Embed presentation
Downloaded 27 times

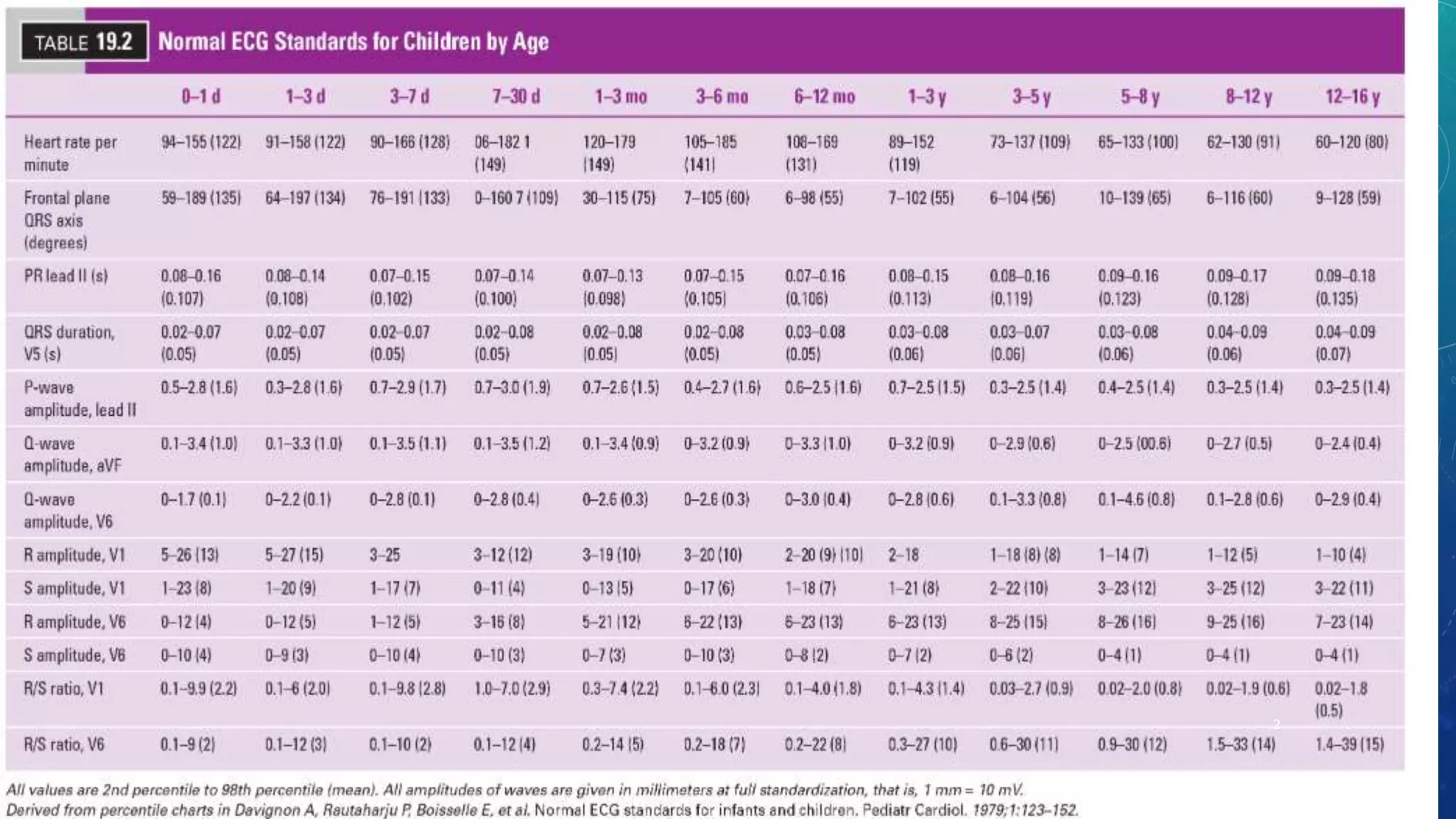







The ECG of children is different from adults due to developmental changes. As children age, their heart rate decreases while measurements like P-wave duration and QRS duration increase. In newborns, the right ventricle dominates but over the first year the left ventricle becomes the dominant chamber. The T-wave also changes significantly in infants in the first week of life as right ventricular pressure changes. Premature infants have shorter ECG intervals and less right ventricular dominance compared to full-term infants.








