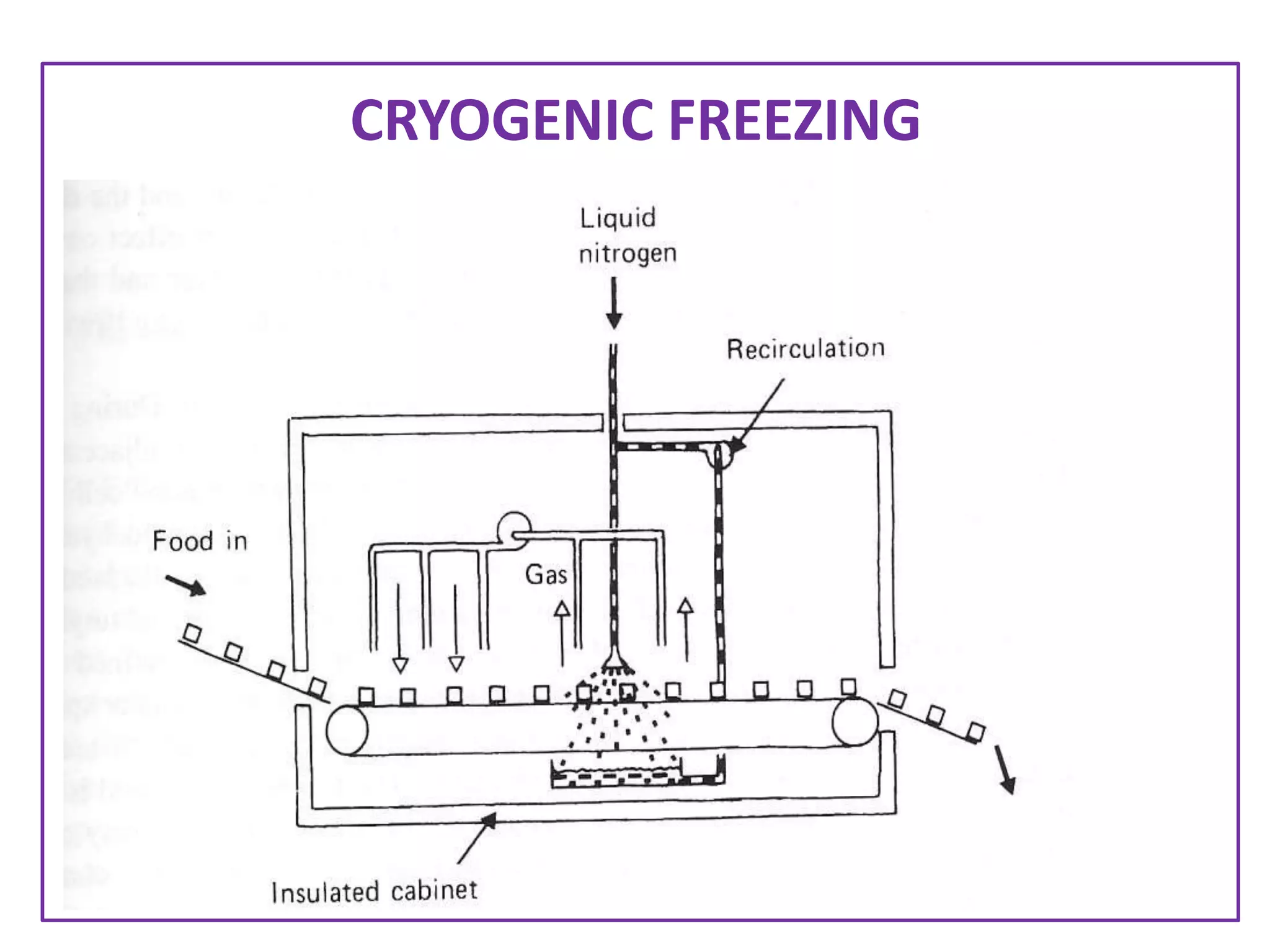
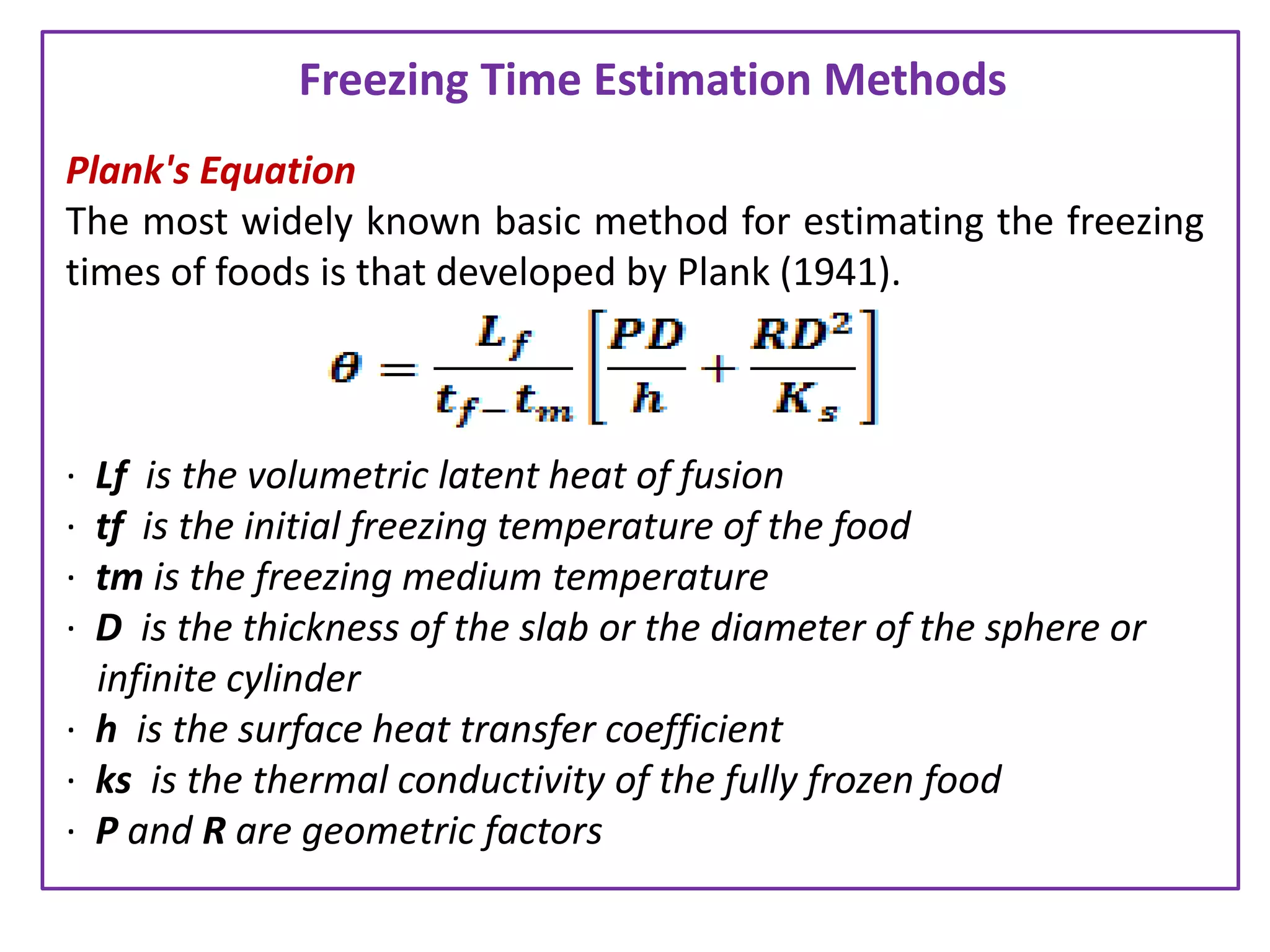
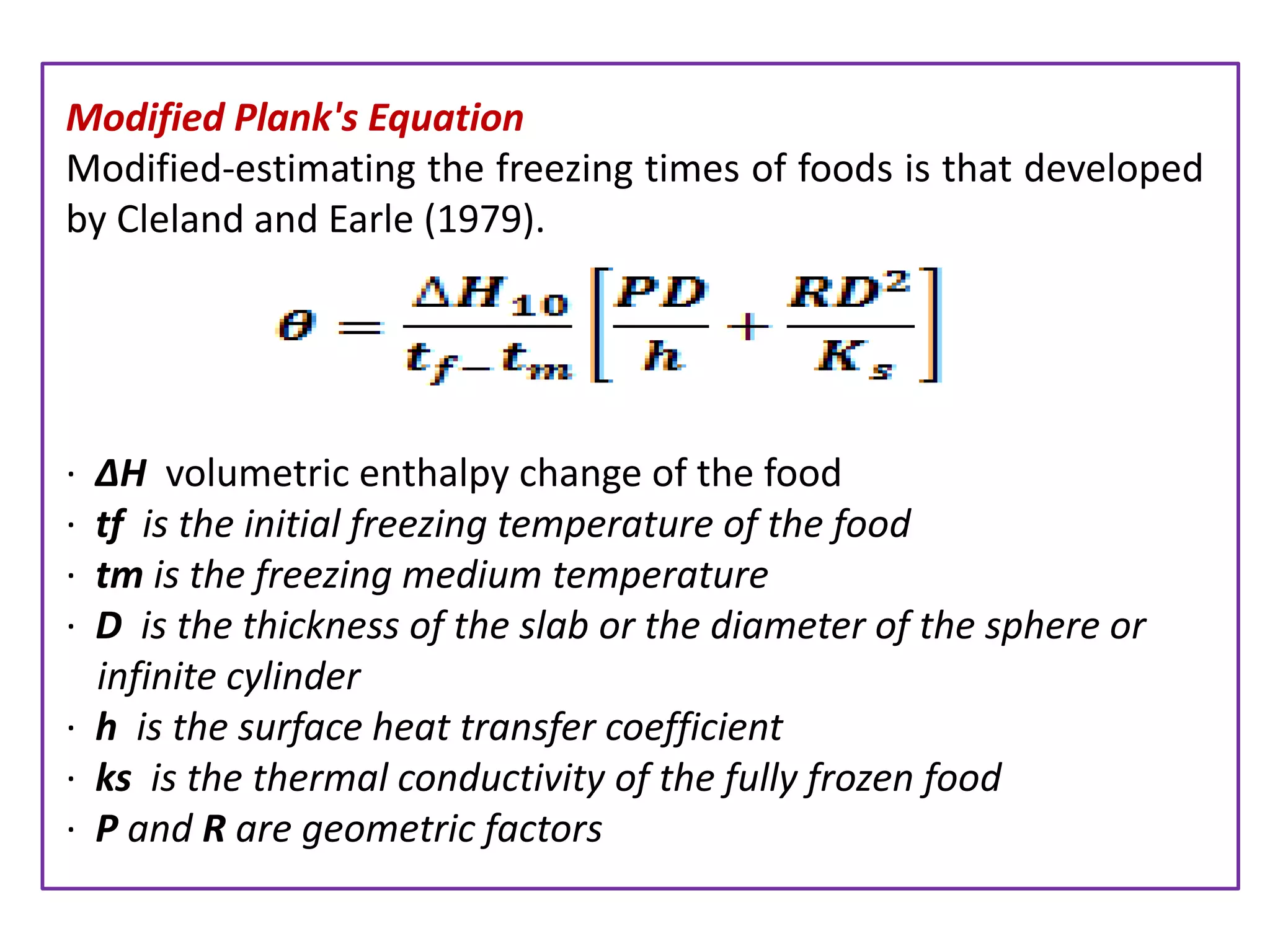
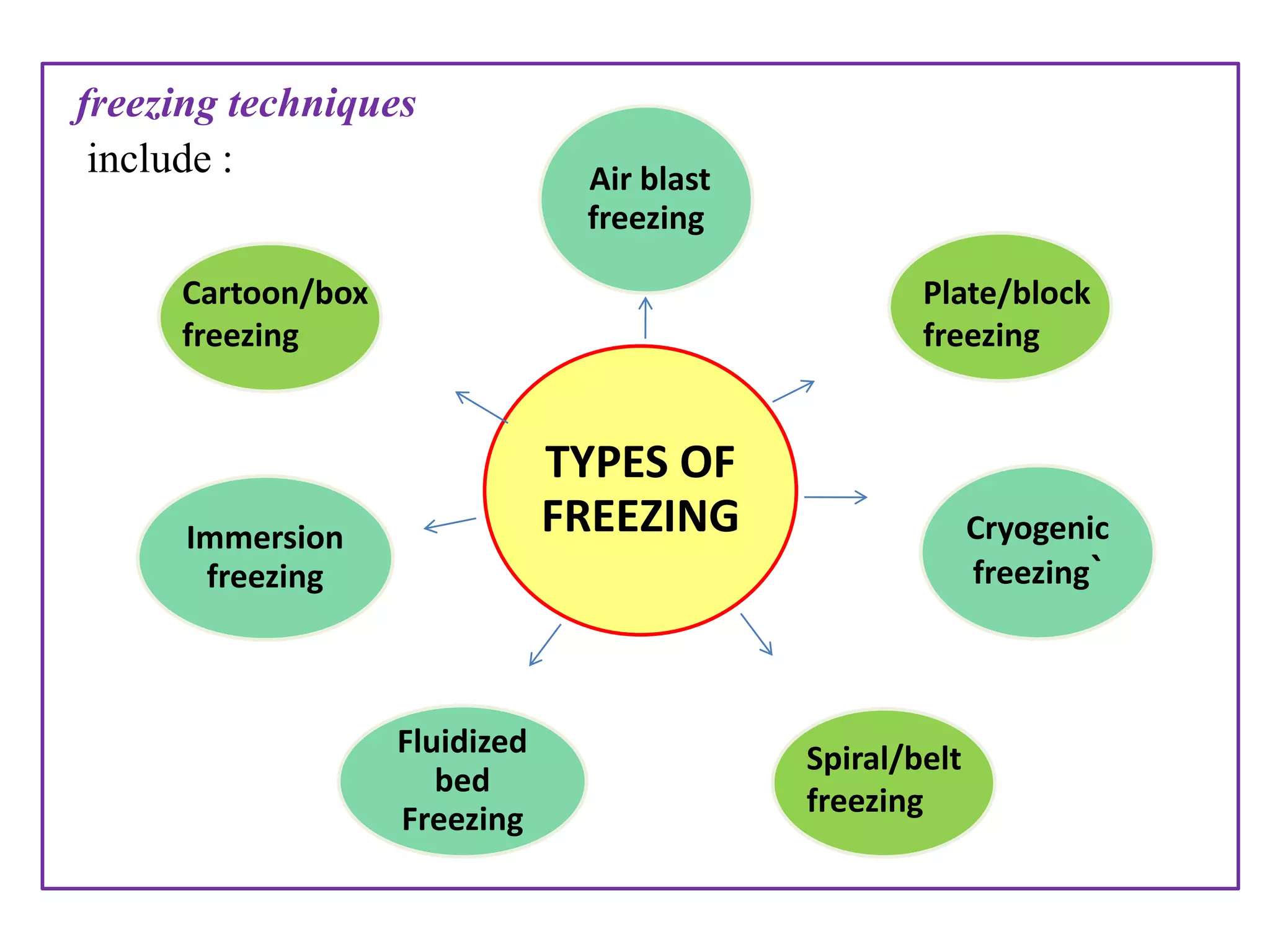
There are two main methods of freezing food commercially - fast freezing at temperatures below -25°C which forms small ice crystals, and slow freezing above -24°C which forms larger crystals that can damage the food. Common freezing techniques include air blast, fluidized bed, plate or belt, immersion, and cryogenic freezing using liquid nitrogen or carbon dioxide. The freezing method chosen depends on factors like the food quality desired, type and shape of the food, package used, required flexibility, and costs. Equations can be used to estimate freezing times based on properties of the food and freezing conditions.








![• Immersion method is the fastest freezing method
• It is commonly used as a pre-treatment of large products in order to
create a frozen layer before the product is exposed to longer freezing
time, in order to avoid dehydration.
• Traditionally foods were immersed in solutions of salt and ice for
several hours, e.g. brine, freezing of fish at sea. However, modern
methods of freezing have meant that this process is rarely used.
Refrigerants are now sprayed directly onto the food.
• Direct immersion in refrigerants [(glycols, glycerol, sodium chloride,
calcium chloride, and mixtures of salt and sugars)].
• The challenge with this method is that the solution becomes quickly
diluted with the product which can change the process speed and
efficiency.
IMMERSION FREEZING](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/freezingppt-p-190805045952/75/Freezing-ppt-p-divya-11-2048.jpg)