Embed presentation
Download to read offline


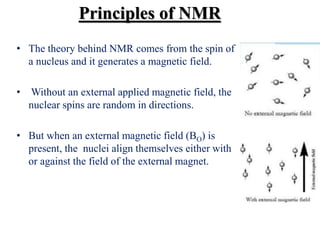



This presentation discusses nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (NMR), an analytical technique used to characterize organic molecules. It explains that NMR exploits the magnetic properties of atomic nuclei to determine physical and chemical properties of atoms and molecules. Two common types of NMR spectroscopy, 1H NMR and 13C NMR, are used to determine the types and numbers of hydrogen and carbon atoms in a molecule. The presentation also provides an overview of the principles of NMR, including how an external magnetic field causes nuclear spins to align and allows for energy transfer and emission of radiofrequency signals that produce the NMR spectrum. Finally, some applications of NMR are mentioned, such as distinguishing structural isomers and determining aromaticity or double bond character.






