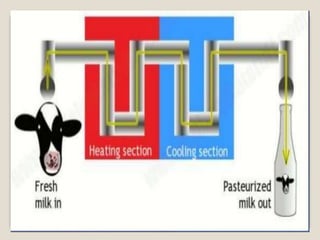
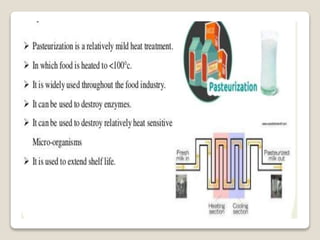
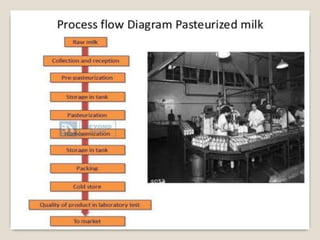
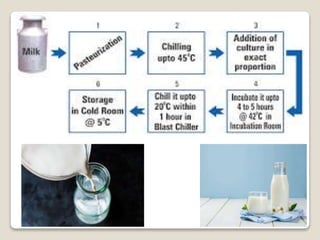
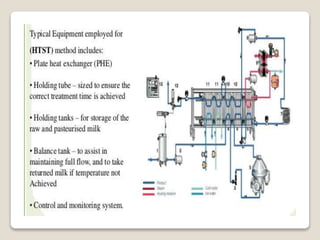
This document provides a comprehensive overview of food preservation through pasteurization, particularly focusing on milk. It details the steps involved in pasteurization, different methods (including vat, HTST, and UHT), advantages and disadvantages, and the importance of maintaining temperature control throughout the process. The document emphasizes the need for proper agitation and heating balance to ensure effective pasteurization and safety in milk production.