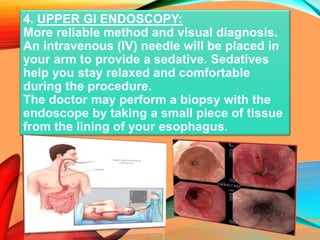
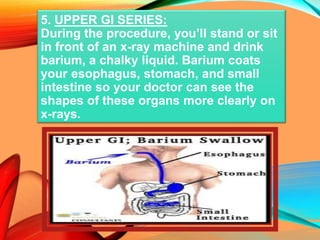
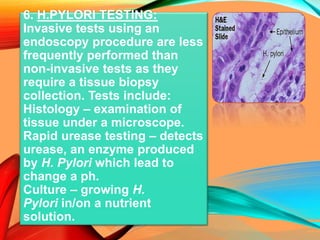
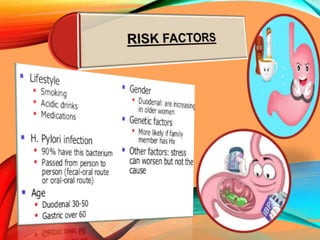
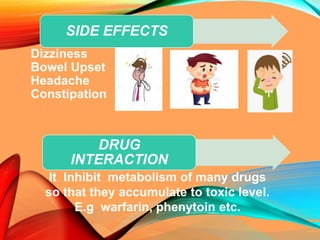
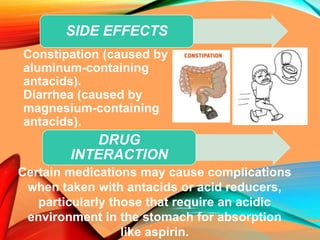
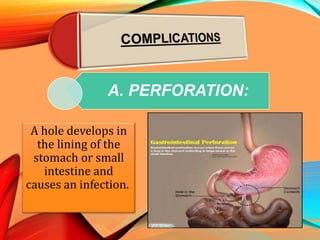
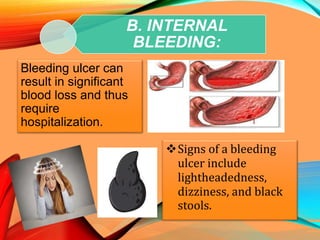
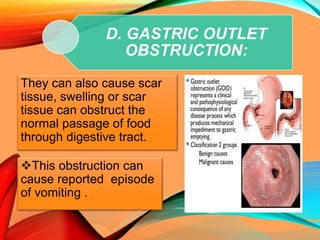
Peptic ulcers develop in the stomach, esophagus, or duodenum (upper small intestine) and are usually caused by H. pylori bacteria or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like aspirin. Symptoms include abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, weight loss, and bloody stools. Diagnosis involves blood tests, breath tests, stool tests, endoscopy, or imaging. Treatment involves antibiotics to kill H. pylori, proton pump inhibitors to reduce acid, and medications to protect the stomach lining. Complications can include bleeding, perforation, and scarring.