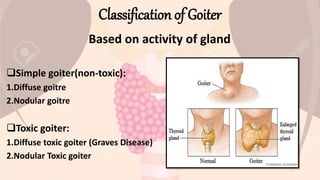
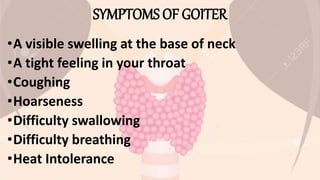
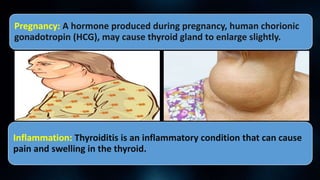
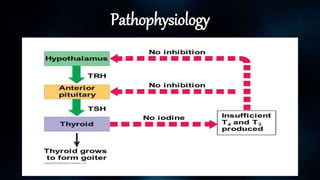
Goiter is an abnormal enlargement of the thyroid gland. It can be caused by iodine deficiency, Graves' disease, Hashimoto's disease, or multinodular goiter. Symptoms include a visible swelling in the neck, tightness in the throat, coughing, hoarseness, difficulty swallowing or breathing. Treatment depends on the cause but may include medications to relieve symptoms, anti-thyroid drugs, radioactive iodine treatment, or thyroid surgery followed by thyroid replacement therapy. Maintaining adequate iodine intake through iodized foods can help prevent iodine deficiency goiters.