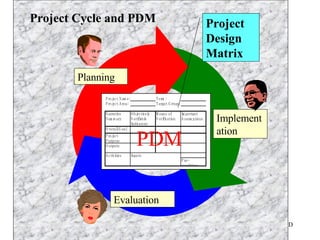
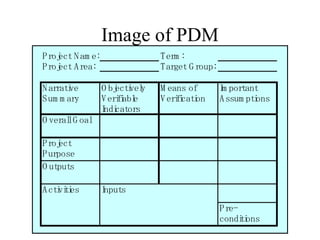
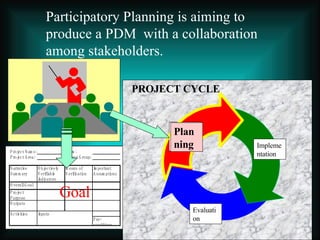
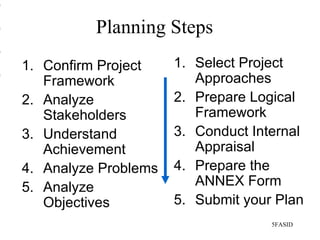
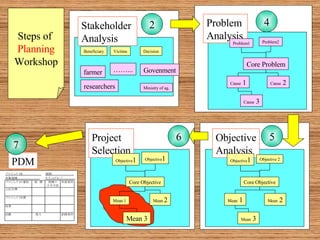
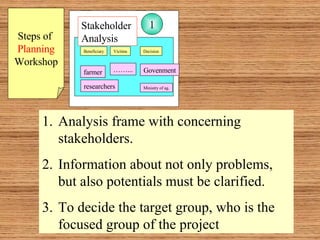
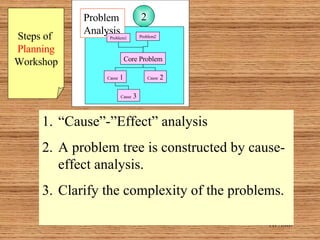
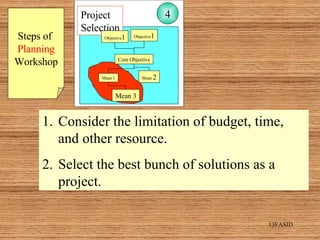
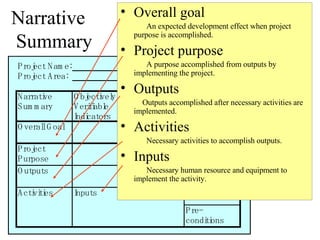
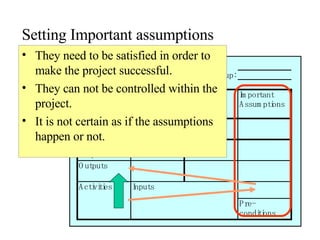
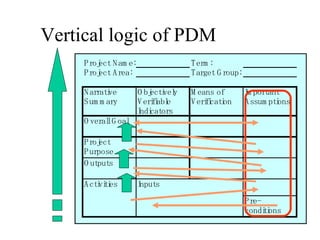
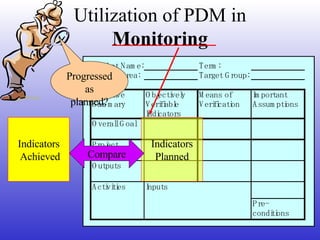
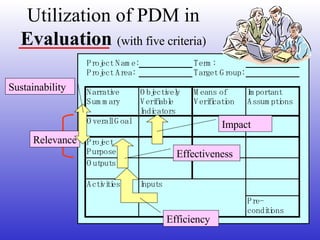
This document introduces participatory project planning and the project design matrix (PDM). It discusses the project cycle and how participatory planning aims to create a PDM through collaboration among stakeholders. The key steps in planning include stakeholder analysis, problem analysis, objective analysis, project selection, and developing the PDM. These steps are conducted through participatory workshops where stakeholders analyze problems, objectives, and potential solutions using techniques like problem trees and objective trees. The resulting PDM outlines the project goals, objectives, indicators, assumptions and provides a framework for monitoring and evaluation.