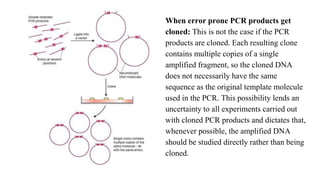
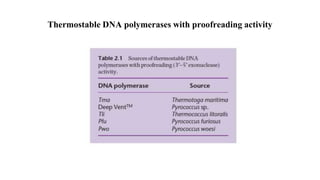
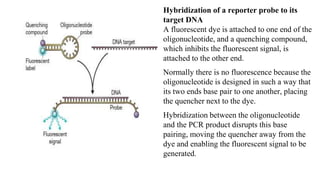
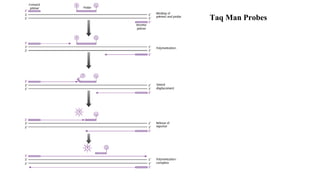
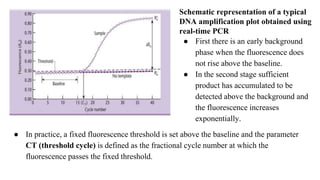
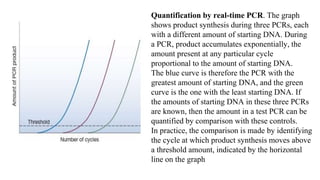
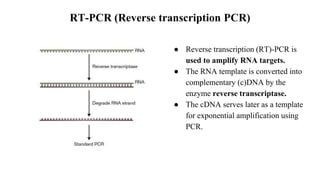
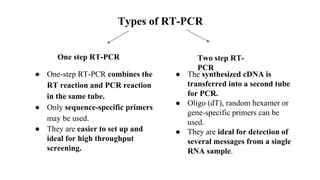
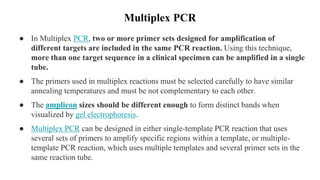
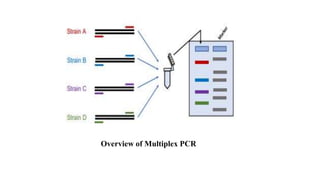
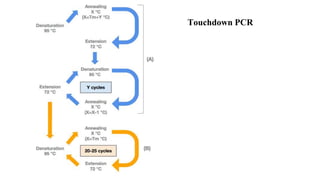
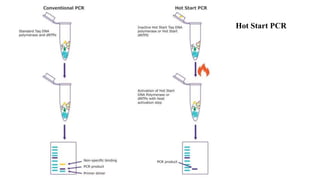
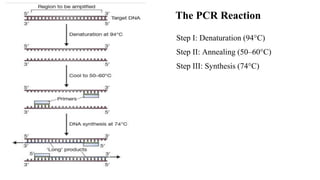
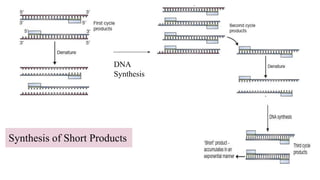
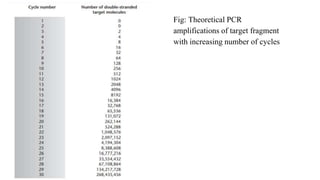
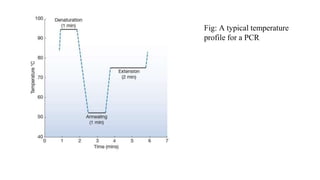
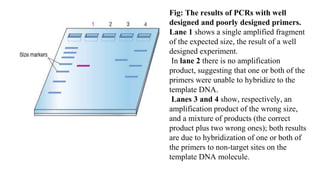
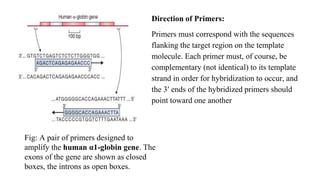
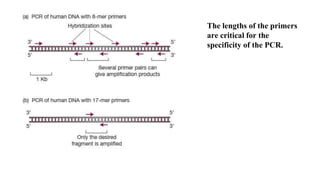
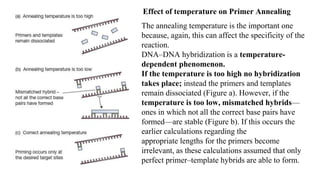
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) is a DNA amplification technique that utilizes specific primers and Taq polymerase to repeatedly denature, anneal, and synthesize target DNA regions. The process is sensitive enough to work with very small quantities of DNA and is affected by primer design and temperature, impacting the specificity and accuracy of the outcome. Various PCR types, such as real-time and multiplex PCR, are utilized for different purposes, including quantitative analysis and amplification of multiple targets from a single sample.










![Calculating Tm
Calculate Tm of following primer
sequences:
1. 5’GAATTAACACCGTT3’
2. 5’TATACCGGTCGAATT3
’
The Tm can be determined experimentally but is more usually calculated from the
simple formula:
Tm = (4 × [G + C]) + (2 × [A + T])°C
in which [G + C] is the number of G and C nucleotides in the primer sequence, and
[A + T] is the number of A and T nucleotides.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pcranditsdifferenttypes-230227135147-e29a9da2/85/_PCR-and-its-different-types-pptx-20-320.jpg)