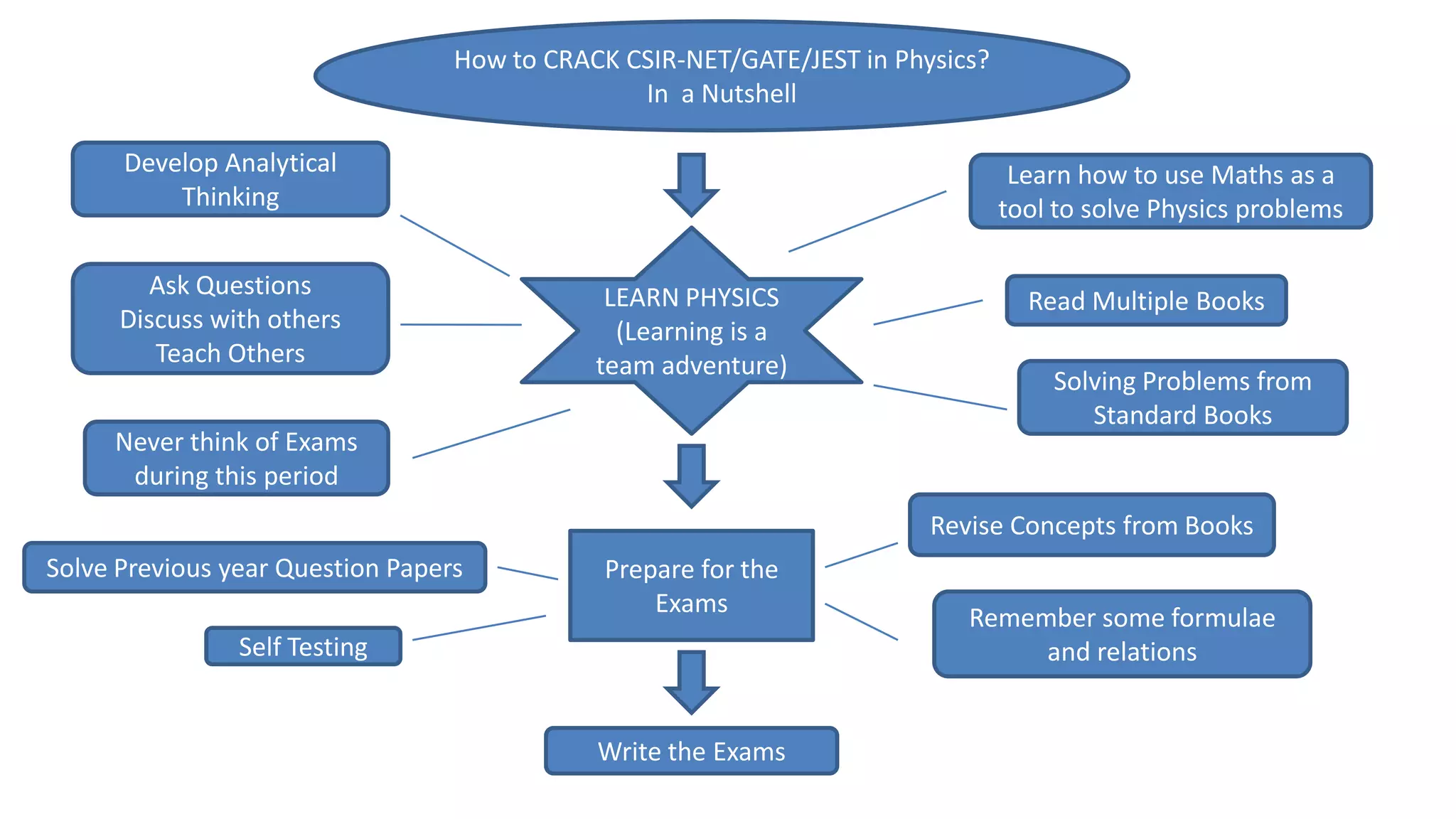
This document provides tips and strategies for preparing for the CSIR-UGC NET exam. It discusses the exam pattern, important topics to focus on, and general preparation steps. The key points are:
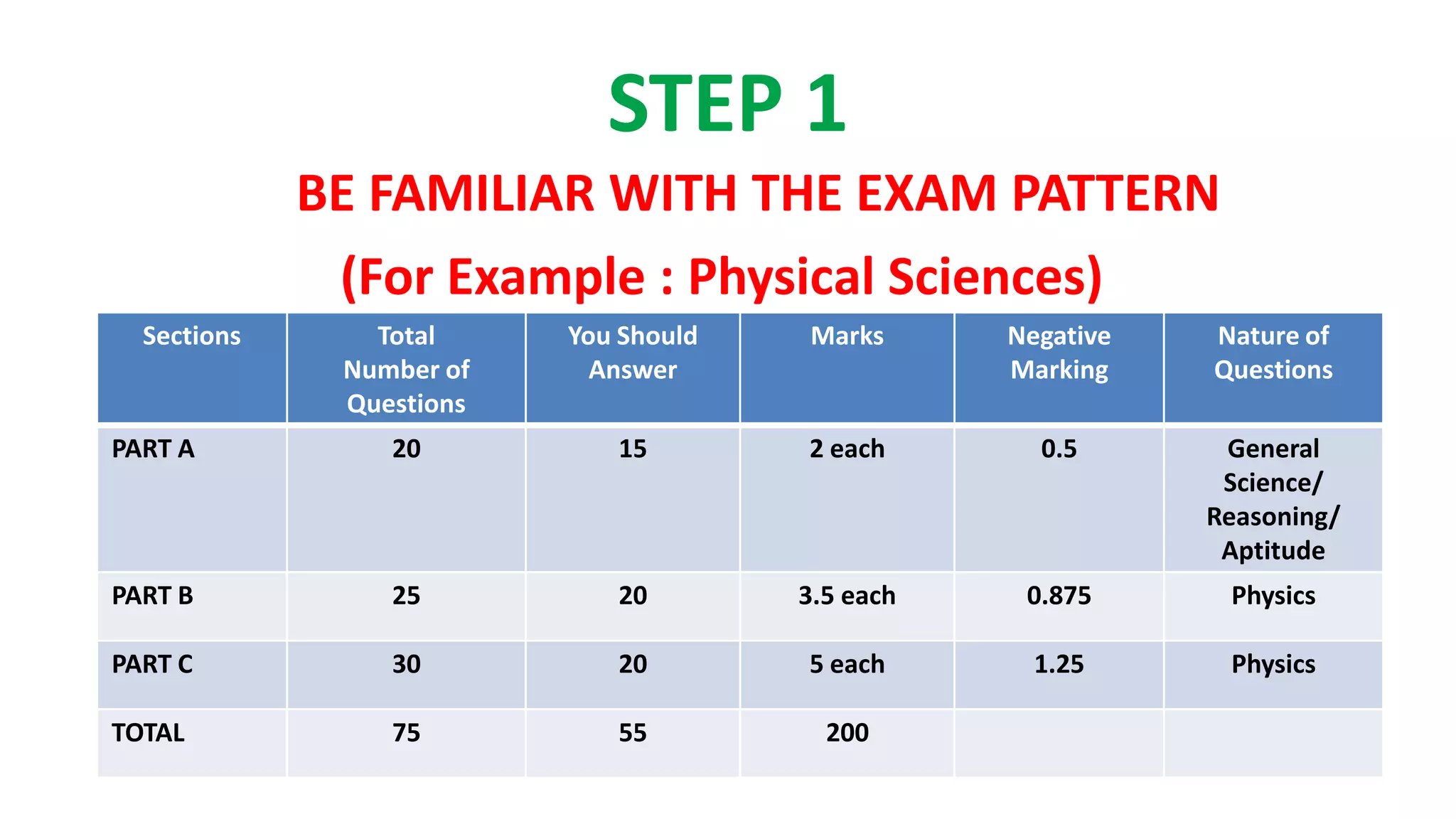
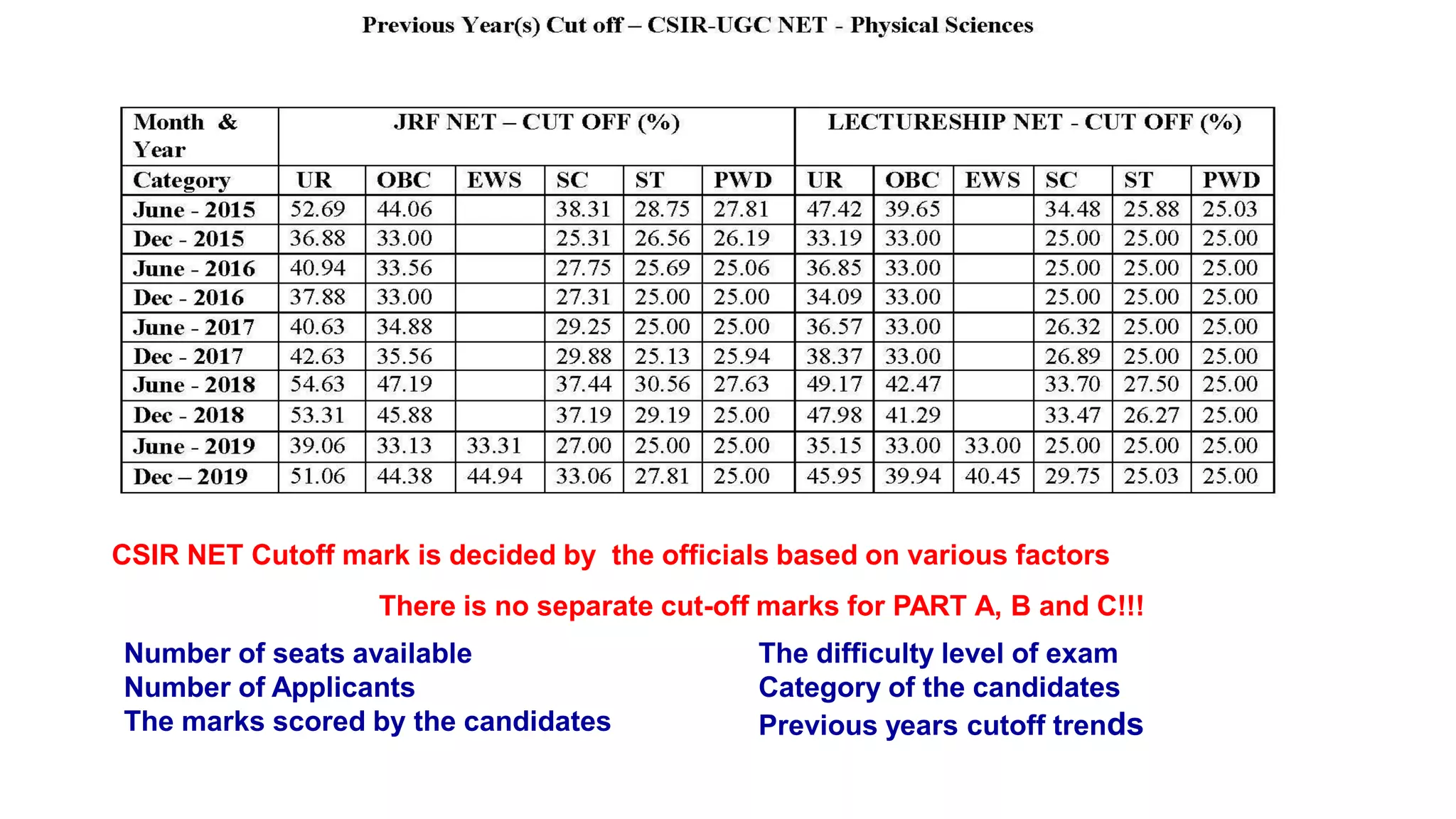
1. Familiarize yourself with the exam pattern, prioritize important topics from previous papers, and set a target score.
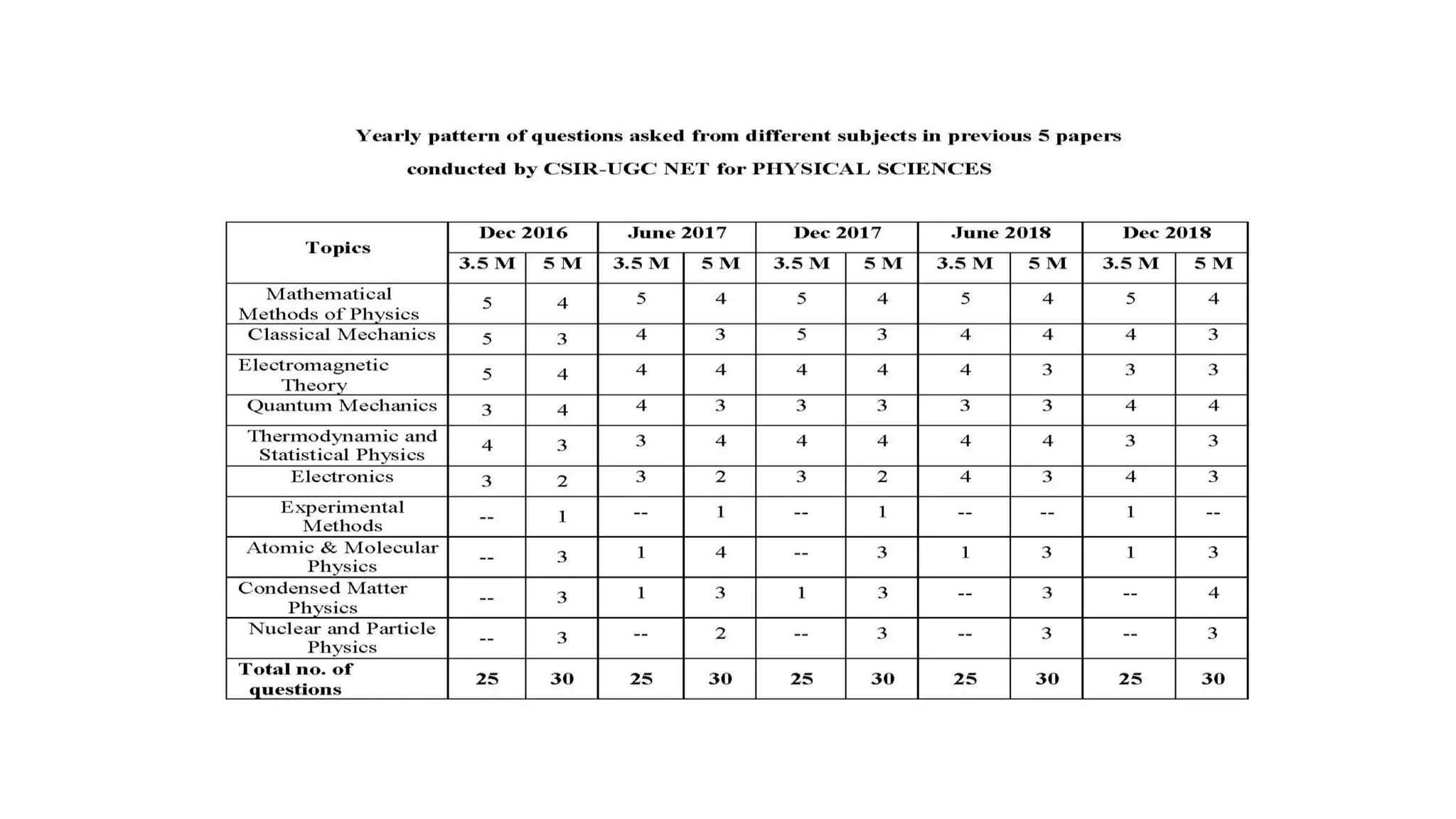
2. Develop a study plan that focuses on high-priority topics from previous papers, spends 1-1.5 hours daily on Part A, and uses time management strategies.
3. Practice is key - analyze previous papers, use different strategies for different question types, and take mock tests to assess weaknesses.





























![1,2,3,4….9 – 1 digit (9)
10, 11, 12….99 – 2 digits (90 x 2 = 180)
2019 – (189) = 1830 ; 1830/3 = 610 ; 9 + 90 + 610 =709
100, 101, 102 …. 999 – 3 digits
Ans : 3 [(1 x 9) + (2 x 90) + (3 x 610) = 2019]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/csir-ugcnet-part-a-tipsandtricks-june-2020-200608143343/75/CSIR-UGC-NET-TIPS-and-Tricks-to-prepare-Part-A-Aptitude-and-Reasoning-37-2048.jpg)