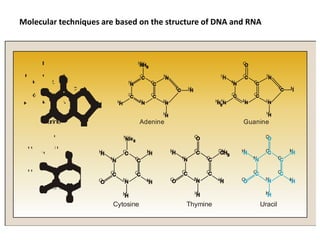
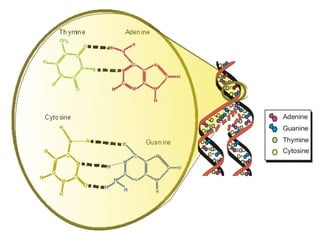
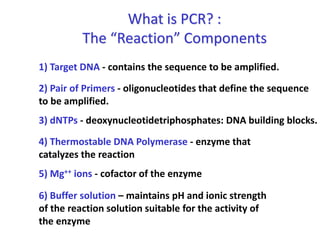
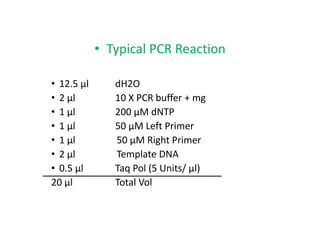
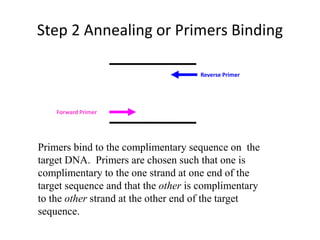
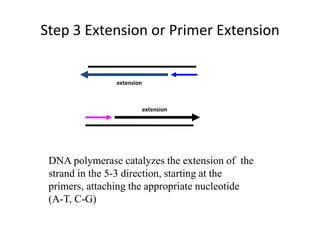
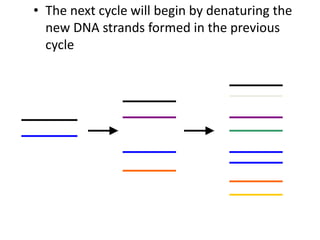
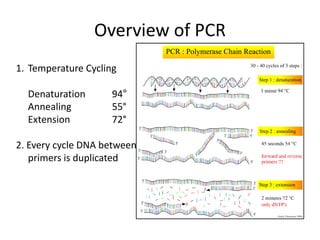
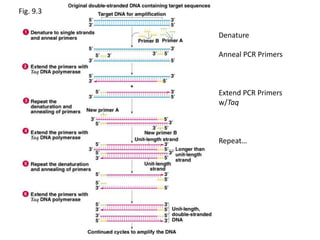
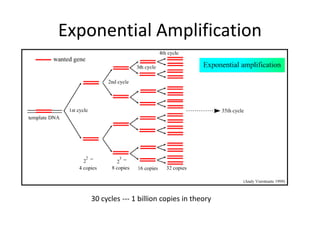
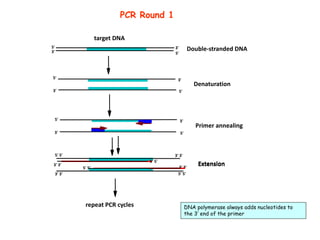
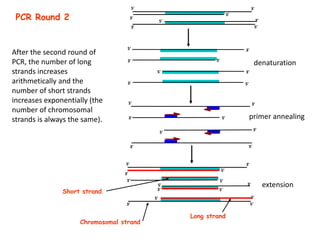
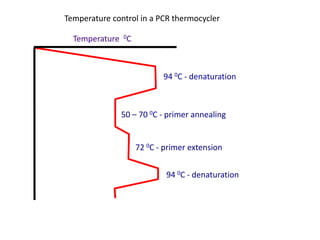
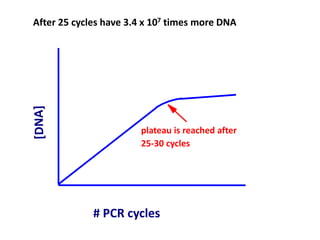
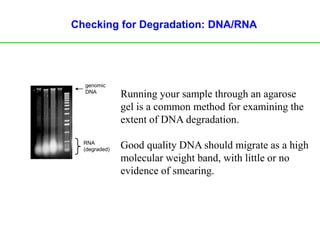
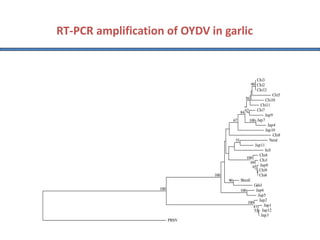
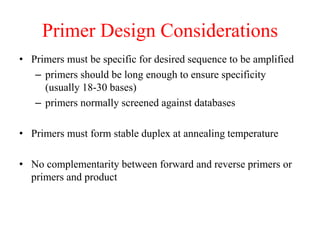
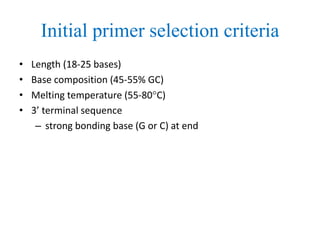
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) is a technique used to amplify a specific DNA sequence. It involves repeated cycles of heating and cooling of the DNA sample in the presence of DNA polymerase, primers, and nucleotides. Each cycle doubles the amount of target DNA. After 20-30 cycles, there can be over a billion copies of the original DNA sequence. PCR is used for a variety of applications including disease diagnosis, cloning genes, forensic analysis, and more. It is a powerful technique that has revolutionized molecular biology.