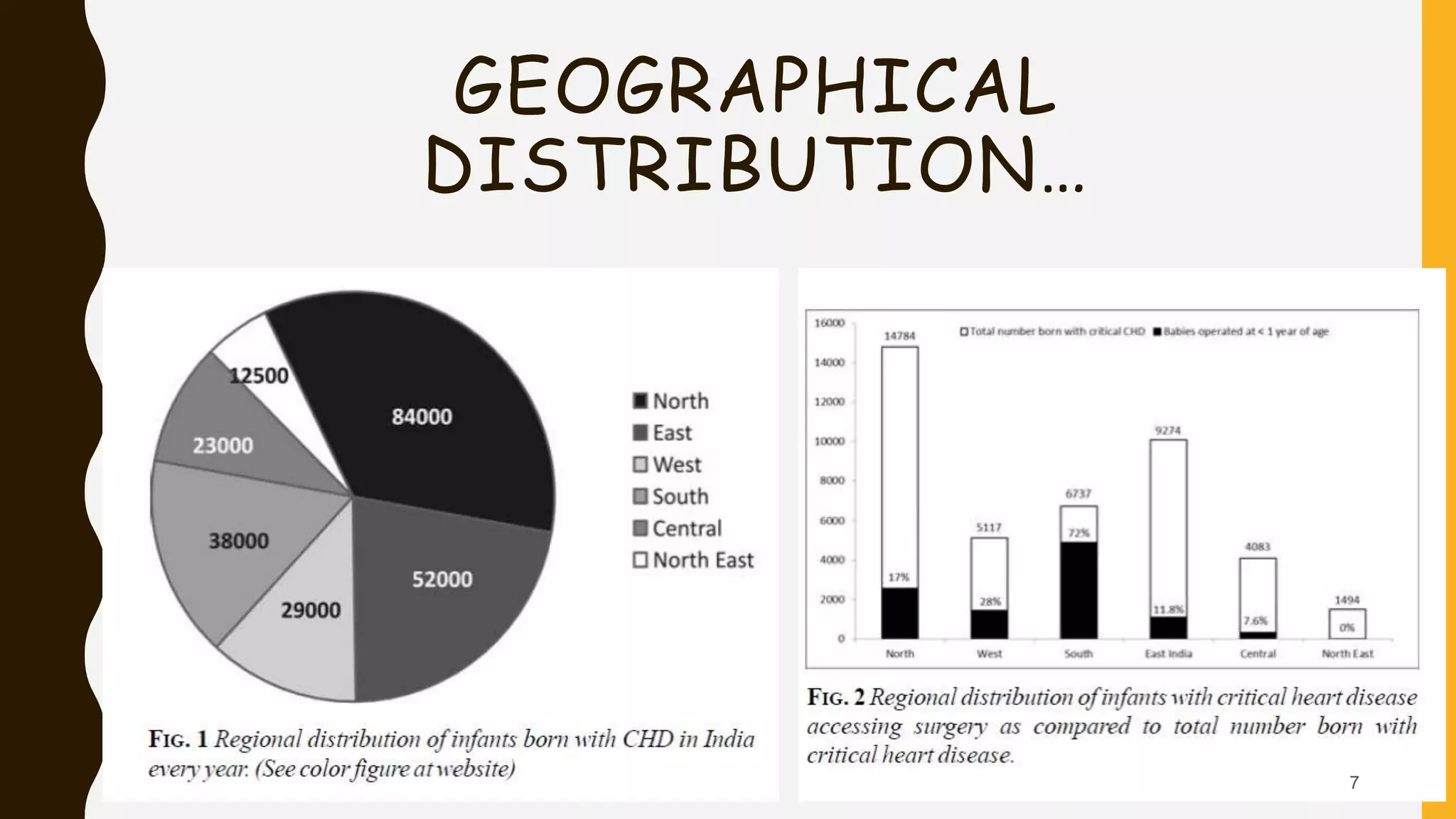
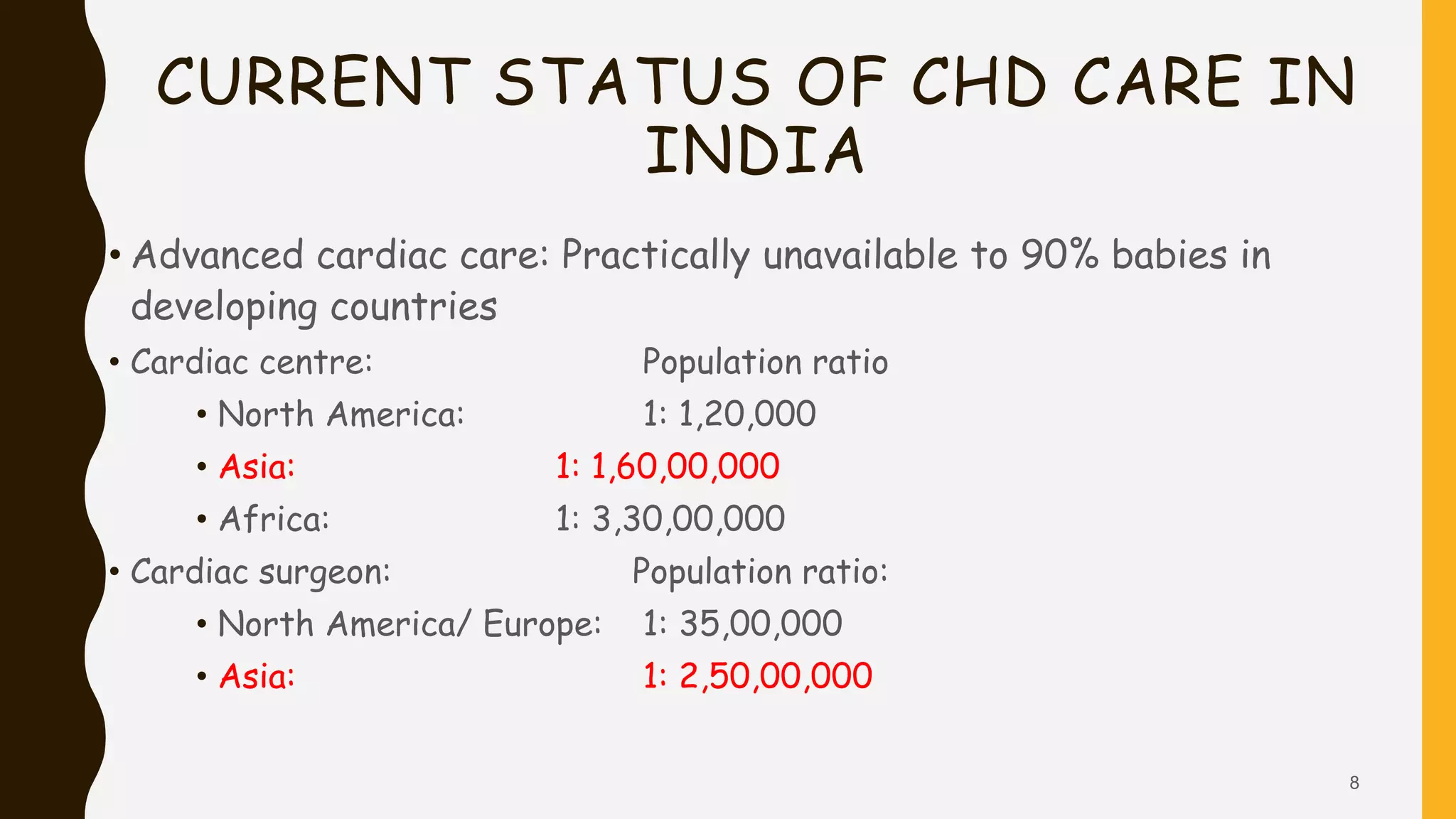
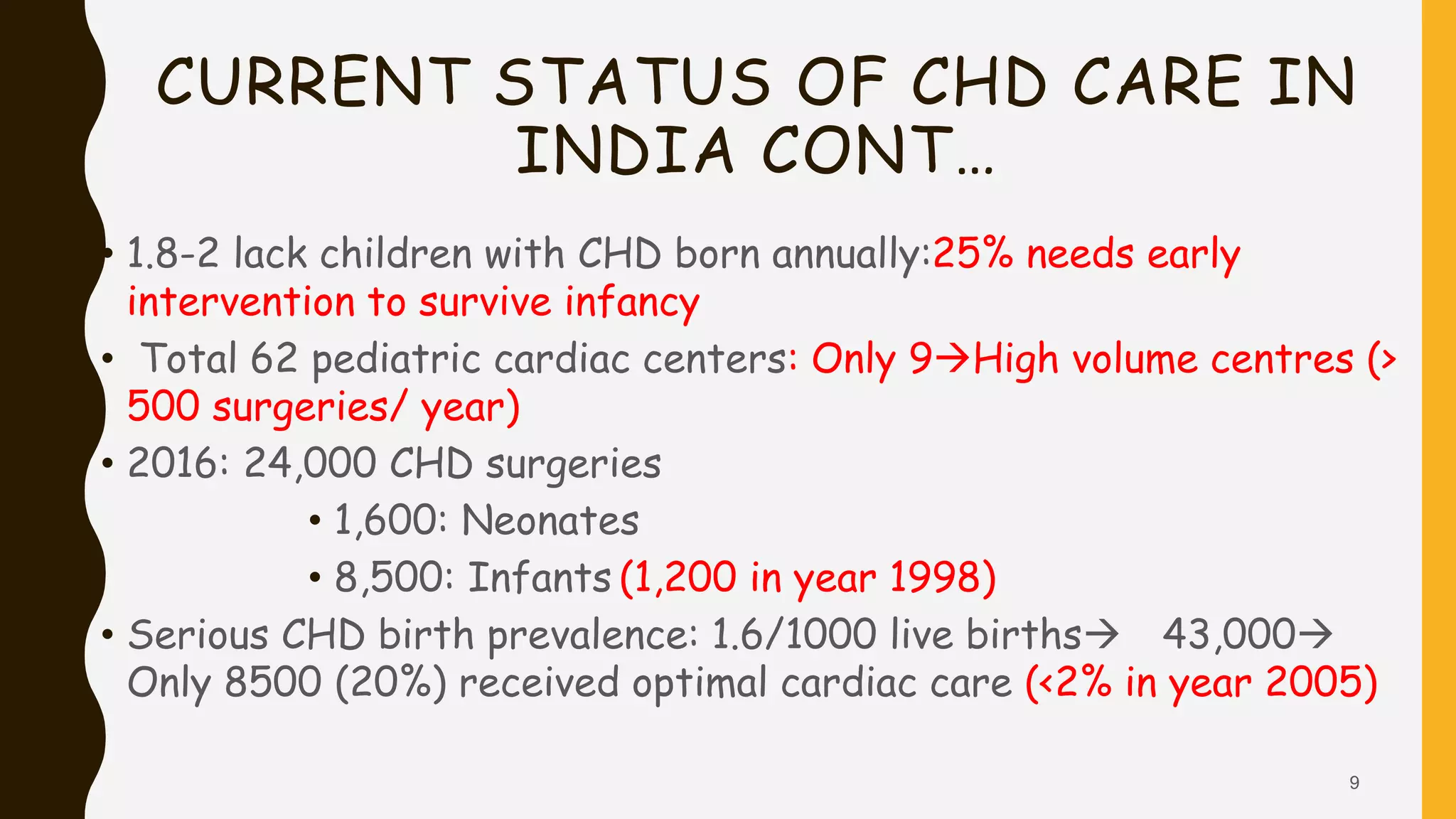
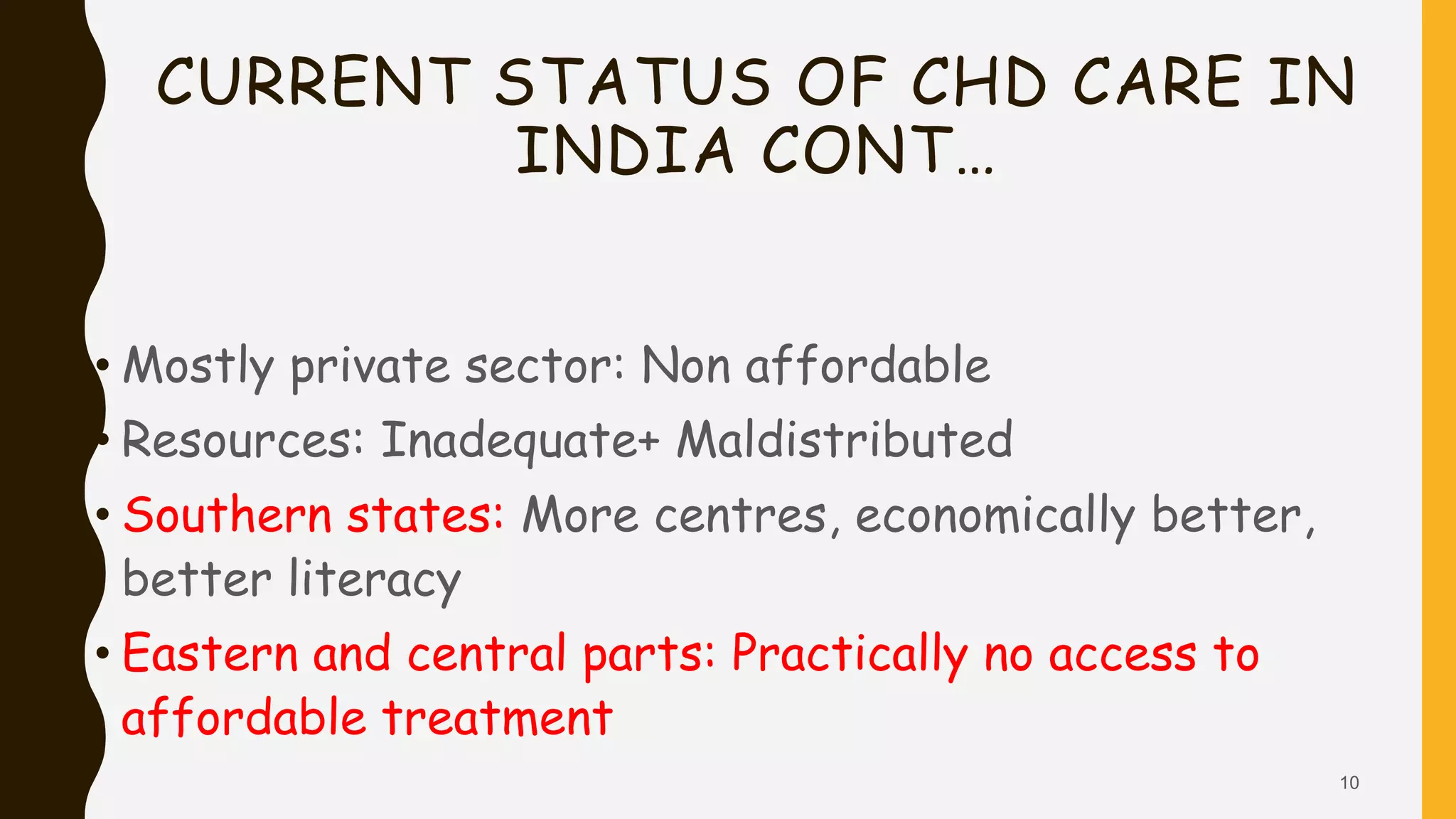
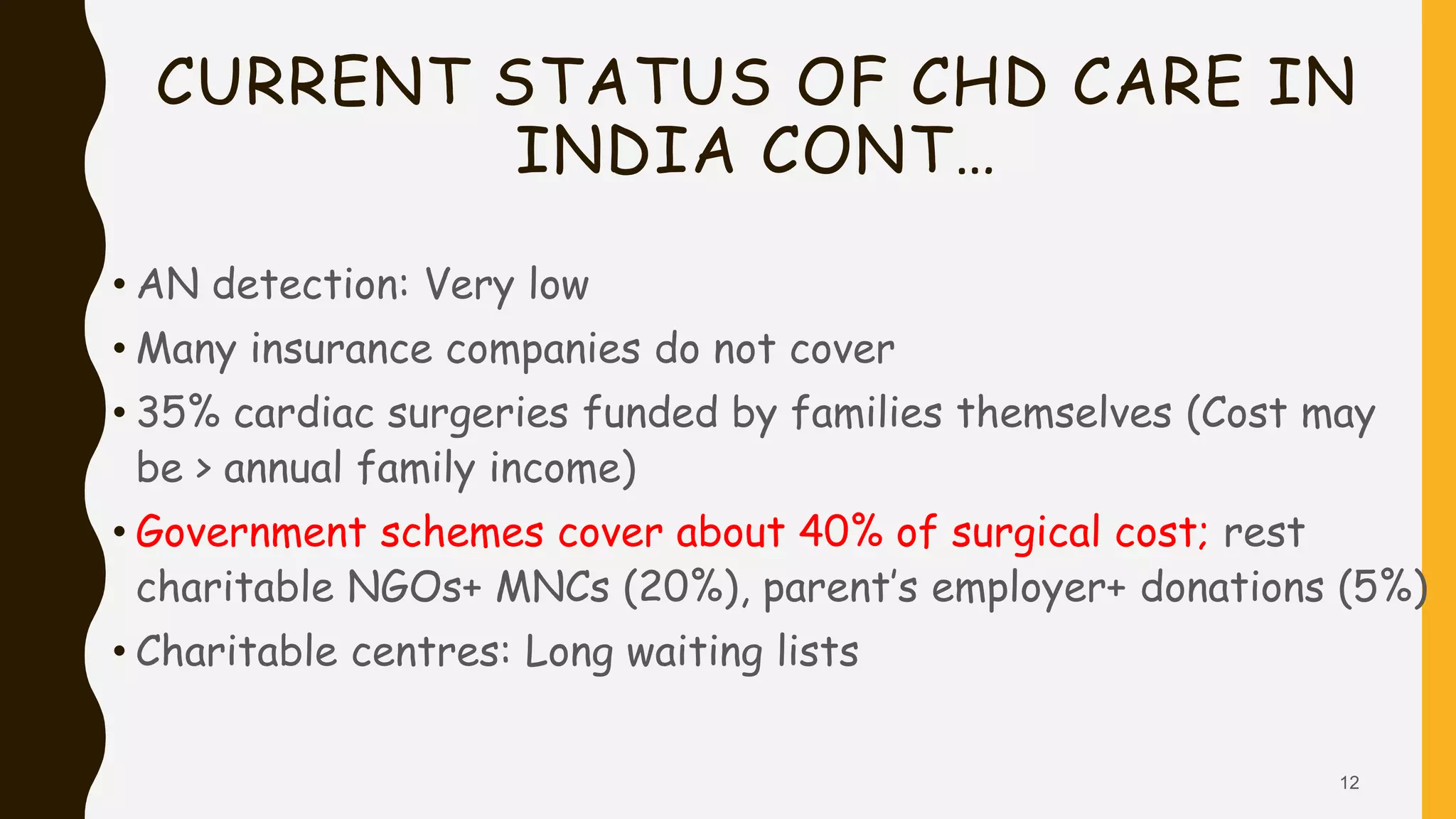
This document discusses the current state of pediatric cardiac services in India. It notes that India has a high birth prevalence of congenital heart disease (CHD), with approximately 242,390 children born with CHD each year. However, the availability of advanced cardiac care is very limited, with only 9 high-volume centers performing over 500 surgeries per year. While an estimated 43,000 children are born annually with serious forms of CHD requiring treatment, only around 8,500 (20%) currently receive optimal cardiac care. The document outlines several challenges facing the improvement and expansion of pediatric cardiac services in India, including limited resources, infrastructure, and trained staff. It proposes various strategies to address these issues, such as establishing more specialized