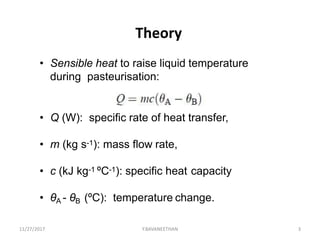
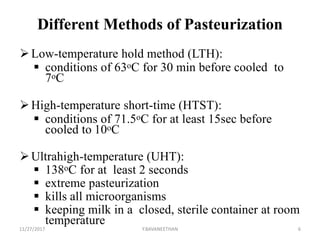
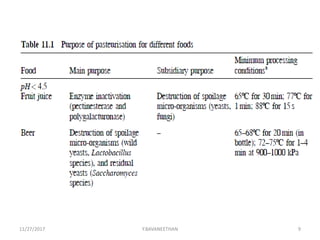
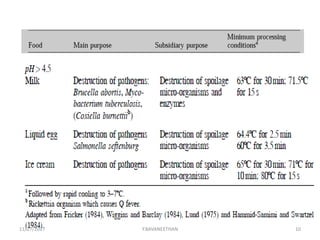
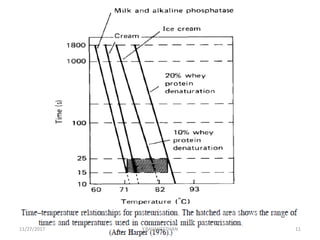
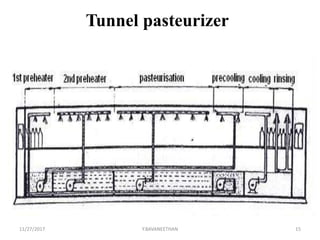
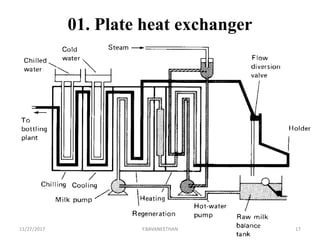
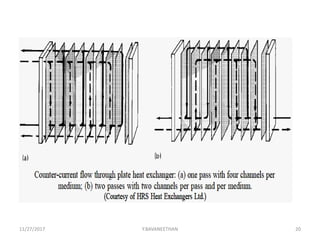
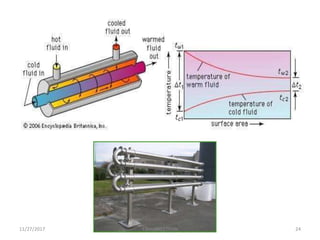
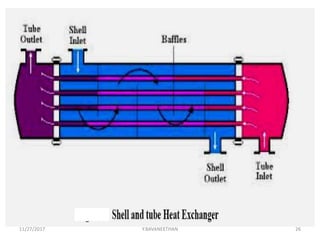
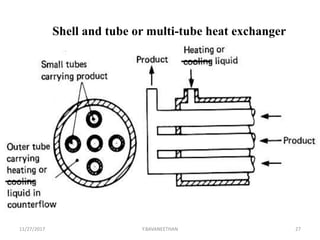
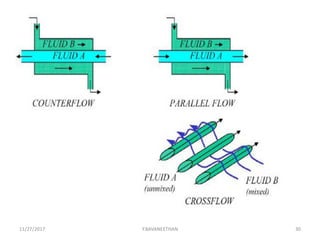
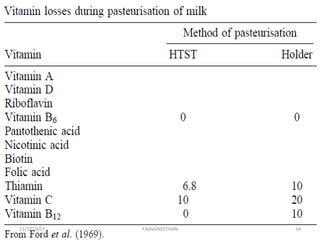
Pasteurization is a mild heat treatment used to minimize hazards from pathogenic microorganisms and extend the shelf life of foods. It involves heating foods to temperatures below 100°C. In low acid foods like milk, it is used to reduce pathogens and extend shelf life to several days. In acidic foods like bottled fruits, it extends shelf life to several months by destroying pathogens and inactivating enzymes. Common pasteurization methods include high-temperature short-time (HTST), low-temperature hold (LTH), and ultra-high temperature (UHT) processing. Pasteurization minimally impacts sensory and nutritional properties when done properly.