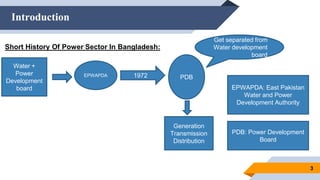
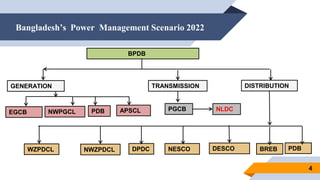
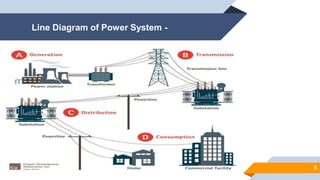
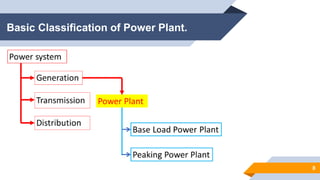
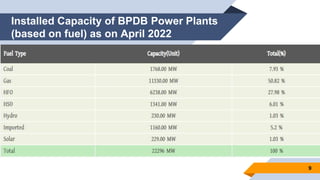
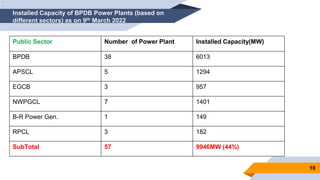
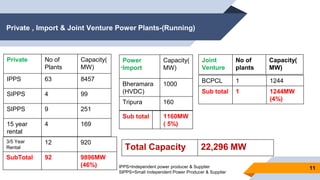
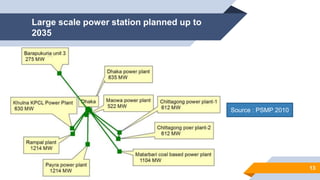
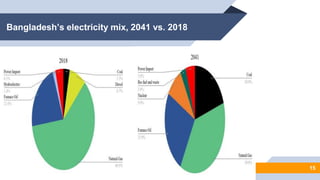
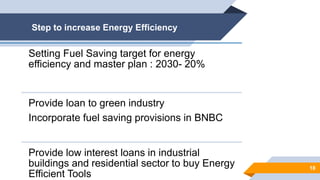
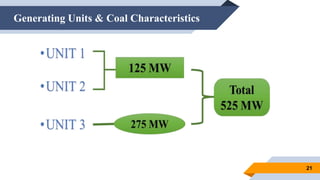
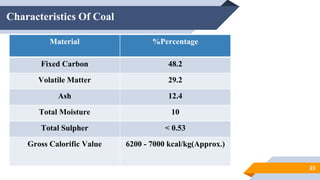
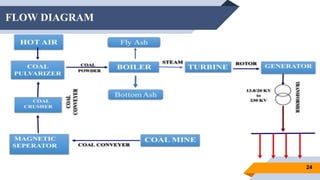
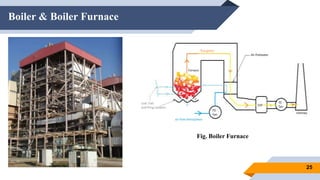
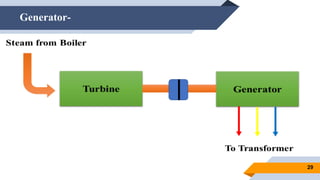
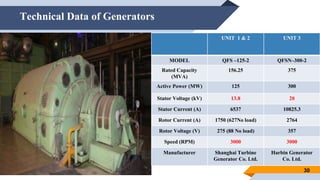
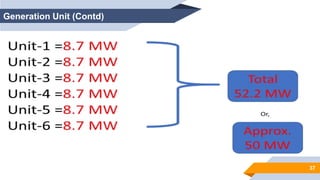
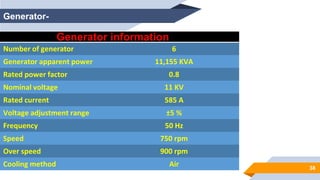
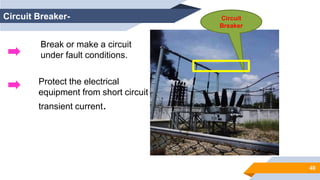
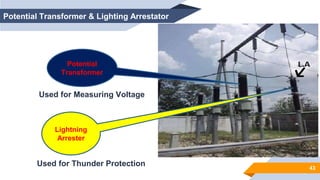
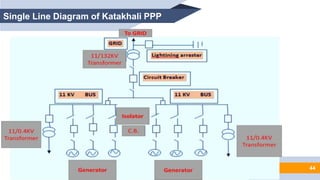
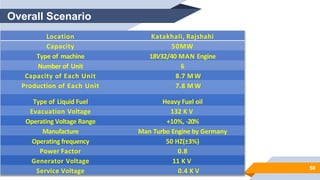
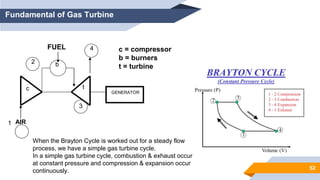
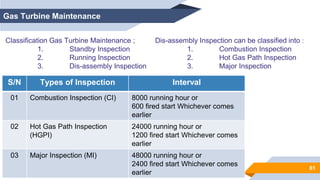
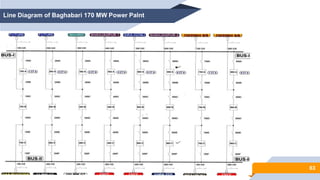
The document provides an overview of power generation in Bangladesh, including different types of power plants. It discusses the Barapukuria coal power plant, including its key components like the boiler, turbine, and generator. It also describes the Katakhali oil power plant and its diesel engines and generators. Finally, it outlines the Baghabari gas power plant and components of the gas turbine system like the compressor and turbine. The document thus summarizes different fossil fuel power generation technologies used in Bangladesh.