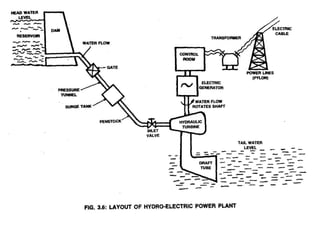
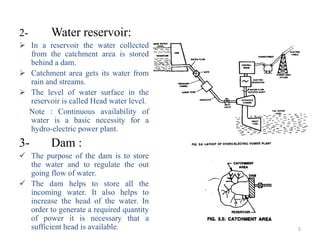
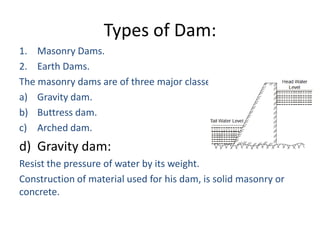
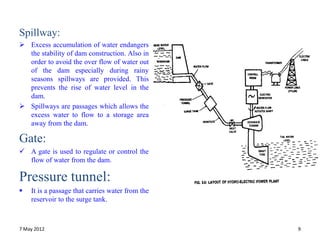
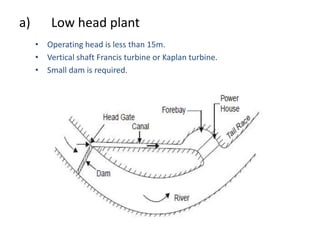
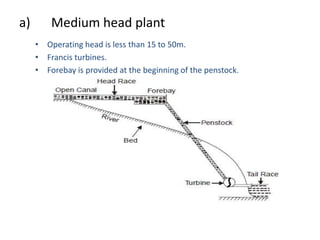
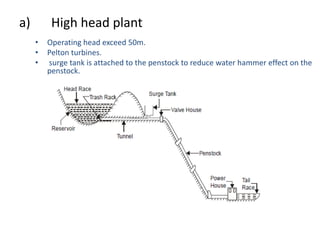
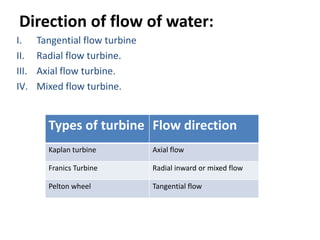
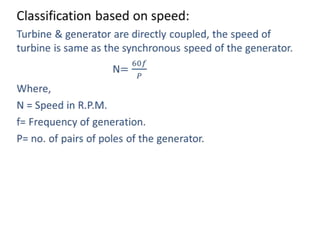
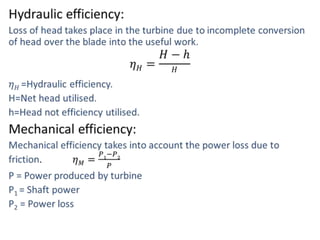
This document provides information on hydroelectric power plants. It discusses the essential components which include a catchment area, reservoir, dam, intake house, waterways, power house, and tailrace. It describes the different types of dams and turbines used. Hydroelectric power is a renewable source of energy since water is continuously available from rainfall and rivers. While hydroelectric power plants have many advantages like low operating costs, they also have disadvantages such as high initial costs and reduced power production during drought seasons.