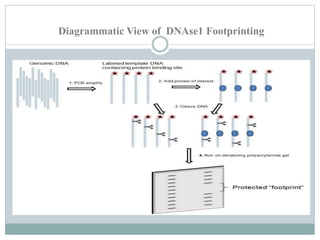
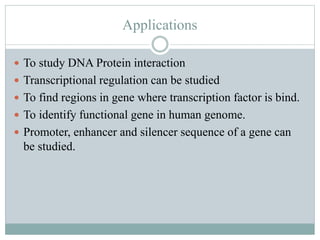
The document provides an overview of DNase I footprinting, a technique used to identify DNA binding sites for proteins. It details the principles, methodology, and various applications of the technique in studying DNA-protein interactions and transcriptional regulation. Key points include the historical background, comparison with similar techniques, and procedural steps for conducting the DNase I footprinting assay.