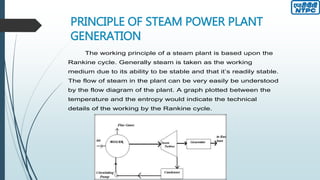
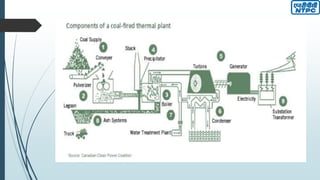
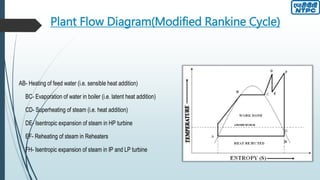
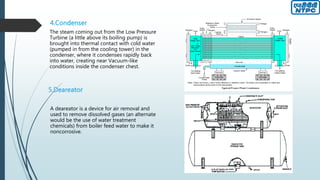
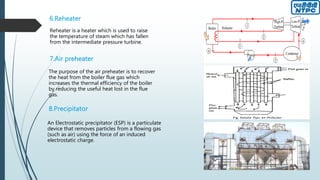
This document provides an overview of the Badarpur Thermal Power Station (BTPS) owned and operated by NTPC Limited, the largest power generation company in India. It summarizes that BTPS was established in 1973 and transferred to NTPC in 1978. It now has a total installed capacity of 720 MW from 5 units. The document then describes the basic working principles of a steam power plant using the Rankine cycle. It provides diagrams of the typical processes and components involved, including the boiler, turbines, condenser, reheater, and others. Finally, it gives more details on some of the key components and maintenance departments at BTPS.