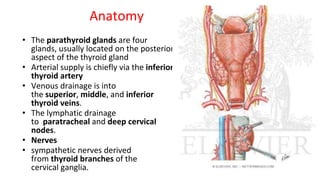
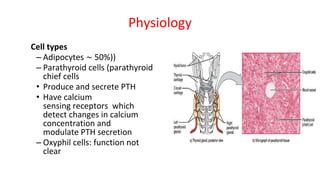
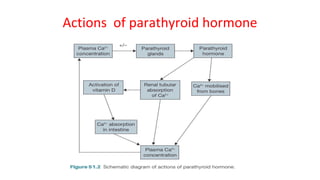
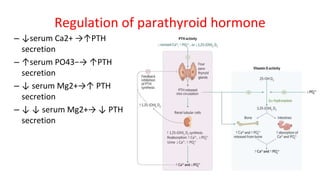
This document provides information about the parathyroid gland, including its anatomy, physiology, diseases, and presenting problems. It discusses the following key points:
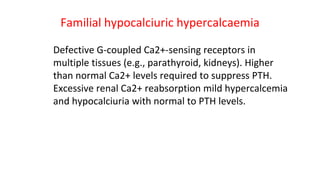
- The parathyroid glands regulate calcium levels in the blood through secretion of parathyroid hormone (PTH). High calcium levels decrease PTH secretion while low calcium increases it.
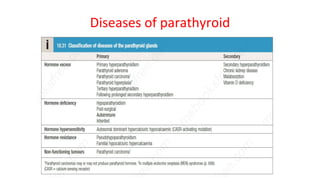
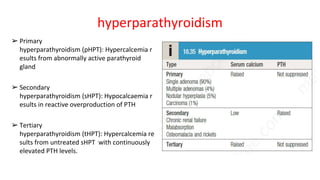
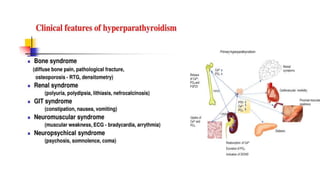
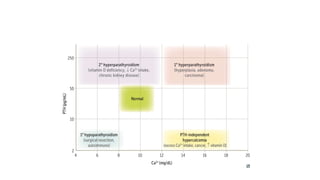
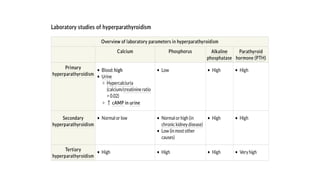
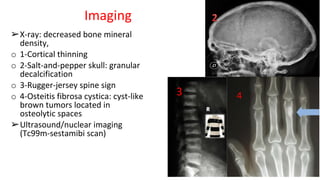
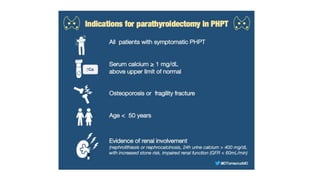
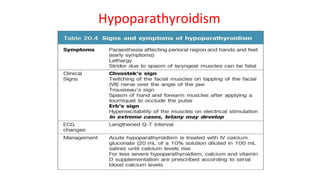
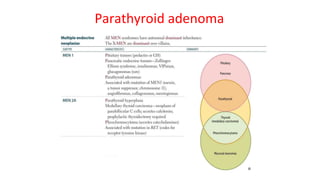
- Primary diseases include primary hyperparathyroidism from overactive parathyroid glands and hypoparathyroidism from underactive glands.
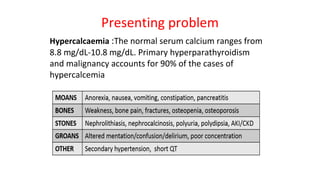
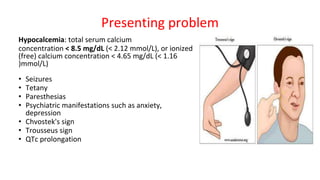
- Hyperparathyroidism causes hypercalcemia and is usually treated by surgically removing the overactive gland(s). Hypoparathyroidism causes hypocalcemia and is treated with calcium and vitamin