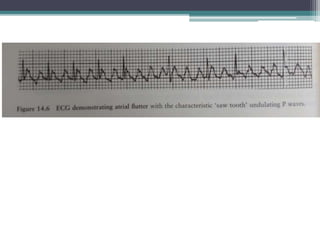
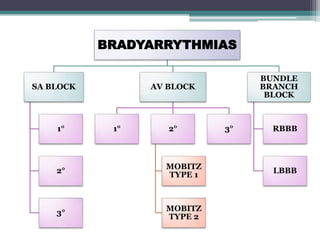
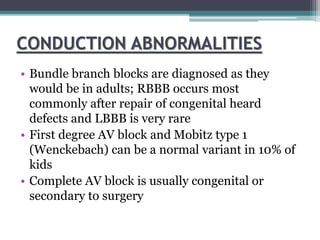
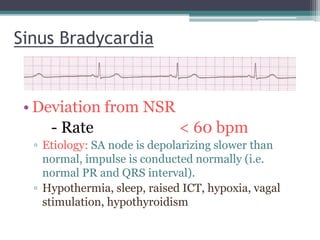
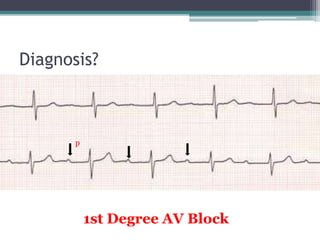
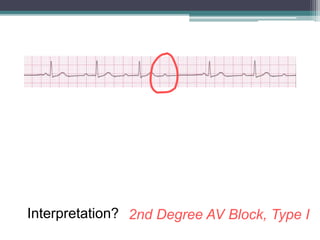
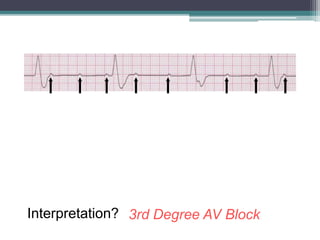
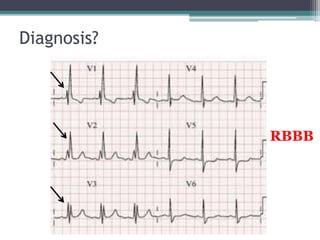
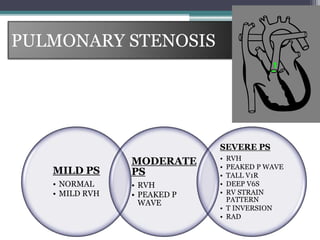
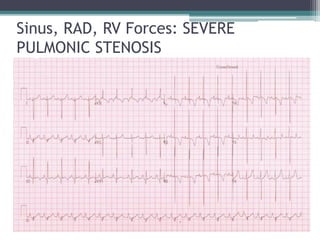
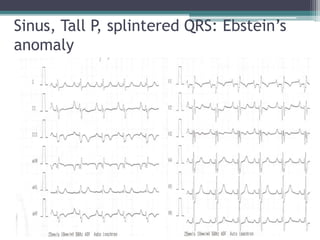
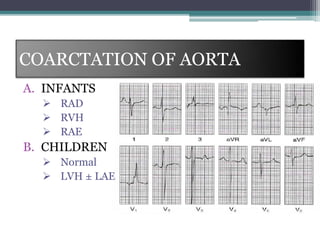
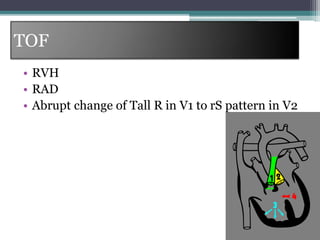
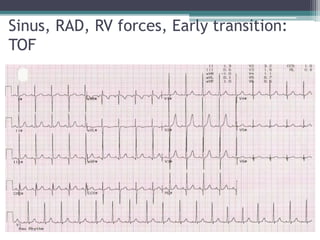
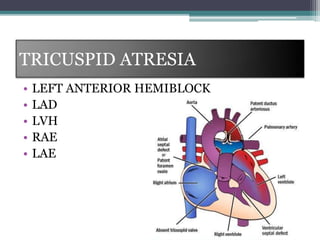
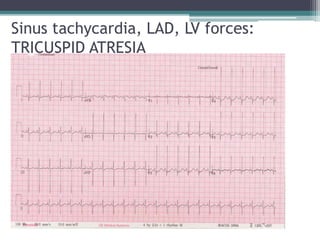
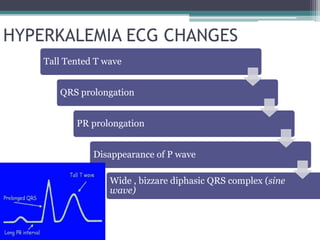
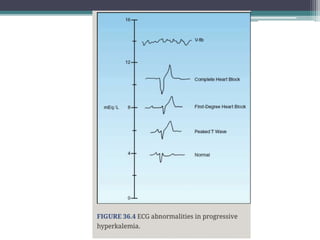
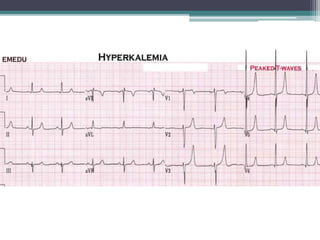
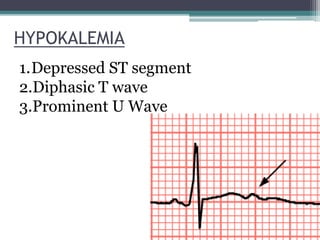
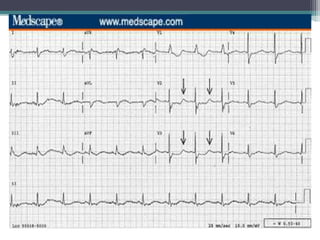
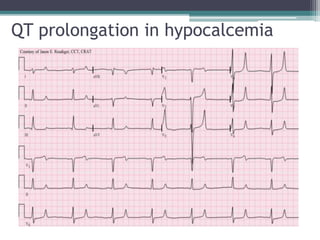
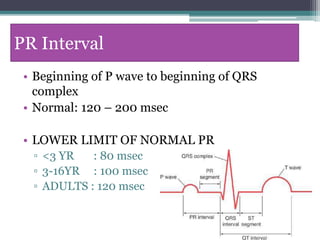
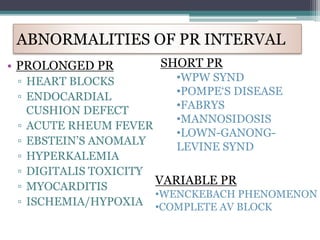
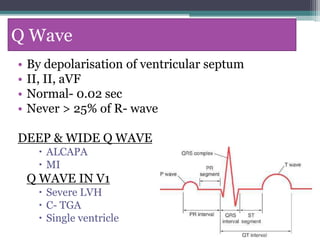
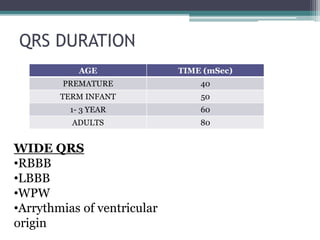
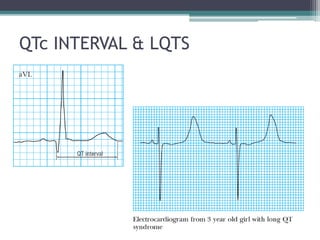
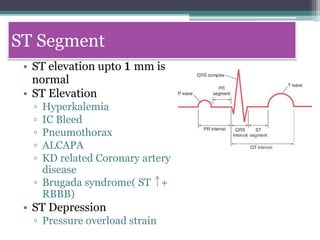
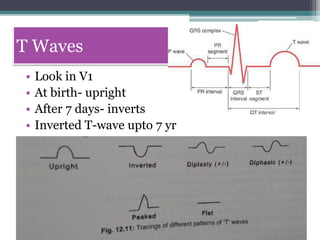
This document provides an overview of pediatric ECG abnormalities and interpretations. It discusses normal variations in pediatric ECGs as well as abnormalities related to conditions like heart blocks, chamber enlargements, congenital heart disease, arrhythmias, and electrolyte imbalances. Examples of ECG readings are provided for abnormalities in P waves, PR interval, QRS complex, QT interval, ST segment, T waves, and U waves. Interpretations of ECG findings related to conditions like chamber hypertrophy, conduction abnormalities, tachyarrhythmias, bradyarrhythmias, bundle branch blocks, WPW syndrome, and various congenital heart defects are also summarized.





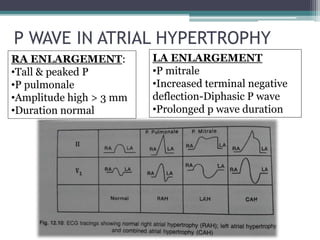
![P waves
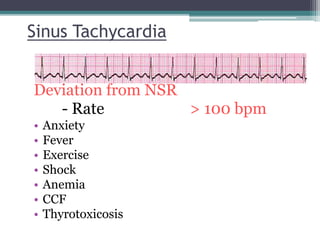
• Normal findings
• Upright in I, II, aVL
• Inverted in aVR
• amplitude < 2.5 mm [> 3mm abnormal]
• Duration < 9o msec [ > 120 msec abnormal]
• 1st half by RA Depolarisation & 2nd half by LA](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/habeebecgfinal-230302145729-6c5c85f1/85/Pediatric-ECG-final-pptx-8-320.jpg)










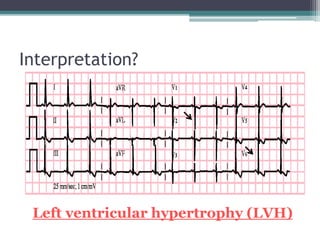
![• LAD
• Tall R in I, II, II, aVL,aVF, V5,
V6
• Deep S in V1/ V2
• R/S ratio in V1 < 1
• Deep Q wave [Q > 5 mm] +
tall symmetrical T wave in V5
& V6 (“LV diastolic load”)
• Strain pattern
• Inverted T wave in I, aVF
Criteria FOR LVH](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/habeebecgfinal-230302145729-6c5c85f1/85/Pediatric-ECG-final-pptx-31-320.jpg)
![• RVH + LVH in the absence of BBB /
preexcitation
• Large equiphasic QRS complexes in two or more
of the limb leads and in the mid- precordial
leads[V2-V5] KATZ-WACHTEL
PHENOMENON
Criteria FOR BVH](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/habeebecgfinal-230302145729-6c5c85f1/85/Pediatric-ECG-final-pptx-32-320.jpg)